rev8thgrade - PAMS
... Atomic Structure: Isotopeshave the number of protons but different number of neutrons How many neutrons in the ...
... Atomic Structure: Isotopeshave the number of protons but different number of neutrons How many neutrons in the ...
Atom (A) or Ion
... 53. What are valance electrons and oxidation numbers? Know how to identify them from the periodic table. 54. When you put an element in a flame, you see different colors of light given off. How/why? 55. Write the long and short electron configuration for: Al Pt ...
... 53. What are valance electrons and oxidation numbers? Know how to identify them from the periodic table. 54. When you put an element in a flame, you see different colors of light given off. How/why? 55. Write the long and short electron configuration for: Al Pt ...
Atom (A) or Ion (I)
... 53. What are valance electrons and oxidation numbers? Know how to identify them from the periodic table. 54. When you put an element in a flame, you see different colors of light given off. How/why? 55. Write the long and short electron configuration for: Al Pt ...
... 53. What are valance electrons and oxidation numbers? Know how to identify them from the periodic table. 54. When you put an element in a flame, you see different colors of light given off. How/why? 55. Write the long and short electron configuration for: Al Pt ...
Atom (A) or Ion (I)
... 53. What are valance electrons and oxidation numbers? Know how to identify them from the periodic table. 54. When you put an element in a flame, you see different colors of light given off. How/why? 55. Write the long and short electron configuration for: Al Pt ...
... 53. What are valance electrons and oxidation numbers? Know how to identify them from the periodic table. 54. When you put an element in a flame, you see different colors of light given off. How/why? 55. Write the long and short electron configuration for: Al Pt ...
CP-Chem Ch 3 PowerPoint(Atomic Theory
... atomic theory that he created using the laws of matter and previously known atomic theory • 1) All matter is composed of atoms • 2) All atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties • 3) Atoms can not be divided, created or destroyed • 4) Atoms of different elements comb ...
... atomic theory that he created using the laws of matter and previously known atomic theory • 1) All matter is composed of atoms • 2) All atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties • 3) Atoms can not be divided, created or destroyed • 4) Atoms of different elements comb ...
- Catalyst
... 2. Atoms of one element cannot be converted into atoms of another element in a chemical reaction. Elements can only be converted into other elements in nuclear reactions in which protons are changed. 3. All atoms of an element have the same number of protons and electrons, which determine the chemic ...
... 2. Atoms of one element cannot be converted into atoms of another element in a chemical reaction. Elements can only be converted into other elements in nuclear reactions in which protons are changed. 3. All atoms of an element have the same number of protons and electrons, which determine the chemic ...
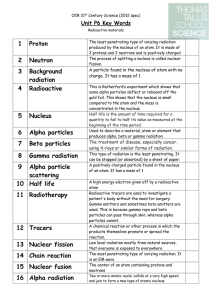
3 Background radiation
... A high energy electron given off by a radioactive atom Radioactive tracers are used to investigate a patient's body without the need for surgery. Gamma emitters and sometimes beta emitters are used. This is because gamma rays and beta particles can pass through skin, whereas alpha particles cannot. ...
... A high energy electron given off by a radioactive atom Radioactive tracers are used to investigate a patient's body without the need for surgery. Gamma emitters and sometimes beta emitters are used. This is because gamma rays and beta particles can pass through skin, whereas alpha particles cannot. ...
Nuclear Processes
... • Involve a nucleus collapsing to form a smaller nucleus • Usually involve atoms with large nucleii such as the Lathanides and Actinides • They produce , and emissions. ...
... • Involve a nucleus collapsing to form a smaller nucleus • Usually involve atoms with large nucleii such as the Lathanides and Actinides • They produce , and emissions. ...
Objective 2 Average Atomic Mass
... Another term used to describe the process by which one element spontaneously changes into another element is (14) ____________________. Any isotope that undergoes such changes is called a(n) (15)___________________. There are three common forms of radiation. One type is a form of energy known as (16 ...
... Another term used to describe the process by which one element spontaneously changes into another element is (14) ____________________. Any isotope that undergoes such changes is called a(n) (15)___________________. There are three common forms of radiation. One type is a form of energy known as (16 ...
Remediation_unit 2_standard
... Another term used to describe the process by which one element spontaneously changes into another element is (14) ____________________. Any isotope that undergoes such changes is called a(n) (15)___________________. There are three common forms of radiation. One type is a form of energy known as (16 ...
... Another term used to describe the process by which one element spontaneously changes into another element is (14) ____________________. Any isotope that undergoes such changes is called a(n) (15)___________________. There are three common forms of radiation. One type is a form of energy known as (16 ...
Periodic Trends
... When electrons are shared by two atoms a covalent bond is formed. When the atoms are the same they pull on the electrons equally. Example, H-H. ...
... When electrons are shared by two atoms a covalent bond is formed. When the atoms are the same they pull on the electrons equally. Example, H-H. ...
NYS Regents Chemistry June 21, 2002
... b. The number of moles of H2(g) decreases, less H2(g) is made, or more H2(g) is consumed. c. There is no effect on the production of NH 3(g) or that the number of moles remains the same. and ...
... b. The number of moles of H2(g) decreases, less H2(g) is made, or more H2(g) is consumed. c. There is no effect on the production of NH 3(g) or that the number of moles remains the same. and ...
Periodic Trends in Atomic Radius, Ionization Energy and
... Atomic Radius decreases Ionization energy increases ...
... Atomic Radius decreases Ionization energy increases ...
Average Atomic Mass
... • The third common type of radiation is gamma radiation or gamma rays. • Gamma rays are high-energy radiation that possess no mass and have no charge. • Gamma rays are denoted by the symbol 00γ. • Gamma rays usually accompany alpha and beta radiation and account for most of the energy lost during th ...
... • The third common type of radiation is gamma radiation or gamma rays. • Gamma rays are high-energy radiation that possess no mass and have no charge. • Gamma rays are denoted by the symbol 00γ. • Gamma rays usually accompany alpha and beta radiation and account for most of the energy lost during th ...
Prerequisite Knowledge for Chemistry
... All atoms of one element will have the same number of protons. If you change the number of protons then the element changes. For instance, all carbon atoms have 6 protons. If a proton is added to a carbon atom, the atom would become nitrogen. All atoms with 7 protons are nitrogen. ...
... All atoms of one element will have the same number of protons. If you change the number of protons then the element changes. For instance, all carbon atoms have 6 protons. If a proton is added to a carbon atom, the atom would become nitrogen. All atoms with 7 protons are nitrogen. ...