Econ 100Practice Exam 2
... 1. It increases by $400 [multiply $100 times the multiplier, which is 4]. 2. Marginal propensity to consume [MPC]. 3. It increases. 4. When the Fed buys and sells bonds to private bank to increase or decrease the money supply. 5. downward 6. both increase 7. Monetary policy is controlled by the Fed ...
... 1. It increases by $400 [multiply $100 times the multiplier, which is 4]. 2. Marginal propensity to consume [MPC]. 3. It increases. 4. When the Fed buys and sells bonds to private bank to increase or decrease the money supply. 5. downward 6. both increase 7. Monetary policy is controlled by the Fed ...
Money supply, the Fed and Monetary Policy
... government says it’s money and people willingly accept it. The Dollar is backed by FAITH. – This is referred to as an inconvertible fiat standard. ...
... government says it’s money and people willingly accept it. The Dollar is backed by FAITH. – This is referred to as an inconvertible fiat standard. ...
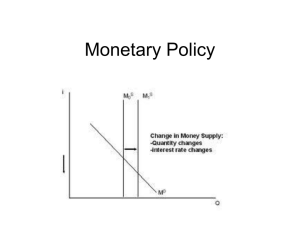
Monetary Policy
... • Stimulates AD (investment and consumption) • Lower interest rates lead to capital outflow, so dollar depreciates, and exports stimulated (higher AD) • Asset prices increase (housing) ...
... • Stimulates AD (investment and consumption) • Lower interest rates lead to capital outflow, so dollar depreciates, and exports stimulated (higher AD) • Asset prices increase (housing) ...
Money, output and Prices in LR Macro_Module_32 money
... What you will learn in this Module: • The effects of an inappropriate monetary policy • The concept of monetary neutrality and its relationship to the long-term economic effects of monetary policy ...
... What you will learn in this Module: • The effects of an inappropriate monetary policy • The concept of monetary neutrality and its relationship to the long-term economic effects of monetary policy ...
William A. Niskanen POLITICAL GUIDANCE ON MONETARY POLICY
... tions, and a price rule can lead to considerable instability in other markets. The long experience with the several types of gold standards, for example, included several short periods ofinflation caused by major gold discoveries, long periods of deflation, frequent recessions, and the Great Depress ...
... tions, and a price rule can lead to considerable instability in other markets. The long experience with the several types of gold standards, for example, included several short periods ofinflation caused by major gold discoveries, long periods of deflation, frequent recessions, and the Great Depress ...
Monetary Policy Practice
... becomes ______________ expensive. If this is the case, people and businesses want ________________ loans. This will cause economic activity to_________________. If the Fed believes there is not enough money in the economy, they can try to increase lending activity by banks. In order to do this, they ...
... becomes ______________ expensive. If this is the case, people and businesses want ________________ loans. This will cause economic activity to_________________. If the Fed believes there is not enough money in the economy, they can try to increase lending activity by banks. In order to do this, they ...
Aim: How does the Federal Reserve regulate the money supply?
... in this photo? What qualifications do you think this employee needs to do her job? ...
... in this photo? What qualifications do you think this employee needs to do her job? ...
Quiz 9
... (2) 1. Which of the following is true according to The Economist? a. The US federal government can end the financial crisis in the US by adding layers of new regulations on financial institutions b. An expected increase in state and local government spending will help keep the US economy our of rece ...
... (2) 1. Which of the following is true according to The Economist? a. The US federal government can end the financial crisis in the US by adding layers of new regulations on financial institutions b. An expected increase in state and local government spending will help keep the US economy our of rece ...
Units 4 Breakdown: Money Market, Banking and Multiple Deposit
... Open Market Operations Excess Reserves Discount Rate Federal Funds Rate Key Information to Know (answer): 1. List and explain the 3 tools of monetary 3. How does the government target interest policy. rates of banks? 2. If there is a recession, what monetary policy 4. What changes the demand for mon ...
... Open Market Operations Excess Reserves Discount Rate Federal Funds Rate Key Information to Know (answer): 1. List and explain the 3 tools of monetary 3. How does the government target interest policy. rates of banks? 2. If there is a recession, what monetary policy 4. What changes the demand for mon ...
Abstract
... also refers to how the central bank uses interest rates and the money supply to guide economic growth by controlling inflation and stabilizing currency. Like any other central bank, Bangladesh Bank is performing the role to formulate monetary policy in Bangladesh. The control of money supply is an i ...
... also refers to how the central bank uses interest rates and the money supply to guide economic growth by controlling inflation and stabilizing currency. Like any other central bank, Bangladesh Bank is performing the role to formulate monetary policy in Bangladesh. The control of money supply is an i ...
Ch 18 Milton Friedman
... positive effect on employment and production in the short run – This is because of “money illusion”. ...
... positive effect on employment and production in the short run – This is because of “money illusion”. ...
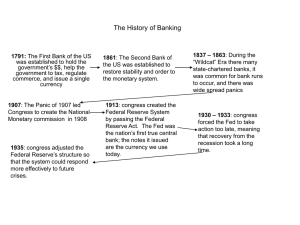
The History of Banking
... government’s $$, help the government to tax, regulate commerce, and issue a single currency ...
... government’s $$, help the government to tax, regulate commerce, and issue a single currency ...
Chapter 16
... policy increases the money supply. 5. Actions the Fed takes to influence the real GDP and the inflation rate are called policy. 6. Funds over and above Fed requirements make up a bank’s ...
... policy increases the money supply. 5. Actions the Fed takes to influence the real GDP and the inflation rate are called policy. 6. Funds over and above Fed requirements make up a bank’s ...