Economics Final Exam Review
... Discuss demand and supply. What are their determinants? What is equilibrium and how is it affected by changes in demand or supply? What is perfect competition? Define the types of mergers. What is the FDIC and what is its purpose? What are the types of business organizations and their advantages and ...
... Discuss demand and supply. What are their determinants? What is equilibrium and how is it affected by changes in demand or supply? What is perfect competition? Define the types of mergers. What is the FDIC and what is its purpose? What are the types of business organizations and their advantages and ...
Fiscal Policy
... – Laissez-faire economics – Theory that opposes governmental interference in economic affairs beyond what is necessary to protect life and property. • Balanced budget ...
... – Laissez-faire economics – Theory that opposes governmental interference in economic affairs beyond what is necessary to protect life and property. • Balanced budget ...
Lecture 1: Why study Money, Banking and Financial Markets? Intro
... impact on incomes, investment, savings of the local economy? How are the effects from one stock market transferring to another? How are banks and the other financial institutions working? What are the functions of money... these will be the issues we are discussing in this class. 1. Financial market ...
... impact on incomes, investment, savings of the local economy? How are the effects from one stock market transferring to another? How are banks and the other financial institutions working? What are the functions of money... these will be the issues we are discussing in this class. 1. Financial market ...
Objective of MP - qazieconometrics
... By virtue of its special position, the central bank can persuade commercial banks to follow a specific credit policy. In this connection the central bank employ oral or written appeals or warnings. ...
... By virtue of its special position, the central bank can persuade commercial banks to follow a specific credit policy. In this connection the central bank employ oral or written appeals or warnings. ...
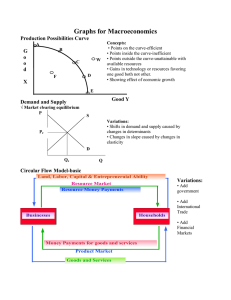
Graphs for Macroeconomics Production Possibilities Curve G o
... interest rate falls. Interest rate includes Expected inflation. ...
... interest rate falls. Interest rate includes Expected inflation. ...
Ch. 13 Study Guide Multiple Choice ____ 1. Which of the following
... A. It has become more equal. B. It has become less equal. C. It became more equal for about 10 years but has become less equal. D. It has not changed appreciably. 5. Economists look to which of the following explanations for inflation? A. too much money in the economy B. demand for goods exceeds sup ...
... A. It has become more equal. B. It has become less equal. C. It became more equal for about 10 years but has become less equal. D. It has not changed appreciably. 5. Economists look to which of the following explanations for inflation? A. too much money in the economy B. demand for goods exceeds sup ...
EC 102 Fall 2007 – Homework #5
... h) Looking at your multiplier equation, what is the difference between the variables in the denominator of the multiplier and those which aren’t (the variables that the multiplier is multiplying)? Is there any intuition which may explain this? ...
... h) Looking at your multiplier equation, what is the difference between the variables in the denominator of the multiplier and those which aren’t (the variables that the multiplier is multiplying)? Is there any intuition which may explain this? ...
Fiscal and Monetary Policy in the Growth Model Introduction A. Our
... transfer payments (F) and interest on the government debt (R×D). 2. Budget surplus (deficit) = T – G – F – R×D. 3. Fiscal policy is determined by the President and Congress. 4. Fiscal policy primarily affects output in long-run by adjusting the supply of a. technology by changing R&D spending. b. la ...
... transfer payments (F) and interest on the government debt (R×D). 2. Budget surplus (deficit) = T – G – F – R×D. 3. Fiscal policy is determined by the President and Congress. 4. Fiscal policy primarily affects output in long-run by adjusting the supply of a. technology by changing R&D spending. b. la ...
Money and Banking
... It is a security (claim on earnings and assets) Issuing a stock and selling it to finance a firm’s activity. 2- The Foreign Exchange Market: To convert funds from one currency to another, we use the FEM. Foreign exchange rate: the price of one country’s currency in terms of another’s is determined i ...
... It is a security (claim on earnings and assets) Issuing a stock and selling it to finance a firm’s activity. 2- The Foreign Exchange Market: To convert funds from one currency to another, we use the FEM. Foreign exchange rate: the price of one country’s currency in terms of another’s is determined i ...
ECONOMICS DPM REVIEW
... contraction in business cycle) Contractionary Fiscal Policy: Government raises taxes and decreases spending (practiced during inflationary period) ...
... contraction in business cycle) Contractionary Fiscal Policy: Government raises taxes and decreases spending (practiced during inflationary period) ...
Macroeconomic Views
... velocity of circulation, or average number of times $1 is spent on final goods and services in a time period. (think rate of change) Price level (P) = average price level of final goods and services in GDP, also known as the GDP deflator Real Output (Q) = real output, the quantity of goods and servi ...
... velocity of circulation, or average number of times $1 is spent on final goods and services in a time period. (think rate of change) Price level (P) = average price level of final goods and services in GDP, also known as the GDP deflator Real Output (Q) = real output, the quantity of goods and servi ...
File
... impossible without putting the nation into serious debt. So, we usually have to pick one. This issue is one major difference between Democrats and Republicans. - Democrats prefer to increase govt. spending hoping to employ more people and encourage them to spend their income. - Republicans prefer to ...
... impossible without putting the nation into serious debt. So, we usually have to pick one. This issue is one major difference between Democrats and Republicans. - Democrats prefer to increase govt. spending hoping to employ more people and encourage them to spend their income. - Republicans prefer to ...