Monetary Policy and Financial Markets
... volatility of real economic growth in the United States to better stabilization policy by the Fed, others blame monetary policymakers for exacerbating cycles in financial markets (e.g. ECB paper). Indeed, the New Keynesian model predicts that the shortterm interest rate can be manipulated to smooth ...
... volatility of real economic growth in the United States to better stabilization policy by the Fed, others blame monetary policymakers for exacerbating cycles in financial markets (e.g. ECB paper). Indeed, the New Keynesian model predicts that the shortterm interest rate can be manipulated to smooth ...
Macroeconomics
... EOCT Practice Q’s 1. Which of the following is responsible for the monetary policy of the U.S.? A. Congress B. The President C. The Senate D. The Federal Reserve System ...
... EOCT Practice Q’s 1. Which of the following is responsible for the monetary policy of the U.S.? A. Congress B. The President C. The Senate D. The Federal Reserve System ...
Name: Ivan Bakubi Section: 2020 E
... is naturally at AD* but finds itself at AD2, as seen in the graph on the previous page. Briefly explain how each of these policies would work to correct the situation. (12pts) Who does fiscal policy: A fiscal policy is a tool which is used by national governments to influence the direction of the ec ...
... is naturally at AD* but finds itself at AD2, as seen in the graph on the previous page. Briefly explain how each of these policies would work to correct the situation. (12pts) Who does fiscal policy: A fiscal policy is a tool which is used by national governments to influence the direction of the ec ...
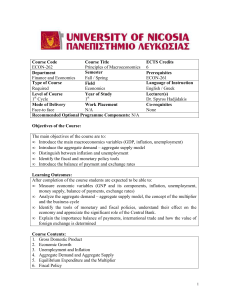
ECON-262 Principles of Macroeconomics
... After completion of the course students are expected to be able to: • Measure economic variables (GNP and its components, inflation, unemployment, money supply, balance of payments, exchange rates) • Analyze the aggregate demand – aggregate supply model, the concept of the multiplier and the busines ...
... After completion of the course students are expected to be able to: • Measure economic variables (GNP and its components, inflation, unemployment, money supply, balance of payments, exchange rates) • Analyze the aggregate demand – aggregate supply model, the concept of the multiplier and the busines ...
ch14revanswers
... 3. What are the three principal tools of monetary policy? Explain how they can be used. The Federal Reserve Banks use three principal tools (techniques or instruments) to control the reserves of banks and the size of the money supply. (1) The Federal Reserve can buy or sell government securities in ...
... 3. What are the three principal tools of monetary policy? Explain how they can be used. The Federal Reserve Banks use three principal tools (techniques or instruments) to control the reserves of banks and the size of the money supply. (1) The Federal Reserve can buy or sell government securities in ...
Money
... Modern Banking Federal Reserve System 1913 – central bank created Private corporation – shares owned by private banks Publicly controlled – chairman appointed by President (approved by Congress) Prints Federal Reserve Notes – inconvertible fiat money since 1934 ...
... Modern Banking Federal Reserve System 1913 – central bank created Private corporation – shares owned by private banks Publicly controlled – chairman appointed by President (approved by Congress) Prints Federal Reserve Notes – inconvertible fiat money since 1934 ...
Test#1
... Keynes and the Keynesians integrated the analysis of the money market and the price level into the general macroeconomic model, rather than leaving it as an appendage to the analysis of the commodity markets. They also introduced bonds as an alternative asset to money in the demand for money and mad ...
... Keynes and the Keynesians integrated the analysis of the money market and the price level into the general macroeconomic model, rather than leaving it as an appendage to the analysis of the commodity markets. They also introduced bonds as an alternative asset to money in the demand for money and mad ...
MonetaryPolicyPractice
... 28. If Matt Taylor gets his $800 loan from the Paris First National Bank in cash rather than in the form of a new checkable deposit, the: a. Paris First National Bank will get $800 in new reserves. b. Paris First National Bank will not get $800 in new reserves. c. assets of the Paris First National ...
... 28. If Matt Taylor gets his $800 loan from the Paris First National Bank in cash rather than in the form of a new checkable deposit, the: a. Paris First National Bank will get $800 in new reserves. b. Paris First National Bank will not get $800 in new reserves. c. assets of the Paris First National ...
Naked Economics: Undressing the Dismal Science
... Reserve requirements are a percentage of commercial banks', and other depository institutions', demand deposit liabilities (i.e. chequing accounts) that must be kept on deposit at the Central Bank as a requirement of Banking Regulations. Though seldom used, this percentage may be changed by the Cen ...
... Reserve requirements are a percentage of commercial banks', and other depository institutions', demand deposit liabilities (i.e. chequing accounts) that must be kept on deposit at the Central Bank as a requirement of Banking Regulations. Though seldom used, this percentage may be changed by the Cen ...
17.2 Monetary Policy in the Short Run
... Explain how changes in the money supply affect interest rates and real GDP in the short run. Discuss the federal funds rate and why the Fed uses this rate to pursue monetary policy goals. ...
... Explain how changes in the money supply affect interest rates and real GDP in the short run. Discuss the federal funds rate and why the Fed uses this rate to pursue monetary policy goals. ...
Chapter 5 Power Point Presentation
... 1. Example, if a bank grants a borrower a loan of $90, what effect does it have on the following? a) A depositor – No effect (1)The depositor can demand money at any time b) The bank (1) The bank acquires the asset (loan) and the liability of the demand deposit c) The borrower (1) The borrower acqui ...
... 1. Example, if a bank grants a borrower a loan of $90, what effect does it have on the following? a) A depositor – No effect (1)The depositor can demand money at any time b) The bank (1) The bank acquires the asset (loan) and the liability of the demand deposit c) The borrower (1) The borrower acqui ...
2. The Liberal Response to Classical Liberalism - ARipkens30-1
... He proposed a solution to this problem through the regulation of government spending, taxation, the regulation of the interest rate and production of money. In doing so, governments could regulate consumer demand, thus regulating the economy. ...
... He proposed a solution to this problem through the regulation of government spending, taxation, the regulation of the interest rate and production of money. In doing so, governments could regulate consumer demand, thus regulating the economy. ...
2. The Liberal Response to Classical Liberalism
... He proposed a solution to this problem through the regulation of government spending, taxation, the regulation of the interest rate and production of money. In doing so, governments could regulate consumer demand, thus regulating the economy. ...
... He proposed a solution to this problem through the regulation of government spending, taxation, the regulation of the interest rate and production of money. In doing so, governments could regulate consumer demand, thus regulating the economy. ...
Money and Inflation - University of Miskolc
... Inflation is an increase in the average level of prices Rate of inflation is the percentage change in the overall level of prices Money: Stock of assets used for that can be readily used to make transactions. Functions of money: • store of value • unit of account • a medium of exchange Types of mone ...
... Inflation is an increase in the average level of prices Rate of inflation is the percentage change in the overall level of prices Money: Stock of assets used for that can be readily used to make transactions. Functions of money: • store of value • unit of account • a medium of exchange Types of mone ...
Inflation
... The crisis led to a large-scale depreciation of the U.S. dollar, followed by a round of price hikes for basic materials such as agricultural products, energy and mineral resources. World food prices had been extremely low for a long time. ...
... The crisis led to a large-scale depreciation of the U.S. dollar, followed by a round of price hikes for basic materials such as agricultural products, energy and mineral resources. World food prices had been extremely low for a long time. ...
OFFICIAL CASH RATE HOW DOES IT WORK?
... • Similarly a bank is not likely to lend shortterm at below the OCR because the same bank can lend to the Reserve Bank and receive interest at the OCR level. • By controlling short-term interest rates in this way, the Reserve Bank can influence short-term demand in the economy, and by that put press ...
... • Similarly a bank is not likely to lend shortterm at below the OCR because the same bank can lend to the Reserve Bank and receive interest at the OCR level. • By controlling short-term interest rates in this way, the Reserve Bank can influence short-term demand in the economy, and by that put press ...