Stabilisation policy in New Zealand: Counting your
... The Reserve Bank of New Zealand Act 1989 specifies that the primary function of the Reserve Bank shall be to deliver “stability in the general level of prices.” The Act says that the Minister of Finance and the Governor of the Reserve Bank shall together have a separate agreement setting out specific ...
... The Reserve Bank of New Zealand Act 1989 specifies that the primary function of the Reserve Bank shall be to deliver “stability in the general level of prices.” The Act says that the Minister of Finance and the Governor of the Reserve Bank shall together have a separate agreement setting out specific ...
The Topology of Danish Interbank Money Flows
... observe the settlement time of the transactions but not the actual point in time where a bank enter into an agreement on an uncollateralized overnight loan with another bank. An uncollateralized money market loan can be agreed upon earlier in the day of settlement or on previous days4 . Third, the a ...
... observe the settlement time of the transactions but not the actual point in time where a bank enter into an agreement on an uncollateralized overnight loan with another bank. An uncollateralized money market loan can be agreed upon earlier in the day of settlement or on previous days4 . Third, the a ...
2. The Sacrifice Ratio - Hal-SHS
... express a relationship between the output gap and inflation variation over a long time series. Okun reports an average sacrifice ratio of 10% for the United States. In other words, he finds that a permanent one-percentage-point reduction in inflation rate should be associated with a cumulative 10% l ...
... express a relationship between the output gap and inflation variation over a long time series. Okun reports an average sacrifice ratio of 10% for the United States. In other words, he finds that a permanent one-percentage-point reduction in inflation rate should be associated with a cumulative 10% l ...
n a flE EDICIVE I OF flhI'2ES1 Ra's
... some evidence which bears on the debate about monetary policy in Section II; for the time being, though, let us just note that the literature following Sims' contribution demonstrated the forecasting power of several alternative interest rates. ...
... some evidence which bears on the debate about monetary policy in Section II; for the time being, though, let us just note that the literature following Sims' contribution demonstrated the forecasting power of several alternative interest rates. ...
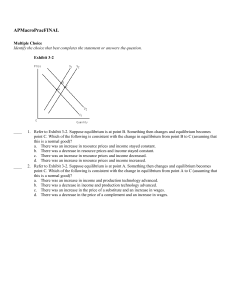
APMacroPracFIN
... a. federal funds market. b. bank loan market. c. Fed market. d. discount market. ____ 54. The discount rate is the interest rate a. banks pay on certificates of deposit. b. the Fed pays on reserves held by banks. c. the Fed charges when it lends reserves to banks. d. banks charge their loan customer ...
... a. federal funds market. b. bank loan market. c. Fed market. d. discount market. ____ 54. The discount rate is the interest rate a. banks pay on certificates of deposit. b. the Fed pays on reserves held by banks. c. the Fed charges when it lends reserves to banks. d. banks charge their loan customer ...
The Financial, Economic, Social, and Political
... economy was on the brink of a major depression. Having rapidly exhausted its conventional monetary policy tools—as the short-term policy rate was already near zero—to stimulate the U.S. economy, the Federal Reserve turned to unconventional monetary policy in the form of large scale asset purchases ( ...
... economy was on the brink of a major depression. Having rapidly exhausted its conventional monetary policy tools—as the short-term policy rate was already near zero—to stimulate the U.S. economy, the Federal Reserve turned to unconventional monetary policy in the form of large scale asset purchases ( ...
Chap11_12q_for print..
... 7. An increase in the money supply shifts the ______ curve to the right, and the aggregate demand curve ______ ______. A) IS; shifts to the right B) IS; does not shift C) LM: shifts to the right D) LM; does not shift 8. One policy response to the U.S. economic slowdown of 2001 were tax cut ...
... 7. An increase in the money supply shifts the ______ curve to the right, and the aggregate demand curve ______ ______. A) IS; shifts to the right B) IS; does not shift C) LM: shifts to the right D) LM; does not shift 8. One policy response to the U.S. economic slowdown of 2001 were tax cut ...
interest rate - Universität Bamberg
... Lehrstuhl für Volkswirtschaftslehre, insbesondere Integration Europäischer Arbeitsmärkte Universität Bamberg | [email protected] | www.uni-bamberg.de/sowi/bruecker ...
... Lehrstuhl für Volkswirtschaftslehre, insbesondere Integration Europäischer Arbeitsmärkte Universität Bamberg | [email protected] | www.uni-bamberg.de/sowi/bruecker ...
This PDF is a selection from an out-of-print volume from... of Economic Research
... better still if it “cheats” on the agreement. That is, it will be able to do better in the short-run, assuming that the other countries leave their policies as agreed; in future periods, the other countries will presumably retaliate by also abandoning the agreement. But economists have probably over ...
... better still if it “cheats” on the agreement. That is, it will be able to do better in the short-run, assuming that the other countries leave their policies as agreed; in future periods, the other countries will presumably retaliate by also abandoning the agreement. But economists have probably over ...
Design and Implementation of a Common Currency Area in the East
... synchronization has increased since 2000, when the EAC treaty came into force. Debrun, Masson, and Pattillo (2010) go beyond to the traditional approaches to develop a full-fledged cost-benefit analysis of monetary integration, calibrated to African data. They apply it to some actual and proposed cu ...
... synchronization has increased since 2000, when the EAC treaty came into force. Debrun, Masson, and Pattillo (2010) go beyond to the traditional approaches to develop a full-fledged cost-benefit analysis of monetary integration, calibrated to African data. They apply it to some actual and proposed cu ...
Macro Syllabusx - IDLA – Blackboard Learn
... 2. Banks and the Creation of Money 3. The Money Market 4. The Central Bank and Monetary Policy Performance Objectives: *Explain the difference between financial assets. *Explain the three functions of money and how it is measured. *Explain how the money supply is measured. *Explain what present and ...
... 2. Banks and the Creation of Money 3. The Money Market 4. The Central Bank and Monetary Policy Performance Objectives: *Explain the difference between financial assets. *Explain the three functions of money and how it is measured. *Explain how the money supply is measured. *Explain what present and ...
Economics 101 Assignment #3 (20 Points) Name
... 3. Most people who buy a home pay for it by borrowing money from a bank, savings and loan, or other such institution. Such a loan is called a mortgage. At present, the interest on a mortgage is deductible for tax purposes. To illustrate how this works, assume that a person is in a tax rate of 25% an ...
... 3. Most people who buy a home pay for it by borrowing money from a bank, savings and loan, or other such institution. Such a loan is called a mortgage. At present, the interest on a mortgage is deductible for tax purposes. To illustrate how this works, assume that a person is in a tax rate of 25% an ...
Inflation Breakeven Rate
... Since the introduction of Treasury Inflation Indexed Securities (TIIS) in 1997, the ex ante real interest rate becomes measurable. By linking value to the Consumer Price Index (CPI), TIIS provide investors with a “real” rate of return. It can be viewed as one of the safest financial assets due to it ...
... Since the introduction of Treasury Inflation Indexed Securities (TIIS) in 1997, the ex ante real interest rate becomes measurable. By linking value to the Consumer Price Index (CPI), TIIS provide investors with a “real” rate of return. It can be viewed as one of the safest financial assets due to it ...
Monetary Policy Transparency and Private Sector Forecasts
... Hakkio, and George Kahn for comments and Brent Bundick for research assistance. This article is on the bank’s website at www.KansasCityFed.org. ...
... Hakkio, and George Kahn for comments and Brent Bundick for research assistance. This article is on the bank’s website at www.KansasCityFed.org. ...
3 estimation of the impact of single monetary policy on - Hal-SHS
... between effective and potential levels of global economy production, i.e. "the output gap". The evolution of potential production can be defined starting from the growth rate of real GDP bearable in medium term. Its evolution is determined by the increase in capital stock and labour supply, and by t ...
... between effective and potential levels of global economy production, i.e. "the output gap". The evolution of potential production can be defined starting from the growth rate of real GDP bearable in medium term. Its evolution is determined by the increase in capital stock and labour supply, and by t ...
146s10_l16a.pdf
... Monetary policy: policy in which the central bank influences the supply of monetary assets Asset market responds very rapidly...goods market less so Fiscal policy: change G or T . Fiscal policy affects aggregates demand and output first Temporary policy changes are expected to be reversed in the nea ...
... Monetary policy: policy in which the central bank influences the supply of monetary assets Asset market responds very rapidly...goods market less so Fiscal policy: change G or T . Fiscal policy affects aggregates demand and output first Temporary policy changes are expected to be reversed in the nea ...