Review of Jens Forssbæck and Lars Oxelheim`s Money
... period of time. Toward that end, Chapter 5 describes developments in national exchange rate policies and the liberalization of cross-border capital movements; Chapter 6 measures the degree to which national monetary markets have been integrated internationally; and Chapter 7 gauges the degree of mon ...
... period of time. Toward that end, Chapter 5 describes developments in national exchange rate policies and the liberalization of cross-border capital movements; Chapter 6 measures the degree to which national monetary markets have been integrated internationally; and Chapter 7 gauges the degree of mon ...
Money Demand (Handa, Chapter 2)
... The Walrasian GE Model determines relative prices but not the absolute price level. QUESTION: Can we marry the two together? This amounts to integrating microeconomic price theory with macroeconomic monetary theory. Can we add some form of the Equation of Exchange to the Walrasian ...
... The Walrasian GE Model determines relative prices but not the absolute price level. QUESTION: Can we marry the two together? This amounts to integrating microeconomic price theory with macroeconomic monetary theory. Can we add some form of the Equation of Exchange to the Walrasian ...
money supply
... Federal Reserve Banks, and the vaults of depository institutions; (2) traveler's checks of nonbank issuers; (3) demand deposits at commercial banks (excluding those amounts held by depository institutions, the U.S. government, and foreign banks and official institutions) less cash items in the proce ...
... Federal Reserve Banks, and the vaults of depository institutions; (2) traveler's checks of nonbank issuers; (3) demand deposits at commercial banks (excluding those amounts held by depository institutions, the U.S. government, and foreign banks and official institutions) less cash items in the proce ...
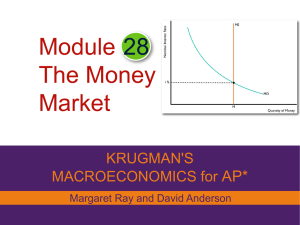
Macro_Module_28 money market
... Shifts of the Money Demand Curve • ∆ Price Level – Right shift when higher P • ∆ Real GDP – right shift when GDP increases • ∆ Technology – left shift with ATM, credit cards, online banking • ∆ Institutions – left shift when regulations make it more attractive to keep $$$ in bank ...
... Shifts of the Money Demand Curve • ∆ Price Level – Right shift when higher P • ∆ Real GDP – right shift when GDP increases • ∆ Technology – left shift with ATM, credit cards, online banking • ∆ Institutions – left shift when regulations make it more attractive to keep $$$ in bank ...
Answer to 1.
... 3. (d) When the Fed purchases bonds, what will happen to the price of bonds in the open market? Explain. Answer to 3. (d) When the Fed purchases bonds, the MS increases and people buy non-money assets like bonds which pushes bond prices up and interest rates down. 3. (e) Suppose that instead of the ...
... 3. (d) When the Fed purchases bonds, what will happen to the price of bonds in the open market? Explain. Answer to 3. (d) When the Fed purchases bonds, the MS increases and people buy non-money assets like bonds which pushes bond prices up and interest rates down. 3. (e) Suppose that instead of the ...
ECON 221 - BrainMass
... a. of the foreign purchases effect b. an increase in prices encourages individuals to reduce purchases c. higher prices lead to higher interest rates, reducing the purchases of interest-rate sensitive goods d. all the above 3. The interest rate effect of aggregate demand: a. is a GDP component that ...
... a. of the foreign purchases effect b. an increase in prices encourages individuals to reduce purchases c. higher prices lead to higher interest rates, reducing the purchases of interest-rate sensitive goods d. all the above 3. The interest rate effect of aggregate demand: a. is a GDP component that ...
Section 3 PowerPoint Slides
... 1. Special interest effect: An issue that generates substantial benefits for a small group by generating minimal costs to a large group. (in aggregate, losses may exceed benefits). ...
... 1. Special interest effect: An issue that generates substantial benefits for a small group by generating minimal costs to a large group. (in aggregate, losses may exceed benefits). ...
Aggregate Demand Aggregate demand
... things – People who produce things are paid. They spend this money on what other people produce – As long as everyone spends everything that he or she earns, the economy is OK • But, the economy begins to have problems when people save part of their incomes ...
... things – People who produce things are paid. They spend this money on what other people produce – As long as everyone spends everything that he or she earns, the economy is OK • But, the economy begins to have problems when people save part of their incomes ...
Day 3 - Mr
... is statistically the most likely to live below the poverty threshold? a. a two-parent family of Hispanic origin living in the inner city b. a black family headed by a single mother living in the inner city c. a black family headed by a single mother living in the suburbs d. a two-parent white family ...
... is statistically the most likely to live below the poverty threshold? a. a two-parent family of Hispanic origin living in the inner city b. a black family headed by a single mother living in the inner city c. a black family headed by a single mother living in the suburbs d. a two-parent white family ...
This PDF is a selection from a published volume from... Economic Research Volume Title: NBER International Seminar on Macroeconom
... interest rates are expected to stay pinned at zero for longer than previously expected, a researcher can show how that surprise plays through the yield curve and influences the economy. Most of the work on the Bank of Japan experience has emphasized this policy duration effect (as discussed in Berna ...
... interest rates are expected to stay pinned at zero for longer than previously expected, a researcher can show how that surprise plays through the yield curve and influences the economy. Most of the work on the Bank of Japan experience has emphasized this policy duration effect (as discussed in Berna ...
Chapter_16
... (a) the ratio of deposits to reserves required of banks by the Federal Reserve. (b) the ratio of accounts to customers required of banks by the Federal Reserve . (c) the ratio of reserves to deposits required of banks by the Federal Reserve. (d) the ratio of paper currency to coins required of banks ...
... (a) the ratio of deposits to reserves required of banks by the Federal Reserve. (b) the ratio of accounts to customers required of banks by the Federal Reserve . (c) the ratio of reserves to deposits required of banks by the Federal Reserve. (d) the ratio of paper currency to coins required of banks ...
Liquidity Trap - Portland State University
... liquidity trap; the government can implement deficit spending policy to jumpstart the demand. A typical example of expansionary fiscal policy is the implementation of the New Deal policy by President Franklin Roosevelt in 1933. This policy included public works programs for the unemployed including ...
... liquidity trap; the government can implement deficit spending policy to jumpstart the demand. A typical example of expansionary fiscal policy is the implementation of the New Deal policy by President Franklin Roosevelt in 1933. This policy included public works programs for the unemployed including ...
14.02 Principles of Macroeconomics Problem Set 4 Fall 2005 ***Solutions***
... example, given our choice of parameters, the results are the same for both settings. However, conceptually the settings are very different. In the first case we are assuming that all contracts are being revised every year and that wage-setters inflation expectations play a crucial role. In the secon ...
... example, given our choice of parameters, the results are the same for both settings. However, conceptually the settings are very different. In the first case we are assuming that all contracts are being revised every year and that wage-setters inflation expectations play a crucial role. In the secon ...
ECN 111 Chapter 13 Lecture Notes
... 3. In the long run, the price level rises. In the long run, other things remaining the same, a given percentage change in the quantity of money brings an equal percentage change in the price level. C. The Quantity Theory of inflation The quantity theory of money is the proposition that when real GDP ...
... 3. In the long run, the price level rises. In the long run, other things remaining the same, a given percentage change in the quantity of money brings an equal percentage change in the price level. C. The Quantity Theory of inflation The quantity theory of money is the proposition that when real GDP ...
Name:
... accomplished typically through open-market operations (selling bonds), but could also be achieved with an increase in the reserve ratio or discount rate. The restrictive monetary policy would reduce the lending ability of the banking system, increase the real interest rate, reduce investment spendin ...
... accomplished typically through open-market operations (selling bonds), but could also be achieved with an increase in the reserve ratio or discount rate. The restrictive monetary policy would reduce the lending ability of the banking system, increase the real interest rate, reduce investment spendin ...