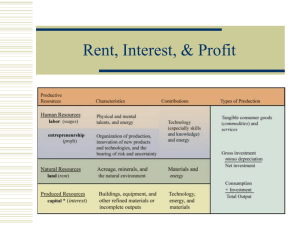
Lecture 2 - The Economics Network
... function, where it is intersected by the aggregate supply function, will be called the effective demand. ... this is the substance of the General Theory of Employment ... .” • “ ‘Supply creates its own Demand’ must mean that f(N) and g(N) are equal for all values of N, i.e. for all levels of output ...
... function, where it is intersected by the aggregate supply function, will be called the effective demand. ... this is the substance of the General Theory of Employment ... .” • “ ‘Supply creates its own Demand’ must mean that f(N) and g(N) are equal for all values of N, i.e. for all levels of output ...
AP Macro Review PP
... Target Federal Funds Rate The interest rate the Fed sets to achieve the desired monetary policy goal - uses open market operations to shift money supply Expansionary Monetary Policy Policy that increases demand which increases Real GDP ...
... Target Federal Funds Rate The interest rate the Fed sets to achieve the desired monetary policy goal - uses open market operations to shift money supply Expansionary Monetary Policy Policy that increases demand which increases Real GDP ...
Semester Final Review Notes
... for something else of value. Examples would be an I.O.U., or a receipt that allows the holder to exchange it for gold or silver. U.S. silver certificates ...
... for something else of value. Examples would be an I.O.U., or a receipt that allows the holder to exchange it for gold or silver. U.S. silver certificates ...
Assignment 4: Macroeconomic Stabilization Policies
... Assume the economy is in recession. Explain how each of the following policies would affect consumption and investment. In each case, indicate any direct effects, any effects resulting from changes in total output, any effects resulting from changes in the interest rate, and the overall effect. If t ...
... Assume the economy is in recession. Explain how each of the following policies would affect consumption and investment. In each case, indicate any direct effects, any effects resulting from changes in total output, any effects resulting from changes in the interest rate, and the overall effect. If t ...
Macro economics 101
... Commodity money – money that takes the form of a commodity with intrinsic value (i.e. value even if it were not used as money) e.g. gold Flat money – money without intrinsic value that is used as money because of government decree e.g. real money Money supply – quantity of money available in the eco ...
... Commodity money – money that takes the form of a commodity with intrinsic value (i.e. value even if it were not used as money) e.g. gold Flat money – money without intrinsic value that is used as money because of government decree e.g. real money Money supply – quantity of money available in the eco ...
Reliving the Crash of `29: How Hoover`s Policies Blazed the Trail for
... several axioms. One was to go back to gold at the old prewar par of $4.86. This would have made deflation necessary, except that a second axiom was that the British continue to pursue a cheap credit, inflationary policy rather than deflation. How to square the circle? What the British tried was poli ...
... several axioms. One was to go back to gold at the old prewar par of $4.86. This would have made deflation necessary, except that a second axiom was that the British continue to pursue a cheap credit, inflationary policy rather than deflation. How to square the circle? What the British tried was poli ...
AP Macro 4-6 Unit Summary
... The reserve requirement (reserve ratio) is the percent of deposits that banks must hold in reserve (the percent they can NOT loan out) • When the FED increases the money supply it increases the amount of money held in bank deposits. • As banks keeps some of the money in reserve and loans out their e ...
... The reserve requirement (reserve ratio) is the percent of deposits that banks must hold in reserve (the percent they can NOT loan out) • When the FED increases the money supply it increases the amount of money held in bank deposits. • As banks keeps some of the money in reserve and loans out their e ...
(G – T) + (X – M)
... Market Rate 市場匯率 Licensed Bank buy US$ from Exchange Fund and sell it to the market for the HK$ arbitrage 持牌銀行 ...
... Market Rate 市場匯率 Licensed Bank buy US$ from Exchange Fund and sell it to the market for the HK$ arbitrage 持牌銀行 ...
2 3 4 ISSUE: 19
... indirect taxes. Direct taxes consist of those imposed on incomes, profits, capital gains and properties. Whereas, indirect taxes consist of domestic taxes on goods and services, international trade and turnover, along with other taxes. An important point with respect to this classification is that t ...
... indirect taxes. Direct taxes consist of those imposed on incomes, profits, capital gains and properties. Whereas, indirect taxes consist of domestic taxes on goods and services, international trade and turnover, along with other taxes. An important point with respect to this classification is that t ...
cyprus international university
... • Define money and list the three functions of money • Explain the role of the central bank in money creation • Explain the money multiplier in a fractional reserve banking system • List and explain the three tools central banks use to change the money supply Chapter 30, Learning objectives “Money G ...
... • Define money and list the three functions of money • Explain the role of the central bank in money creation • Explain the money multiplier in a fractional reserve banking system • List and explain the three tools central banks use to change the money supply Chapter 30, Learning objectives “Money G ...
monetary policy
... Monetary policy by the US Federal Reserve is important for the US economy. However, economists disagree about several aspects of Federal Reserve decision-making powers including the composition of the Federal Reserve committees, Federal Reserve goals, and the actual impact Federal Reserve of policy ...
... Monetary policy by the US Federal Reserve is important for the US economy. However, economists disagree about several aspects of Federal Reserve decision-making powers including the composition of the Federal Reserve committees, Federal Reserve goals, and the actual impact Federal Reserve of policy ...
chapter 25
... borrow money to make the purchase. c. Since people often borrow money to purchase consumer durables, an increase in the interest rate raises the monthly payments on these items. Consequently, consumers purchase fewer durables when interest rates rise. ...
... borrow money to make the purchase. c. Since people often borrow money to purchase consumer durables, an increase in the interest rate raises the monthly payments on these items. Consequently, consumers purchase fewer durables when interest rates rise. ...
Chapter 12
... How Slow is Convergence to PPP? • Two measures: – Speed of convergence: how quickly deviations from PPP disappear over time (estimated to be 15% per year). – Half-life: how long it takes for half of the deviations from PPP to disappear (estimated to be about four years). ...
... How Slow is Convergence to PPP? • Two measures: – Speed of convergence: how quickly deviations from PPP disappear over time (estimated to be 15% per year). – Half-life: how long it takes for half of the deviations from PPP to disappear (estimated to be about four years). ...
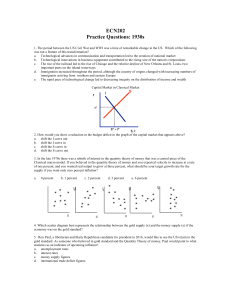
ECN202 Practice Questions: 1930s
... 9. After WWI England (UK) needed to make a decision regarding a return to the gold standard, and if they did return, they needed to set the price of the pound () in terms of gold. The basics of the problem can be seen in the table above. One of the problems was England had very high inflation rates ...
... 9. After WWI England (UK) needed to make a decision regarding a return to the gold standard, and if they did return, they needed to set the price of the pound () in terms of gold. The basics of the problem can be seen in the table above. One of the problems was England had very high inflation rates ...