Main Idea 1
... • Captured Union ship Merrimack, turned it into ironclad, and renamed it the Virginia • Successfully attacked the wooden ships of the Union • Met by Union ironclad, the Monitor, in battle near Hampton Roads, Virginia, in March 1862 and forced to ...
... • Captured Union ship Merrimack, turned it into ironclad, and renamed it the Virginia • Successfully attacked the wooden ships of the Union • Met by Union ironclad, the Monitor, in battle near Hampton Roads, Virginia, in March 1862 and forced to ...
File
... Union moved deeper into the South Start at Fort Henry, then moved to Fort Donelson Union gains control over all KY, and West TN ...
... Union moved deeper into the South Start at Fort Henry, then moved to Fort Donelson Union gains control over all KY, and West TN ...
CIVIL WAR LEADERS
... Career Military Man Helped capture John Brown at Harper’s Ferry • Known as “Eyes of the Army” for skills in scouting and spying • Mortally wounded in Battles of the Wilderness. • Lee surrenders not long after his death. ...
... Career Military Man Helped capture John Brown at Harper’s Ferry • Known as “Eyes of the Army” for skills in scouting and spying • Mortally wounded in Battles of the Wilderness. • Lee surrenders not long after his death. ...
Steph S
... In February, the commander of the Department of the South, Major General Quincy A. Gillmore, launched an expedition into Florida to secure Union enclaves, sever Rebel supply routes, and recruit black soldiers. Brig. General Truman Seymour moved deep into the state, occupying, destroying, and liberat ...
... In February, the commander of the Department of the South, Major General Quincy A. Gillmore, launched an expedition into Florida to secure Union enclaves, sever Rebel supply routes, and recruit black soldiers. Brig. General Truman Seymour moved deep into the state, occupying, destroying, and liberat ...
Second Semester Final Exam Study Guide People and Terms State
... 47. Describe the total war strategy used by Sherman? An army that destroys its opponent’s ability to fight by targeting civilian and economic as well as military resources (total war) 48. What did the Emancipation Proclamation do? Freed slaves in the Confederate states 49. Who first introduced iron ...
... 47. Describe the total war strategy used by Sherman? An army that destroys its opponent’s ability to fight by targeting civilian and economic as well as military resources (total war) 48. What did the Emancipation Proclamation do? Freed slaves in the Confederate states 49. Who first introduced iron ...
Battle of Moore`s Mill - Kingdom of Callaway Civil War Heritage
... guerrillas under fearsome Capt. Alvin Cobb (with a piratelike hook for a hand). There was a considerable delay before Shaffer realized Guitar was engaged and brought his own men into the fight. The weight of numbers took their toll. After four hours of fighting, Porter’s soldiers fled into the brush ...
... guerrillas under fearsome Capt. Alvin Cobb (with a piratelike hook for a hand). There was a considerable delay before Shaffer realized Guitar was engaged and brought his own men into the fight. The weight of numbers took their toll. After four hours of fighting, Porter’s soldiers fled into the brush ...
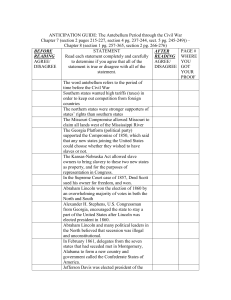
ANTICIPATION GUIDE: The Antebellum Period through the Civil War
... abolished in the United States. One important consequence of the Emancipation Proclamation was to change the Civil War from a war just to save the union to a war also to free slaves. In the early years of the Civil War, the main Union military strategy with respect to Georgia was a naval blockade of ...
... abolished in the United States. One important consequence of the Emancipation Proclamation was to change the Civil War from a war just to save the union to a war also to free slaves. In the early years of the Civil War, the main Union military strategy with respect to Georgia was a naval blockade of ...
The First Two Years of the Civil War
... • The Union army was able to take Vicksburg (Mississippi) and control of the Mississippi. CSA General John Pemberton surrendered on July 4, 1863. Union General Ulysses S. Grant captured 31,600 soldiers, 172 cannons, 60,000 muskets and a large supply of ammunition. ...
... • The Union army was able to take Vicksburg (Mississippi) and control of the Mississippi. CSA General John Pemberton surrendered on July 4, 1863. Union General Ulysses S. Grant captured 31,600 soldiers, 172 cannons, 60,000 muskets and a large supply of ammunition. ...
userfiles/605/my files/ch. 16 pp civil war?id=2958
... The Union forces divided into two major armies. The plan was to fight in the east in Virginia and to fight in the west to control the major port and rivers. The eastern army sought to capture Richmond, Virginia, the new Confederate capital. The western army aimed at taking the Tennessee and Miss ...
... The Union forces divided into two major armies. The plan was to fight in the east in Virginia and to fight in the west to control the major port and rivers. The eastern army sought to capture Richmond, Virginia, the new Confederate capital. The western army aimed at taking the Tennessee and Miss ...
America: A Concise History 3e
... troops were routed by P.G.T. Beauregard’s Confederate troops near Manassas Creek (also called Bull Run). Lincoln replaced McDowell with George B. McClellan and enlisted an additional million men, who would serve for three years in the newly created Army of the Potomac. In 1862,McClellan launched a t ...
... troops were routed by P.G.T. Beauregard’s Confederate troops near Manassas Creek (also called Bull Run). Lincoln replaced McDowell with George B. McClellan and enlisted an additional million men, who would serve for three years in the newly created Army of the Potomac. In 1862,McClellan launched a t ...
major battles of the civil war
... The Civil War became almost two separate conflicts. In the East, the Union wanted to capture Richmond, the capital of the Confederate States. West of the Appalachian Mountains, the Union hoped to gain control of the Mississippi River, thereby dividing the Confederacy. After the disastrous Battle of ...
... The Civil War became almost two separate conflicts. In the East, the Union wanted to capture Richmond, the capital of the Confederate States. West of the Appalachian Mountains, the Union hoped to gain control of the Mississippi River, thereby dividing the Confederacy. After the disastrous Battle of ...
the civil war - OCPS TeacherPress
... -- Hooker shortly after removed and replaced by General George Meade 3. Significance: Stonewall Jackson killed accidentally by own man -- Lee: "I have lost my right arm." 4. Casualties: Confederates lost 13,000 men (22% of Lee’s army) C. Battle of Gettysburg (July 1-3, 1863) 1. Lee decided to invad ...
... -- Hooker shortly after removed and replaced by General George Meade 3. Significance: Stonewall Jackson killed accidentally by own man -- Lee: "I have lost my right arm." 4. Casualties: Confederates lost 13,000 men (22% of Lee’s army) C. Battle of Gettysburg (July 1-3, 1863) 1. Lee decided to invad ...
Chapter_21_E-Notes
... D. New Orleans taken by Union in spring of 1862; led by David G. Farragut VII. War in the East: Lee’s last victories and the Battle of Gettysburg A. Lee defeated Gen. Ambrose E. Burnside at Fredericksburg, VA, on Dec. 13, 1862 1. Burnside launched ill-conceived frontal assault on Confederates dug in ...
... D. New Orleans taken by Union in spring of 1862; led by David G. Farragut VII. War in the East: Lee’s last victories and the Battle of Gettysburg A. Lee defeated Gen. Ambrose E. Burnside at Fredericksburg, VA, on Dec. 13, 1862 1. Burnside launched ill-conceived frontal assault on Confederates dug in ...
MAJOR EVENTS LEADING TO THE CIVIL WAR PEOPLE OF
... They were eventually killed or captured by Colonel Robert E. Lee. Brown was tried and hung for treason. ...
... They were eventually killed or captured by Colonel Robert E. Lee. Brown was tried and hung for treason. ...
Gettysburg: A Turning Point (HA)
... Union and Confederate troops met on July 1, 1863, west of Gettysburg, Pennsylvania. The Union troops, about 90,000 strong, were led by newly appointed General George C. Meade. After a brief skirmish, they occupied four miles of high ground along an area known as Cemetery Ridge. About a mile to the ...
... Union and Confederate troops met on July 1, 1863, west of Gettysburg, Pennsylvania. The Union troops, about 90,000 strong, were led by newly appointed General George C. Meade. After a brief skirmish, they occupied four miles of high ground along an area known as Cemetery Ridge. About a mile to the ...
Chapter 16- Civil War - Waverly
... General Robert E. Lee. Lee attacked Union forces in series of clashes called Seven Days’ Battles and forced Union army to retreat in June 1862. Lincoln ordered General John Pope to march to Richmond. Jackson’s troops stopped Pope’s army before it met up with the other Union army. The Second Battle o ...
... General Robert E. Lee. Lee attacked Union forces in series of clashes called Seven Days’ Battles and forced Union army to retreat in June 1862. Lincoln ordered General John Pope to march to Richmond. Jackson’s troops stopped Pope’s army before it met up with the other Union army. The Second Battle o ...
Packet Pages
... 4. On the first day of battle, Confederate forces pushed the Union line back to __________________________, just south of the town of Gettysburg. 5. On the second day of battle, the ____________ forces successfully defended Little Round Top. 6. On the third day of battle, General Lee planned to char ...
... 4. On the first day of battle, Confederate forces pushed the Union line back to __________________________, just south of the town of Gettysburg. 5. On the second day of battle, the ____________ forces successfully defended Little Round Top. 6. On the third day of battle, General Lee planned to char ...
(CH 10-12) (1848
... _____________________ was the 1st battle of the Civil War and occurred in South Carolina. _____________________ was the bloodiest single day of battle in the war and Lincoln signed the Emancipation Proclamation afterwards. _______________________ was the last Confederate stronghold on the Mississipp ...
... _____________________ was the 1st battle of the Civil War and occurred in South Carolina. _____________________ was the bloodiest single day of battle in the war and Lincoln signed the Emancipation Proclamation afterwards. _______________________ was the last Confederate stronghold on the Mississipp ...
Chapter 4 Notes
... July, 1863, the tide turned for the North Gettysburg-most decisive battle of Civil War ◦ Union victory ◦ 3-day battle ◦ 23,000 Union deaths/wounded, 28,000 Confederate deaths/wounded ◦ Casualties more than 30 percent ◦ Northerners proved that General Lee was not invincible ...
... July, 1863, the tide turned for the North Gettysburg-most decisive battle of Civil War ◦ Union victory ◦ 3-day battle ◦ 23,000 Union deaths/wounded, 28,000 Confederate deaths/wounded ◦ Casualties more than 30 percent ◦ Northerners proved that General Lee was not invincible ...
The Roll Call - The State of New York and the Civil War
... In an act short of desperation, Lee, on the 25th, ordered General John B. Gordon to make a surprise attack on federal Fort Stedman in the contested ground before Petersburg. Side actions occurred almost simultaneously at Fort Fisher and the Watkins House in the vicinity. This series of actions resul ...
... In an act short of desperation, Lee, on the 25th, ordered General John B. Gordon to make a surprise attack on federal Fort Stedman in the contested ground before Petersburg. Side actions occurred almost simultaneously at Fort Fisher and the Watkins House in the vicinity. This series of actions resul ...
A. Sectionalism – _______________________________________________________________________ The Nation Splits Apart (Ch. 10)
... A. Union strategy – developed by ___________________________________________________ 1. ___________________________________________________ 2. Halt the ___________________________________________________ 3. Seize ____________________________________________________________________ 4. Seize _________ ...
... A. Union strategy – developed by ___________________________________________________ 1. ___________________________________________________ 2. Halt the ___________________________________________________ 3. Seize ____________________________________________________________________ 4. Seize _________ ...
April—Charleston Harbor
... Davis was nevertheless responsible for the raising of the formidable Confederate armies, the notable appointment of General Robert E. Lee as commander of the Army of Virginia, and the encouragement of industrial enterprise throughout the South. His zeal, energy, and faith in the cause of the South w ...
... Davis was nevertheless responsible for the raising of the formidable Confederate armies, the notable appointment of General Robert E. Lee as commander of the Army of Virginia, and the encouragement of industrial enterprise throughout the South. His zeal, energy, and faith in the cause of the South w ...