Debate on Climate Shifts to Issue of Irreparable Change
... could disrupt this "conveyor belt," which, according to one study, is already slower than it was 30 years ago. According to these simulations, there is a 50 percent chance the current will collapse within 200 years. Some scientists, including President Bush's chief science adviser, John H. Marburger ...
... could disrupt this "conveyor belt," which, according to one study, is already slower than it was 30 years ago. According to these simulations, there is a 50 percent chance the current will collapse within 200 years. Some scientists, including President Bush's chief science adviser, John H. Marburger ...
Clarity on clouds Flourishing forests sea level spike Water
... decade 2000–2009 was the warmest on record, average global temperatures levelled off during this period despite a continued rise in greenhouse gas emissions. Now a team led by Susan Solomon of the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration in Boulder, ...
... decade 2000–2009 was the warmest on record, average global temperatures levelled off during this period despite a continued rise in greenhouse gas emissions. Now a team led by Susan Solomon of the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration in Boulder, ...
Global warming
... the mid-20th century, and its projected continuation. In media, it is synomonous with the term "climate change. • Global surface temperature increased 0.74 ± 0.18 °C during the 100 years ending in 2005.The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) concludes "most of the observed increase in g ...
... the mid-20th century, and its projected continuation. In media, it is synomonous with the term "climate change. • Global surface temperature increased 0.74 ± 0.18 °C during the 100 years ending in 2005.The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) concludes "most of the observed increase in g ...
The pros and cons of Cardiff Bay
... dioxide now, the effects of what we have already done will influence our weather for years. ...
... dioxide now, the effects of what we have already done will influence our weather for years. ...
Donner on climate science for CONS449C
... There are several ways, statistically-speaking, in which the climate might change (in response to some external or internal forcing – these examples are not specifically about greenhouse gases!) ...
... There are several ways, statistically-speaking, in which the climate might change (in response to some external or internal forcing – these examples are not specifically about greenhouse gases!) ...
PDF
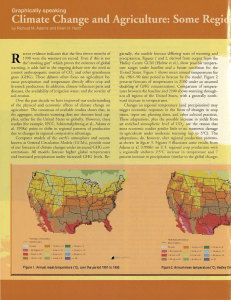
... soil erosion . Over the past decade we have improved our understanding of the physical and economic effects of climate change on agriculture. The consensus of available studies shows that, in me aggregate, moderate warming does not threaten food supplies, either for me United States or globally. How ...
... soil erosion . Over the past decade we have improved our understanding of the physical and economic effects of climate change on agriculture. The consensus of available studies shows that, in me aggregate, moderate warming does not threaten food supplies, either for me United States or globally. How ...
The oceans warm and cool much slower than land for a number of
... Major Oscillations and Their Effects Although ocean temperature anomalies tend to persist for long periods, there are oscillations or flip-flops that take place on scales of a few years to multiple decades. Both types have profound effect of global temperatures. El Nino and La Nina ...
... Major Oscillations and Their Effects Although ocean temperature anomalies tend to persist for long periods, there are oscillations or flip-flops that take place on scales of a few years to multiple decades. Both types have profound effect of global temperatures. El Nino and La Nina ...
1.1.1 Student Hook A..
... Waters are rising and warming, increasing the destructive power of storms, they said, and seas are becoming more acidic, threatening to throw entire food chains into chaos. “In the long run, sea level rises are going to be the most severe impact of global warming on human society,” said Professor St ...
... Waters are rising and warming, increasing the destructive power of storms, they said, and seas are becoming more acidic, threatening to throw entire food chains into chaos. “In the long run, sea level rises are going to be the most severe impact of global warming on human society,” said Professor St ...
Science of Climate Change
... (national/global) • Get the US back at the negotiation table • Stabilize Global population (empower women) ...
... (national/global) • Get the US back at the negotiation table • Stabilize Global population (empower women) ...
Al Gore`s An Inconvenient Truth: unscientific? It has been a week
... change, yet given that hurricanes collect their power from the temperature of surface water, there is a plausible physical link. One paper published recently comes down more strongly in favour of a link than any other previous study. I recently discussed this finding with a hurricane specialist at t ...
... change, yet given that hurricanes collect their power from the temperature of surface water, there is a plausible physical link. One paper published recently comes down more strongly in favour of a link than any other previous study. I recently discussed this finding with a hurricane specialist at t ...
Notes 19.1
... - Average atmospheric concentrations of CO2 rose from 280 ppm to 400 ppm since Industrial Revolution - 70% of CH4 emissions over the last 275 years are a result from human activities (probably even shorter than this) - Since 2010, U.S. and China accounted for 41% of the world’s greenhouse gas emissi ...
... - Average atmospheric concentrations of CO2 rose from 280 ppm to 400 ppm since Industrial Revolution - 70% of CH4 emissions over the last 275 years are a result from human activities (probably even shorter than this) - Since 2010, U.S. and China accounted for 41% of the world’s greenhouse gas emissi ...
global warming
... What is climate change? (Sometimes referred to as Global Warming) Climate Change is the process by which human emissions of Greenhouse Gases are believed to be causing changes in the Earth’s climate system. Watch out for the difference! ...
... What is climate change? (Sometimes referred to as Global Warming) Climate Change is the process by which human emissions of Greenhouse Gases are believed to be causing changes in the Earth’s climate system. Watch out for the difference! ...
File
... State the range of temperature change which could cause real damage to ecosystems. Explain why a range so seemingly small can have such major consequences. Summarize the projections of possible effects of global warming on (a) food production, (b) water supplies, (c) forests, (d) biodiversity, (e) s ...
... State the range of temperature change which could cause real damage to ecosystems. Explain why a range so seemingly small can have such major consequences. Summarize the projections of possible effects of global warming on (a) food production, (b) water supplies, (c) forests, (d) biodiversity, (e) s ...
Atmospheric science: Increasing wind sinks heat
... with the sea surface temperature and feeds back to the trade-wind changes. A natural pattern of decade-to-decade variability called the Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO), also known as the Interdecadal Pacific Oscillation, highlights this tropical Pacific feature. The negative phase of the PDO, char ...
... with the sea surface temperature and feeds back to the trade-wind changes. A natural pattern of decade-to-decade variability called the Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO), also known as the Interdecadal Pacific Oscillation, highlights this tropical Pacific feature. The negative phase of the PDO, char ...
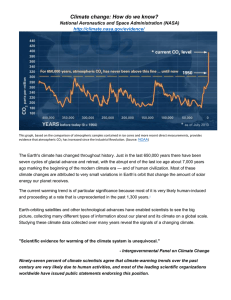
Climate change: How do we know?
... The Earth's climate has changed throughout history. Just in the last 650,000 years there have been seven cycles of glacial advance and retreat, with the abrupt end of the last ice age about 7,000 years ago marking the beginning of the modern climate era — and of human civilization. Most of these cli ...
... The Earth's climate has changed throughout history. Just in the last 650,000 years there have been seven cycles of glacial advance and retreat, with the abrupt end of the last ice age about 7,000 years ago marking the beginning of the modern climate era — and of human civilization. Most of these cli ...
2Dclimate / Uploaded File
... – Anywhere pollen can be found, it will tell you the plant species that lived around the location at the time the sediments were deposited, thus the temperature range at the time of deposition ...
... – Anywhere pollen can be found, it will tell you the plant species that lived around the location at the time the sediments were deposited, thus the temperature range at the time of deposition ...
Houghton CDFS 1 - University of California, Irvine
... Global carbon emissions from fossil fuel use, 1850 to 1990, and for scenarios to 2100, in GtC. For each scenario, the range shows the difference between gross and net emissions. From IIASA/WEC Global Energy Perspectives 1998. ...
... Global carbon emissions from fossil fuel use, 1850 to 1990, and for scenarios to 2100, in GtC. For each scenario, the range shows the difference between gross and net emissions. From IIASA/WEC Global Energy Perspectives 1998. ...
TRUE OR FALSE: 97% of all scientists support global warming theory
... funding of climate science, the opinions of scientists whose jobs and government grants can depend on arriving at pro-warming conclusions hardly constitute a reliable sampling of non-self-interested scientific opinion. No one knows what the climate will be like in the future. But if global warming s ...
... funding of climate science, the opinions of scientists whose jobs and government grants can depend on arriving at pro-warming conclusions hardly constitute a reliable sampling of non-self-interested scientific opinion. No one knows what the climate will be like in the future. But if global warming s ...
Rebuttal to the Rotarian Comments on Climate Change
... Warming and CO2 fertilization would generally increase biodiversity. Warmer regions are lush with animal and plant life. Colder regions have fewer species because there is less plant growth for food and survival is harder. Numerous studies show that warming in northern regions has resulted in an inc ...
... Warming and CO2 fertilization would generally increase biodiversity. Warmer regions are lush with animal and plant life. Colder regions have fewer species because there is less plant growth for food and survival is harder. Numerous studies show that warming in northern regions has resulted in an inc ...
26 Jul 2003
... alterations were so unscientific that the EPA decided to just delete the report’s entire section on global warming. In March of 2001, Bush reversed a campaign commitment to regulate fossil fuel emissions from power plants, and announced that the Kyoto Treaty is no longer acceptable to the United St ...
... alterations were so unscientific that the EPA decided to just delete the report’s entire section on global warming. In March of 2001, Bush reversed a campaign commitment to regulate fossil fuel emissions from power plants, and announced that the Kyoto Treaty is no longer acceptable to the United St ...
Global warming hiatus
A global warming hiatus, also sometimes referred to as a global warming pause or a global warming slowdown, is a period of relatively little change in globally averaged surface temperatures. In the current episode of global warming many such periods are evident in the surface temperature record, along with robust evidence of the long term warming trend.The exceptionally warm El Niño year of 1998 was an outlier from the continuing temperature trend, and so gave the appearance of a hiatus: by January 2006 assertions had been made that this showed that global warming had stopped. A 2009 study showed that decades without warming were not exceptional, and in 2011 a study showed that if allowances were made for known variability, the rising temperature trend continued unabated. There was increased public interest in 2013 in the run-up to publication of the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report, and despite concerns that a 15-year period was too short to determine a meaningful trend, the IPCC included a section on a hiatus, which it defined as a much smaller increasing linear trend over the 15 years from 1998 to 2012, than over the 60 years from 1951 to 2012. Various studies examined possible causes of the short term slowdown. Even though the overall climate system had continued to accumulate energy due to Earth's positive energy budget, the available temperature readings at the earth's surface indicated slower rates of increase in surface warming than in the prior decade. Since measurements at the top of the atmosphere show that Earth is receiving more energy than it is radiating back into space, the retained energy should be producing warming in at least one of the five parts of Earth's climate system.A July 2015 paper on the updated NOAA dataset cast doubt on the existence of this supposed hiatus, and found no indication of a slowdown. This analysis incorporated the latest corrections for known biases in ocean temperature measurements, and new land temperature data. Scientists working on other datasets welcomed this study, though the view was expressed that the short term warming trend had been slower than in previous periods of the same length.