here
... shorter-lived greenhouse gases, such as methane and some types of particles, would begin to reduce the warming influence within weeks to decades. ...
... shorter-lived greenhouse gases, such as methane and some types of particles, would begin to reduce the warming influence within weeks to decades. ...
Global Warming and Its Effect on the Arctic
... oceans • The oceans density, currently at 1.03*10^3, is expected to decrease which could shut down the deep ocean currents, such as the Thermohaline Circulation. Since this current modifies Europe's weather, if it shuts down, Europe could go into an ice age. • With more water in liquid state, more w ...
... oceans • The oceans density, currently at 1.03*10^3, is expected to decrease which could shut down the deep ocean currents, such as the Thermohaline Circulation. Since this current modifies Europe's weather, if it shuts down, Europe could go into an ice age. • With more water in liquid state, more w ...
A meteorological Pearl Harbor
... having to pump out their basements this week, the New England flooding bears out a pattern that climate scientists have followed. Last year, Thomas Knutson, a climate scientist with the National Oceanic ...
... having to pump out their basements this week, the New England flooding bears out a pattern that climate scientists have followed. Last year, Thomas Knutson, a climate scientist with the National Oceanic ...
Why are global temperatures changing? File
... Why might some people disagree that global warming is occurring or that it is caused by human activities? Science can only disprove theories, not prove them Correlation does not equal causation Limitations of the data: we can’t measure exactly how much of each gas comes from each source Computer mod ...
... Why might some people disagree that global warming is occurring or that it is caused by human activities? Science can only disprove theories, not prove them Correlation does not equal causation Limitations of the data: we can’t measure exactly how much of each gas comes from each source Computer mod ...
Doris Beaver`s Newsletters
... caused by volcanic eruptions emitting clouds of ash and smoke or the rising and lowering of mountain ranges due to the Earth’s plate tectonics. Remnants of ancient rivers now found on hillsides in the Alps were studied by German geologists who determined four major ice ages. Other paleoclimatologist ...
... caused by volcanic eruptions emitting clouds of ash and smoke or the rising and lowering of mountain ranges due to the Earth’s plate tectonics. Remnants of ancient rivers now found on hillsides in the Alps were studied by German geologists who determined four major ice ages. Other paleoclimatologist ...
Chapter 14: Climate Change
... On average, it lives more than a hundred years in the atmosphere and therefore affects climate over long time scales. ...
... On average, it lives more than a hundred years in the atmosphere and therefore affects climate over long time scales. ...
Great Lakes Climate - Associated Yacht Clubs
... change because of its distance from oceans, which moderate temperatures. Mr. Hansen, called the "godfather of global warming," is a controversial figure. His 1988 testimony to the U.S. Senate was the first from an expert witness who claimed that man-made pollution was changing the planet's climate b ...
... change because of its distance from oceans, which moderate temperatures. Mr. Hansen, called the "godfather of global warming," is a controversial figure. His 1988 testimony to the U.S. Senate was the first from an expert witness who claimed that man-made pollution was changing the planet's climate b ...
Global Climate Change
... Greenhouse gases from fossil fuel combustion are responsible for most of the warming of the last 50 years. (EPA, 2006) ...
... Greenhouse gases from fossil fuel combustion are responsible for most of the warming of the last 50 years. (EPA, 2006) ...
No Slide Title
... past millennium •It is difficult to explain the recent surface warming in terms of natural climate variability •Recent surface warming is largely consistent with simulations of the effects of anthropogenic influence on climate •Unresolved issues regarding the precise sensitivity of the climate to fo ...
... past millennium •It is difficult to explain the recent surface warming in terms of natural climate variability •Recent surface warming is largely consistent with simulations of the effects of anthropogenic influence on climate •Unresolved issues regarding the precise sensitivity of the climate to fo ...
Global Warming Can Be Stopped, World Climate Experts Say John
... Achieving this would shave about 0.12 percent off global gross domestic product (GDP) each year, panel co-chair Bert Metz explained at the briefing. Stabilization at the high end of the range—710 parts per million—would see a temperature rise as high as 7.2 degrees Fahrenheit (4 degrees Celsius) and ...
... Achieving this would shave about 0.12 percent off global gross domestic product (GDP) each year, panel co-chair Bert Metz explained at the briefing. Stabilization at the high end of the range—710 parts per million—would see a temperature rise as high as 7.2 degrees Fahrenheit (4 degrees Celsius) and ...
global warming - running into myself
... between 0.5 and 0.74 degrees C during the past century. • An average 2 degrees C warming is predicted by 2100. • Sea level has risen between 10 to 25 cm in the last 100 years. ...
... between 0.5 and 0.74 degrees C during the past century. • An average 2 degrees C warming is predicted by 2100. • Sea level has risen between 10 to 25 cm in the last 100 years. ...
Pacific puzzle
... attention, the global warming hiatus is pretty poorly defined. Although scientists have made huge headway in explaining it, they have struggled to agree on when it started. Most commonly, scientists have chosen 1998 as the starting point, as has the media, because that is when global surface warming ...
... attention, the global warming hiatus is pretty poorly defined. Although scientists have made huge headway in explaining it, they have struggled to agree on when it started. Most commonly, scientists have chosen 1998 as the starting point, as has the media, because that is when global surface warming ...
Introduction to Global Warming and Climate Change
... activities are responsible for most of the warming observed in the past fifty years. The warming is projected to continue and to increase over the course of the 21st century and beyond. Climate change already has a measurable impact on many natural and human systems: snow and ice are melting and fro ...
... activities are responsible for most of the warming observed in the past fifty years. The warming is projected to continue and to increase over the course of the 21st century and beyond. Climate change already has a measurable impact on many natural and human systems: snow and ice are melting and fro ...
Observed Changes to the Climate and their Causes Some human
... temperatures, mean 14.0°C, and carbon dioxide concentrations from ice cores and Mauna Loa (1958 on), mean 333.7 ppmv. Updated from Karl and Trenberth 2003. ...
... temperatures, mean 14.0°C, and carbon dioxide concentrations from ice cores and Mauna Loa (1958 on), mean 333.7 ppmv. Updated from Karl and Trenberth 2003. ...
The Kyoto protocol is an international treaty aiming at the reduction
... varies in time, as proves it the analysis of the geological coats. Our planet was colder for example of about ten degrees 20 000 years ago, during the peak of the last glacial period. These variations are nevertheless very slow, the temperature fluctuated between 0,2 degrees between the year one tho ...
... varies in time, as proves it the analysis of the geological coats. Our planet was colder for example of about ten degrees 20 000 years ago, during the peak of the last glacial period. These variations are nevertheless very slow, the temperature fluctuated between 0,2 degrees between the year one tho ...
climate_change_notes_and_assignment
... atmosphere. They are found in water vapor, carbon dioxide (plants and animals), methane (from the wetlands, oceans and termites), and nitrous oxide (soil, vegetation and oceans). ...
... atmosphere. They are found in water vapor, carbon dioxide (plants and animals), methane (from the wetlands, oceans and termites), and nitrous oxide (soil, vegetation and oceans). ...
Chapter 20 Climate Change and Ozone Depletion Core Case Study
... warming and ozone depletion are false and are being used by scientists and environmentalists to raise funds. What is your response to such claims? ...
... warming and ozone depletion are false and are being used by scientists and environmentalists to raise funds. What is your response to such claims? ...
Climate Change 1-physical factors
... ash was thrown into the atmosphere, cooling the world’s climate by about 1°C. ...
... ash was thrown into the atmosphere, cooling the world’s climate by about 1°C. ...
Carbon Footprints
... out the CO2. This finishes the cycle. Lately, the cycle has been disrupted by humans. We have affected it by using cars, factories, things in our homes, etc. You may have heard of the greenhouse effect. It’s what keeps our planet from becoming an ice box. It’s called the greenhouse effect because ou ...
... out the CO2. This finishes the cycle. Lately, the cycle has been disrupted by humans. We have affected it by using cars, factories, things in our homes, etc. You may have heard of the greenhouse effect. It’s what keeps our planet from becoming an ice box. It’s called the greenhouse effect because ou ...
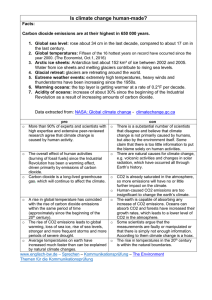
Is climate change human
... the blame solely on human activities. There are natural causes for climate change, e.g. volcanic activities and changes in solar radiation, which have occurred all through Earth’s history. CO2 is already saturated in the atmosphere, so more emissions will have no or little further impact on the clim ...
... the blame solely on human activities. There are natural causes for climate change, e.g. volcanic activities and changes in solar radiation, which have occurred all through Earth’s history. CO2 is already saturated in the atmosphere, so more emissions will have no or little further impact on the clim ...
Global warming hiatus
A global warming hiatus, also sometimes referred to as a global warming pause or a global warming slowdown, is a period of relatively little change in globally averaged surface temperatures. In the current episode of global warming many such periods are evident in the surface temperature record, along with robust evidence of the long term warming trend.The exceptionally warm El Niño year of 1998 was an outlier from the continuing temperature trend, and so gave the appearance of a hiatus: by January 2006 assertions had been made that this showed that global warming had stopped. A 2009 study showed that decades without warming were not exceptional, and in 2011 a study showed that if allowances were made for known variability, the rising temperature trend continued unabated. There was increased public interest in 2013 in the run-up to publication of the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report, and despite concerns that a 15-year period was too short to determine a meaningful trend, the IPCC included a section on a hiatus, which it defined as a much smaller increasing linear trend over the 15 years from 1998 to 2012, than over the 60 years from 1951 to 2012. Various studies examined possible causes of the short term slowdown. Even though the overall climate system had continued to accumulate energy due to Earth's positive energy budget, the available temperature readings at the earth's surface indicated slower rates of increase in surface warming than in the prior decade. Since measurements at the top of the atmosphere show that Earth is receiving more energy than it is radiating back into space, the retained energy should be producing warming in at least one of the five parts of Earth's climate system.A July 2015 paper on the updated NOAA dataset cast doubt on the existence of this supposed hiatus, and found no indication of a slowdown. This analysis incorporated the latest corrections for known biases in ocean temperature measurements, and new land temperature data. Scientists working on other datasets welcomed this study, though the view was expressed that the short term warming trend had been slower than in previous periods of the same length.