No Slide Title
... normal proportion of total annual precipitation from 1-day extreme events (more than 2 inches or 50.8mm) ...
... normal proportion of total annual precipitation from 1-day extreme events (more than 2 inches or 50.8mm) ...
Climate Change and Wetlands: Impacts and Mitigation
... The focus of this paper is the impacts of climate change on wetlands, and adaptation and mitigation options. To set the context for this, the paper also provides a brief overview of the importance and global distribution of wetlands, as well as of recent and projected changes in global and regional ...
... The focus of this paper is the impacts of climate change on wetlands, and adaptation and mitigation options. To set the context for this, the paper also provides a brief overview of the importance and global distribution of wetlands, as well as of recent and projected changes in global and regional ...
Investing in a Time of Climate Change
... Study”) to gain further insights into the investment implications of climate change. The timing is no coincidence: 2015 is a critical year, with global governments meeting in Paris in December to negotiate a new global climate change agreement. Climate change is an environmental, social and economic ...
... Study”) to gain further insights into the investment implications of climate change. The timing is no coincidence: 2015 is a critical year, with global governments meeting in Paris in December to negotiate a new global climate change agreement. Climate change is an environmental, social and economic ...
Federal Decision-Making on the Uncertain Impacts of Climate Change
... impacts information needs of federal decision‐making, and discusses the challenges associated with the information currently available for decisions that can have either minor or significant climate implications. The paper draws a clear distinction between policies with incremental climate effect ...
... impacts information needs of federal decision‐making, and discusses the challenges associated with the information currently available for decisions that can have either minor or significant climate implications. The paper draws a clear distinction between policies with incremental climate effect ...
Rechtspraak.nl - Print uitspraak
... It is also clear that collective, global actions are required to keep climate change within acceptable limits. In this context of collective actions, the 25%-40% reduction you refer to in your letter was always the objective. The EU’s offer to pursue a 30% reduction by 2020, on the condition that ot ...
... It is also clear that collective, global actions are required to keep climate change within acceptable limits. In this context of collective actions, the 25%-40% reduction you refer to in your letter was always the objective. The EU’s offer to pursue a 30% reduction by 2020, on the condition that ot ...
Antagonism, The Commons and Solidarity
... liberalization in diverse parts of the globe opens up different ways of understanding such interventions. The ways that these geographies of power are contested frequently produce antagonistic politics of climate change. They also produce a set of political interventions that can usefully be descri ...
... liberalization in diverse parts of the globe opens up different ways of understanding such interventions. The ways that these geographies of power are contested frequently produce antagonistic politics of climate change. They also produce a set of political interventions that can usefully be descri ...
Soil temperature response to 21st century global warming: the role
... Revised: 18 May 2011 – Accepted: 15 June 2011 – Published: 24 June 2011 ...
... Revised: 18 May 2011 – Accepted: 15 June 2011 – Published: 24 June 2011 ...
End of Program Report - Pacific Climate Change Science
... • Mean temperatures in the region have increased by 0.08 to 0.20°C/ decade since 1960. Sea level in the region has risen by 2 to 10 mm/year from 1993-2009, with significant year-to-year variability. The global average rate of rise over the same period is 3.2 mm/year. Rainfall data since 1960 show l ...
... • Mean temperatures in the region have increased by 0.08 to 0.20°C/ decade since 1960. Sea level in the region has risen by 2 to 10 mm/year from 1993-2009, with significant year-to-year variability. The global average rate of rise over the same period is 3.2 mm/year. Rainfall data since 1960 show l ...
Climate Change and Extreme Events
... Climate and land-use change complicate current and future water management challenges through their complex and shifting interactions that alter space–time patterns of hydrological variability and induce uncertainty in the decision making processes. Limitations of traditional hydrological analyses a ...
... Climate and land-use change complicate current and future water management challenges through their complex and shifting interactions that alter space–time patterns of hydrological variability and induce uncertainty in the decision making processes. Limitations of traditional hydrological analyses a ...
Utilization of Science-Based Information on Climate Change in
... Witness Position on Human Activity as Cause of Global Warming – Scientists Only....................................................................................................................... 31 ...
... Witness Position on Human Activity as Cause of Global Warming – Scientists Only....................................................................................................................... 31 ...
Update on Selected Climate Issues of Concern
... The Arctic Monitoring and Assessment Programme (AMAP) is a Working Group of the Arctic Council. The Arctic Council Ministers have requested AMAP to: • produce integrated assessment reports on the status and trends of the conditions of the Arctic ecosystems, including humans; • identify possible caus ...
... The Arctic Monitoring and Assessment Programme (AMAP) is a Working Group of the Arctic Council. The Arctic Council Ministers have requested AMAP to: • produce integrated assessment reports on the status and trends of the conditions of the Arctic ecosystems, including humans; • identify possible caus ...
CHAPTER 2: ARCTIC CLIMATE – Past and Present Lead Author
... The Arctic region is the northern polar component of the global climate system. The global climate system has been thoroughly examined in the recent reports of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC, 2001), including a description of the global climate system (IPCC, WGI, pp 85-98) and t ...
... The Arctic region is the northern polar component of the global climate system. The global climate system has been thoroughly examined in the recent reports of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC, 2001), including a description of the global climate system (IPCC, WGI, pp 85-98) and t ...
Australia`s future emissions reduction targets
... Emissions—Targets and Progress Review, which was provided to the Minister (and released publicly) on 27 February 2014. That report, which reflected extensive public consultation, presented the Authority’s comprehensive assessment of the evidence coming from climate scientists, the efforts being made ...
... Emissions—Targets and Progress Review, which was provided to the Minister (and released publicly) on 27 February 2014. That report, which reflected extensive public consultation, presented the Authority’s comprehensive assessment of the evidence coming from climate scientists, the efforts being made ...
The Northeast Asia mountain glaciers in the near
... Krenke, 2005). Comparison of data obtained between the late 1950s and 2001 about the glaciers of northeast Asia and their mass exchange, shows that they have undergone appreciable changes – as revealed through retreat of their termini, surface lowering, formation of new morainic deposits, etc. By ou ...
... Krenke, 2005). Comparison of data obtained between the late 1950s and 2001 about the glaciers of northeast Asia and their mass exchange, shows that they have undergone appreciable changes – as revealed through retreat of their termini, surface lowering, formation of new morainic deposits, etc. By ou ...
what is climate change? and how it will affect bangladesh
... destructive of life; it steals from future generations, it penalises the poor, it is exaggerated by greed, it puts diversity at risk. Environmental pollution hurts all of life; it is in the interest of every living thing for human beings to do something about it’. As Christians ‘we care about what h ...
... destructive of life; it steals from future generations, it penalises the poor, it is exaggerated by greed, it puts diversity at risk. Environmental pollution hurts all of life; it is in the interest of every living thing for human beings to do something about it’. As Christians ‘we care about what h ...
- Wiley Online Library
... warmer climate, a negative SLP anomaly occurs off the west coast of the United States, which corresponds to a decrease (increase) in southerly wind on the western (eastern) side of the anomaly. This pattern explains the dipole pattern in marine fog changes in the eastern North Pacific in January. In ...
... warmer climate, a negative SLP anomaly occurs off the west coast of the United States, which corresponds to a decrease (increase) in southerly wind on the western (eastern) side of the anomaly. This pattern explains the dipole pattern in marine fog changes in the eastern North Pacific in January. In ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES LIFE David Albouy
... change forecast, we rely primarily on the business-as-usual A2 scenario used in the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) fourth assessment report (2007), which predicts an 8.3°F increase in U.S. temperatures by 2100. Our simulated welfare effects are predicated on technology and preferen ...
... change forecast, we rely primarily on the business-as-usual A2 scenario used in the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) fourth assessment report (2007), which predicts an 8.3°F increase in U.S. temperatures by 2100. Our simulated welfare effects are predicated on technology and preferen ...
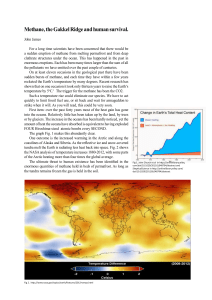
Methane, the Gakkel Ridge and human survival.
... massive explosion of methane would unfold is unknown, but being so much more potent than CO2, its release in large quantities would have an enormous impact on global temperature. The disastrous outcome of continued release of methane is displayed in the historical records, mainly derived from ice co ...
... massive explosion of methane would unfold is unknown, but being so much more potent than CO2, its release in large quantities would have an enormous impact on global temperature. The disastrous outcome of continued release of methane is displayed in the historical records, mainly derived from ice co ...
Workshop Report - Ontario Centre for Climate Impacts and
... atmosphere and are tracking in line with the ‘worst case’ scenarios developed by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). This combined with continued emissions commits the planet to further global climate change. Globally, temperatures have increased 0.74°C over the last 100 years. The ...
... atmosphere and are tracking in line with the ‘worst case’ scenarios developed by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). This combined with continued emissions commits the planet to further global climate change. Globally, temperatures have increased 0.74°C over the last 100 years. The ...
Climate change and the greenhouse effect
... daily, weekly and even annual atmospheric conditions of Earth (such as humidity, rainfall, maximum and minimum temperatures, and wind). Climate is these weather conditions at a certain locality, statistically averaged over a period of at least 30 years9. Global warming and climate change It is neces ...
... daily, weekly and even annual atmospheric conditions of Earth (such as humidity, rainfall, maximum and minimum temperatures, and wind). Climate is these weather conditions at a certain locality, statistically averaged over a period of at least 30 years9. Global warming and climate change It is neces ...
Global warming hiatus
A global warming hiatus, also sometimes referred to as a global warming pause or a global warming slowdown, is a period of relatively little change in globally averaged surface temperatures. In the current episode of global warming many such periods are evident in the surface temperature record, along with robust evidence of the long term warming trend.The exceptionally warm El Niño year of 1998 was an outlier from the continuing temperature trend, and so gave the appearance of a hiatus: by January 2006 assertions had been made that this showed that global warming had stopped. A 2009 study showed that decades without warming were not exceptional, and in 2011 a study showed that if allowances were made for known variability, the rising temperature trend continued unabated. There was increased public interest in 2013 in the run-up to publication of the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report, and despite concerns that a 15-year period was too short to determine a meaningful trend, the IPCC included a section on a hiatus, which it defined as a much smaller increasing linear trend over the 15 years from 1998 to 2012, than over the 60 years from 1951 to 2012. Various studies examined possible causes of the short term slowdown. Even though the overall climate system had continued to accumulate energy due to Earth's positive energy budget, the available temperature readings at the earth's surface indicated slower rates of increase in surface warming than in the prior decade. Since measurements at the top of the atmosphere show that Earth is receiving more energy than it is radiating back into space, the retained energy should be producing warming in at least one of the five parts of Earth's climate system.A July 2015 paper on the updated NOAA dataset cast doubt on the existence of this supposed hiatus, and found no indication of a slowdown. This analysis incorporated the latest corrections for known biases in ocean temperature measurements, and new land temperature data. Scientists working on other datasets welcomed this study, though the view was expressed that the short term warming trend had been slower than in previous periods of the same length.