Name Block ______
... Means to withdraw: Seven Southern states did this after Abraham Lincoln was elected President in 1860; Four more States followed soon after 33. Emancipation Proclamation Document that ended slavery in the Confederate states 34. Gettysburg Address Lincoln’s speech that said the Civil War was fought t ...
... Means to withdraw: Seven Southern states did this after Abraham Lincoln was elected President in 1860; Four more States followed soon after 33. Emancipation Proclamation Document that ended slavery in the Confederate states 34. Gettysburg Address Lincoln’s speech that said the Civil War was fought t ...
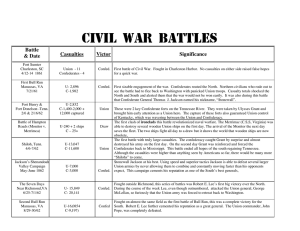
Civil War Battles Chart
... heights but the soldiers were unable to help their fallen comrades. Lincoln’s quest for a winning general continued with Joseph Hooker. At Chancellorsville he was totally outmaneuvered by Robert E. Lee and Stonewall Jackson. This battle was the greatest Confederate victory of the war. It was tainted ...
... heights but the soldiers were unable to help their fallen comrades. Lincoln’s quest for a winning general continued with Joseph Hooker. At Chancellorsville he was totally outmaneuvered by Robert E. Lee and Stonewall Jackson. This battle was the greatest Confederate victory of the war. It was tainted ...
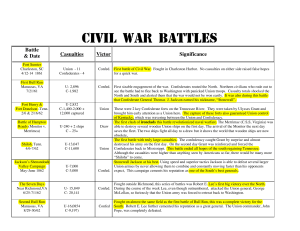
Civil War Battles Chart
... heights but the soldiers were unable to help their fallen comrades. Lincoln’s quest for a winning general continued with Joseph Hooker. At Chancellorsville he was totally outmaneuvered by Robert E. Lee and Stonewall Jackson. This battle was the greatest Confederate victory of the war. It was tainted ...
... heights but the soldiers were unable to help their fallen comrades. Lincoln’s quest for a winning general continued with Joseph Hooker. At Chancellorsville he was totally outmaneuvered by Robert E. Lee and Stonewall Jackson. This battle was the greatest Confederate victory of the war. It was tainted ...
CIvil War/Reconstruction Review
... 14. Who was the commander-in-chief of Union forces? Ulysses S. Grant 15. Who was commander-in-chief of Confederate forces? Robert E. Lee 16. How and when did the Civil War end? Lee surrendered to Grant at Appomattox Courthouse on April 9, 1865 17. What were the lasting impacts of Reconstruction on t ...
... 14. Who was the commander-in-chief of Union forces? Ulysses S. Grant 15. Who was commander-in-chief of Confederate forces? Robert E. Lee 16. How and when did the Civil War end? Lee surrendered to Grant at Appomattox Courthouse on April 9, 1865 17. What were the lasting impacts of Reconstruction on t ...
People of the Civil War
... _____________ was known as the “Angel of the Battlefield”. _____________ General of the Union Army. _____________ President of the United States during the War. _____________ General of the Confederate Army. _____________ 1st African American to be awarded the Congressional Medal of Honor. _________ ...
... _____________ was known as the “Angel of the Battlefield”. _____________ General of the Union Army. _____________ President of the United States during the War. _____________ General of the Confederate Army. _____________ 1st African American to be awarded the Congressional Medal of Honor. _________ ...
Name
... production, and so on. reconnaissance Operations designed specifically to observe and ferret out pertinent information about an adversary. proclamation An official announcement or publicly declared order. flank The side of an army, where it is vulnerable to attack. court-martial A military court or ...
... production, and so on. reconnaissance Operations designed specifically to observe and ferret out pertinent information about an adversary. proclamation An official announcement or publicly declared order. flank The side of an army, where it is vulnerable to attack. court-martial A military court or ...
Chapter 16.5 Vocabulary Two Column Notes
... ● Total war would ruin south’s economy and will to fight/destroy bridges, crops, livestock, plantations, railways, freed slaves ● December 10, 1864 - Sherman arrives at Savannah, Georgia/leaves destruction behind him ...
... ● Total war would ruin south’s economy and will to fight/destroy bridges, crops, livestock, plantations, railways, freed slaves ● December 10, 1864 - Sherman arrives at Savannah, Georgia/leaves destruction behind him ...
APUSH Civil War I - OCPS TeacherPress
... • Impact in South? In North? • Result when slaves are later freed in South? ...
... • Impact in South? In North? • Result when slaves are later freed in South? ...
Southern Victories African Americans in the Civil War
... troops in an attack on the Union's position at Cemetery Ridge. Putting themselves directly in the line of fire, they advanced across open land in what came to be remembered as Pickett's Charge. At first, it seemed that Pickett's Charge might work. The Confederates broke the first line of Union defen ...
... troops in an attack on the Union's position at Cemetery Ridge. Putting themselves directly in the line of fire, they advanced across open land in what came to be remembered as Pickett's Charge. At first, it seemed that Pickett's Charge might work. The Confederates broke the first line of Union defen ...
The American Civil War
... • In May 1863, Hooker tried to attack Lee's forces from a side or flanking position. • In just ten minutes, Confederate forces routed the Union army at the Battle of Chancellorsville. • But the Confederate victory came at a high cost. Lee's ablest lieutenant, Stonewall Jackson, was accidentally shot ...
... • In May 1863, Hooker tried to attack Lee's forces from a side or flanking position. • In just ten minutes, Confederate forces routed the Union army at the Battle of Chancellorsville. • But the Confederate victory came at a high cost. Lee's ablest lieutenant, Stonewall Jackson, was accidentally shot ...
Chapter 11 The Civil War Essential Question What were the
... The Union would control the MS River and split the Confederacy in half. 6. What is total warfare? A. Not only fight against the army and government but, against the civilians as well. Did not kill civilians! Destroyed their property, land, and food sources. B. Because, civilians produced the weapons ...
... The Union would control the MS River and split the Confederacy in half. 6. What is total warfare? A. Not only fight against the army and government but, against the civilians as well. Did not kill civilians! Destroyed their property, land, and food sources. B. Because, civilians produced the weapons ...
United States History EOC Review
... Causes of the Civil War - Election of 1860- Candidates: Stephen Douglas, John Breckinridge, John Bell, and Abraham Lincoln; Lincoln received only 40% of the popular vote but his electoral vote was a landslide with 180 votes; seven southern states decided to secede because Lincoln won without winning ...
... Causes of the Civil War - Election of 1860- Candidates: Stephen Douglas, John Breckinridge, John Bell, and Abraham Lincoln; Lincoln received only 40% of the popular vote but his electoral vote was a landslide with 180 votes; seven southern states decided to secede because Lincoln won without winning ...
Standard IV: The student will understand
... People could pay for a substitute if they were drafted Irish immigrants had no money to pay for substitute Rioters in New York killed over 1000 people & did $2 million dollars worth of damage • Emancipation Proclamation- issued by Lincoln in 1863; freed slaves in the Confederacy ...
... People could pay for a substitute if they were drafted Irish immigrants had no money to pay for substitute Rioters in New York killed over 1000 people & did $2 million dollars worth of damage • Emancipation Proclamation- issued by Lincoln in 1863; freed slaves in the Confederacy ...
Civil War Battles and Technology
... State: Pennsylvania Dates: July 1-3, 1863 Principal Forces Engaged: 158,300 total (83,289 [US];75,054 [CS]) Estimated Casualties: 51,000 total (US 23,000; CS 28,000) Results: Union victory ...
... State: Pennsylvania Dates: July 1-3, 1863 Principal Forces Engaged: 158,300 total (83,289 [US];75,054 [CS]) Estimated Casualties: 51,000 total (US 23,000; CS 28,000) Results: Union victory ...
HERE - Gallopade International
... Confederacy. On April 10, 1861, after learning that newly elected President Lincoln planned to send reinforcements to Fort Sumter, the Confederacy gave General Beauregard an order to attack “in such a manner as you may determine to reduce it,” unless Anderson removed his troops from the fort. ...
... Confederacy. On April 10, 1861, after learning that newly elected President Lincoln planned to send reinforcements to Fort Sumter, the Confederacy gave General Beauregard an order to attack “in such a manner as you may determine to reduce it,” unless Anderson removed his troops from the fort. ...
The Civil War - Cloudfront.net
... African American Soldiers • Even though they couldn’t fight for the Union army early in the war, African Americans helped as guides and spies. • By 1862 they were allowed to enlist. By the end of the war 10% of the army and 18% of the navy was made up of African Americans. • African American soldie ...
... African American Soldiers • Even though they couldn’t fight for the Union army early in the war, African Americans helped as guides and spies. • By 1862 they were allowed to enlist. By the end of the war 10% of the army and 18% of the navy was made up of African Americans. • African American soldie ...
Chapter 12 slide show
... • In the first three hours of fighting, 12,000 soldiers from both sides were either killed or wounded. • The North won the battle, but failed to chase down the southern army and destroy it. • It was the bloodiest day of the Civil War. ...
... • In the first three hours of fighting, 12,000 soldiers from both sides were either killed or wounded. • The North won the battle, but failed to chase down the southern army and destroy it. • It was the bloodiest day of the Civil War. ...
CIVIL WAR In the spring of 1861, decades of simmering tensions
... response to the election of Abraham Lincoln as President of the United States, 11 southern slave states declared their secession from the United States and formed the Confederate States of America ("the Confederacy"); the other 25 states supported the federal government ("the Union"). After four yea ...
... response to the election of Abraham Lincoln as President of the United States, 11 southern slave states declared their secession from the United States and formed the Confederate States of America ("the Confederacy"); the other 25 states supported the federal government ("the Union"). After four yea ...
The Civil War
... Proclamation to try to rebuild northern support for the war. The Proclamation ordered that all slaves in Confederate states would be free if the state did not return to the Union by Jan. 1, 1863. The Proclamation did not apply to the 800,000 slaves living in the border states that were part of t ...
... Proclamation to try to rebuild northern support for the war. The Proclamation ordered that all slaves in Confederate states would be free if the state did not return to the Union by Jan. 1, 1863. The Proclamation did not apply to the 800,000 slaves living in the border states that were part of t ...
The Civil War
... – Although southerners did not trust slaves enough to become soldiers, they became so desperate for soldiers by the end of the war that they did consider it – 54th Massachusetts ...
... – Although southerners did not trust slaves enough to become soldiers, they became so desperate for soldiers by the end of the war that they did consider it – 54th Massachusetts ...
Girding for War: The North & the South
... Lincoln decided to send supplies to troops promised Governor Pickens(SC) that he was not sending more men or weapons, just provisions. ...
... Lincoln decided to send supplies to troops promised Governor Pickens(SC) that he was not sending more men or weapons, just provisions. ...
The Master Plans The Anaconda Plan
... slight compared to those at the Battle of Shiloh in Tennessee. There, on April 6, 1862, Confederate forces under General Albert Sidney Johnston surprised Union forces commanded by General Ulysses S. Grant. Most of the soldiers had never seen battle. The South pushed back one Union position after ano ...
... slight compared to those at the Battle of Shiloh in Tennessee. There, on April 6, 1862, Confederate forces under General Albert Sidney Johnston surprised Union forces commanded by General Ulysses S. Grant. Most of the soldiers had never seen battle. The South pushed back one Union position after ano ...
Civil War Battles in Texas
... mortar boat into position. One of the Confederate officers then asked if he could be granted time to talk with Col. Cook again. This officer, a major, negotiated with Renshaw for a four-day truce to evacuate the women, children, and aliens from the city. Cook approved the truce but added a stipulati ...
... mortar boat into position. One of the Confederate officers then asked if he could be granted time to talk with Col. Cook again. This officer, a major, negotiated with Renshaw for a four-day truce to evacuate the women, children, and aliens from the city. Cook approved the truce but added a stipulati ...
Battle of Fort Pillow

The Battle of Fort Pillow, also known as the Fort Pillow massacre, was fought on April 12, 1864, at Fort Pillow on the Mississippi River in Henning, Tennessee, during the American Civil War. The battle ended with a massacre of Federal troops (most of them African American) attempting to surrender, by soldiers under the command of Confederate Major General Nathan Bedford Forrest. Military historian David J. Eicher concluded, ""Fort Pillow marked one of the bleakest, saddest events of American military history.""