General U.S. Grant
... Union General He commanded the Union army that captured Atlanta and began the “ march to the sea”. Captured and burned Columbia, SC in February 1865. Most hated man in the South. He believed in waging hard war. ...
... Union General He commanded the Union army that captured Atlanta and began the “ march to the sea”. Captured and burned Columbia, SC in February 1865. Most hated man in the South. He believed in waging hard war. ...
File
... 2. Why did the election of Abraham Lincoln seem to increase sectional tensions in the prewar period? 3. What impact did political and military leadership have on the conduct of the war? 4. How did the war affect minorities during the period ...
... 2. Why did the election of Abraham Lincoln seem to increase sectional tensions in the prewar period? 3. What impact did political and military leadership have on the conduct of the war? 4. How did the war affect minorities during the period ...
Southern secession
... • After Lincoln elected, Southern leaders believe they no longer have a voice in government- many felt that to preserve their economy and their way of life, they needed to leave the union. • South Carolina is the first state to leave the union (December 20, 1860) • 6 more states soon follow ...
... • After Lincoln elected, Southern leaders believe they no longer have a voice in government- many felt that to preserve their economy and their way of life, they needed to leave the union. • South Carolina is the first state to leave the union (December 20, 1860) • 6 more states soon follow ...
Major Battles of the Civil War
... Monitor: North’s Iron-clad ship Ships could not sink each other North successful in keeping the Merrimack in harbor ...
... Monitor: North’s Iron-clad ship Ships could not sink each other North successful in keeping the Merrimack in harbor ...
Major Battles of the Civil War
... Monitor: North’s Iron-clad ship Ships could not sink each other North successful in keeping the Merrimack in harbor ...
... Monitor: North’s Iron-clad ship Ships could not sink each other North successful in keeping the Merrimack in harbor ...
Abraham Lincoln Jefferson Davis Ulysses S. Grant Robert E. Lee
... Wrote the Gettysburg Address that said the Civil War was to preserve a government “of the people, by the people, and for the people ...
... Wrote the Gettysburg Address that said the Civil War was to preserve a government “of the people, by the people, and for the people ...
US History review power point
... Confederate General of the Army of Northern VA Opposed secession as well as force to keep Union together Sided with South after Ft. Sumter ...
... Confederate General of the Army of Northern VA Opposed secession as well as force to keep Union together Sided with South after Ft. Sumter ...
to view Ch 16 sec 1 study highlights!
... Defend itself until the North grew tired of fighting Union Army would have to travel and maintain long supply lines Southerners were familiar with the land ...
... Defend itself until the North grew tired of fighting Union Army would have to travel and maintain long supply lines Southerners were familiar with the land ...
The End is Near…
... In one particular battle, President Lincoln used the Union Navy to blockade southern ports. A blockade is when the ports or waterways are blocked off in an attempt to cut off supply ships from bringing in food, war supplies and/or communication. A major sea battle between the Monitor (a Union ship) ...
... In one particular battle, President Lincoln used the Union Navy to blockade southern ports. A blockade is when the ports or waterways are blocked off in an attempt to cut off supply ships from bringing in food, war supplies and/or communication. A major sea battle between the Monitor (a Union ship) ...
Resources of the North and South
... – Economic conditions and interests in each region vary, each wanting things that are good only for their section of the country • Why did slavery expand in the South not the North? – Climate and soil encouraged plantations • What was the Seneca Falls Convention concerned with? – Women’s rights • Ho ...
... – Economic conditions and interests in each region vary, each wanting things that are good only for their section of the country • Why did slavery expand in the South not the North? – Climate and soil encouraged plantations • What was the Seneca Falls Convention concerned with? – Women’s rights • Ho ...
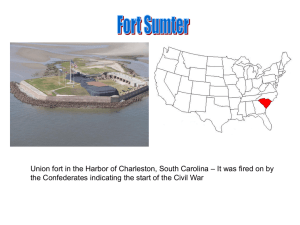
Fort Sumter, in Charleston Harbor (one of the most important federal
... • April 6, 1861 – President Lincoln announces that he is re-supplying Union troops at Fort Sumter, in Charleston Harbor (one of the most important federal posts that controlled the entrance to Charleston Harbor). • Confederate leaders decided to attack Fort Sumter before the ships arrived. They open ...
... • April 6, 1861 – President Lincoln announces that he is re-supplying Union troops at Fort Sumter, in Charleston Harbor (one of the most important federal posts that controlled the entrance to Charleston Harbor). • Confederate leaders decided to attack Fort Sumter before the ships arrived. They open ...
Last thoughts
... Proclamation • A statement issued by Abraham Lincoln • September 22, 1862, it declared that all slaves in the rebellious Confederate states would be free ...
... Proclamation • A statement issued by Abraham Lincoln • September 22, 1862, it declared that all slaves in the rebellious Confederate states would be free ...
1st Bull Run- (1 Manassas) JULY 21, 1861 Battle Notes: •Both sides
... •Since Lee retreated back to Virginia, Antietam is considered a Union strategic victory Battle Significance ...
... •Since Lee retreated back to Virginia, Antietam is considered a Union strategic victory Battle Significance ...
Civil War Plans and Early Battles
... preserve the Union • was aimed at keeping the four border states in the Union, even though they allowed slavery. He thought this was crucial to winning the war ...
... preserve the Union • was aimed at keeping the four border states in the Union, even though they allowed slavery. He thought this was crucial to winning the war ...
Civil War
... • Davis’s First Inaugural Address: Secede or go to war; Based on Declaration of Independence-right to alter or abolish a government • Emancipation Proclamation 1862: Greater purpose to war to end slavery in rebelling states; Prevent Europe from helping South; keep border states; African American to ...
... • Davis’s First Inaugural Address: Secede or go to war; Based on Declaration of Independence-right to alter or abolish a government • Emancipation Proclamation 1862: Greater purpose to war to end slavery in rebelling states; Prevent Europe from helping South; keep border states; African American to ...
LEQ: How will the north and south prepare for war?
... Confederate troops began to take forts Symbol of rebellion Confederate troops won the fort ...
... Confederate troops began to take forts Symbol of rebellion Confederate troops won the fort ...
Chapter 22 Summary The Civil War took up where Napoleon and
... cavalry, artillery, and infantry with support units. The cavalry’s principal job was reconnaissance. Before an attacking army moved, its artillery slugged away at enemy positions with exploding shells. The infantry was the backbone of the army. Except for special units of sharpshooters, there was no ...
... cavalry, artillery, and infantry with support units. The cavalry’s principal job was reconnaissance. Before an attacking army moved, its artillery slugged away at enemy positions with exploding shells. The infantry was the backbone of the army. Except for special units of sharpshooters, there was no ...
The Important People of the Civil War
... Content Objective: Students will learn about the key leaders on and off the Battle Field Language Objective: Students will create a foldable of important Civil War Leaders. ...
... Content Objective: Students will learn about the key leaders on and off the Battle Field Language Objective: Students will create a foldable of important Civil War Leaders. ...
us history 4-2
... Union fort in the Harbor of Charleston, South Carolina – It was fired on by the Confederates indicating the start of the Civil War ...
... Union fort in the Harbor of Charleston, South Carolina – It was fired on by the Confederates indicating the start of the Civil War ...
American Civil War • The Civil War took place from
... whom 3.5 million were enslaved Africans), around 18,000 manufacturing plants, and less than 30% of the railroads. • During February of 1861, the seven Southern states that had seceded up to that time created a Confederate Constitution. Shortly after Lincoln’s inauguration, Fort Sumter in the harbor ...
... whom 3.5 million were enslaved Africans), around 18,000 manufacturing plants, and less than 30% of the railroads. • During February of 1861, the seven Southern states that had seceded up to that time created a Confederate Constitution. Shortly after Lincoln’s inauguration, Fort Sumter in the harbor ...
8th his ch16 study guide
... EMANCIPATION PROCLAMATION JOYFULLY. 6) WILLIAM TECUMSEH SHERMANʼS “MARCH TO THE SEA” HEADED ...
... EMANCIPATION PROCLAMATION JOYFULLY. 6) WILLIAM TECUMSEH SHERMANʼS “MARCH TO THE SEA” HEADED ...
Civil War Review - Social Studies With A Smile
... certain strengths. The North had more __________________, factories, and railroads. The South had better ____________________ leaders, such as Robert E. __________________. The __________________ planned to wage a defensive war. They would also try to capture __________________, the Union’s capital. ...
... certain strengths. The North had more __________________, factories, and railroads. The South had better ____________________ leaders, such as Robert E. __________________. The __________________ planned to wage a defensive war. They would also try to capture __________________, the Union’s capital. ...
Document
... War. Northern victory. General Lee unsuccessfully invaded the north. Battle of Gettysburg ...
... War. Northern victory. General Lee unsuccessfully invaded the north. Battle of Gettysburg ...
Confederate privateer

The Confederate privateers were privately owned ships that were authorized by the government of the Confederate States of America to attack the shipping of the United States. Although the appeal was to profit by capturing merchant vessels and seizing their cargoes, the government was most interested in diverting the efforts of the Union Navy away from the blockade of Southern ports, and perhaps to encourage European intervention in the conflict.At the beginning of the American Civil War, the Confederate government sought to counter the United States Navy in part by appealing to private enterprise world-wide to engage in privateering against United States Shipping. [[