Civil War
... attacted Fort Sumter near Charleston • The Confederate States of America were more successful • The Union started a blockade against the Confederate States ...
... attacted Fort Sumter near Charleston • The Confederate States of America were more successful • The Union started a blockade against the Confederate States ...
Battle of Bull Run
... Battle of Bull Run st (1 Manassas), July, 1861 Lincoln sent 30,000 inexperienced soldiers to fight at Bull Run. Northern troops were pushed back to D.C. South won this battle but “lost the war”. WHY? Failed to capture Washington, D.C. Would never be so close to Washington, D.C. again ...
... Battle of Bull Run st (1 Manassas), July, 1861 Lincoln sent 30,000 inexperienced soldiers to fight at Bull Run. Northern troops were pushed back to D.C. South won this battle but “lost the war”. WHY? Failed to capture Washington, D.C. Would never be so close to Washington, D.C. again ...
11.1
... justice, insure domestic tranquility, and secure the blessings of liberty to ourselves and our posterity — invoking the favor and guidance of Almighty God — do ordain and establish this Constitution for the Confederate States of America.” ...
... justice, insure domestic tranquility, and secure the blessings of liberty to ourselves and our posterity — invoking the favor and guidance of Almighty God — do ordain and establish this Constitution for the Confederate States of America.” ...
1. Abraham Lincoln was elected president in November of 1860. 2
... Jefferson Davis as president in January 1861. 7. The Confederate government ordered Union soldiers to leave Fort Sumter which was located in the Charleston harbor. ...
... Jefferson Davis as president in January 1861. 7. The Confederate government ordered Union soldiers to leave Fort Sumter which was located in the Charleston harbor. ...
Section 1
... preserve the Union • was aimed at keeping the four border states in the Union, even though they allowed slavery. He thought this was crucial to winning the war ...
... preserve the Union • was aimed at keeping the four border states in the Union, even though they allowed slavery. He thought this was crucial to winning the war ...
CIVIL WAR VOCABULARY TERMS Fugitive Slave Act
... Underground Railroad- a series of escape routes used by slaves escaping from the South Harriet Tubman- conductor on the Underground Railroad John Brown’s Raid- attempt by John Brown to arm slaves and begin a slave revolt Confederacy- nation formed by Southern states Border States- slave states that ...
... Underground Railroad- a series of escape routes used by slaves escaping from the South Harriet Tubman- conductor on the Underground Railroad John Brown’s Raid- attempt by John Brown to arm slaves and begin a slave revolt Confederacy- nation formed by Southern states Border States- slave states that ...
Civil War Erupts Vocabulary Copy the vocabulary and the definitions
... Copy the vocabulary and the definitions on a piece of paper. ...
... Copy the vocabulary and the definitions on a piece of paper. ...
Civil War Study Guide - Effingham County Schools
... because it was the center for southern supplies, factories and railroads. ...
... because it was the center for southern supplies, factories and railroads. ...
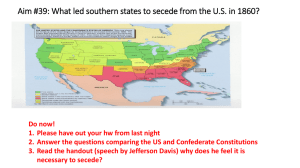
Aim #39: What led southern states to secede
... 1. Jefferson Davis chosen as president of the provisional government d. President Buchanan did little to prevent southern secession 1. Believed Constitution didn’t give him authority to stop secession with force 2. Many of his advisors were prosouthern e. Lincoln’s Inaugural f. Ft. Sumter (April 12, ...
... 1. Jefferson Davis chosen as president of the provisional government d. President Buchanan did little to prevent southern secession 1. Believed Constitution didn’t give him authority to stop secession with force 2. Many of his advisors were prosouthern e. Lincoln’s Inaugural f. Ft. Sumter (April 12, ...
Lecture - West Ada
... • Doing nothing = turns a fort over to the rebels • Confederate leaders were informed by Lincoln that he was sending supplies • 4:30am April, 12,1861 the island is bombarded • After 34 hrs of constant shelling, Anderson surrendered the fort • No one was killed • The war had begun ...
... • Doing nothing = turns a fort over to the rebels • Confederate leaders were informed by Lincoln that he was sending supplies • 4:30am April, 12,1861 the island is bombarded • After 34 hrs of constant shelling, Anderson surrendered the fort • No one was killed • The war had begun ...
4-3
... Most decisive Battle of the Civil War – Lasted three days. Turned the tide squarely in favor of the Union ...
... Most decisive Battle of the Civil War – Lasted three days. Turned the tide squarely in favor of the Union ...
Civil War 1861- 1865
... 5. Houston was removed from office when he refused to take an oath of allegiance to the Confederacy. 6. Confederate Constitution – States were given more power and the Federal Government was given less. 7. Jefferson Davis – President of the Confederacy 8. Robert E. Lee –Commander of the Confederate ...
... 5. Houston was removed from office when he refused to take an oath of allegiance to the Confederacy. 6. Confederate Constitution – States were given more power and the Federal Government was given less. 7. Jefferson Davis – President of the Confederacy 8. Robert E. Lee –Commander of the Confederate ...
Civil War Review Guide
... 3. John Brown was involved in two events leading up to the Civil War. What were those two events and what happened? Pottawatomie Massacre (Bleeding Kansas) and Harpers Ferry 4. What precedent did the Supreme Court establish regarding rights of African Americans in the Dred Scott v. Sanford case? The ...
... 3. John Brown was involved in two events leading up to the Civil War. What were those two events and what happened? Pottawatomie Massacre (Bleeding Kansas) and Harpers Ferry 4. What precedent did the Supreme Court establish regarding rights of African Americans in the Dred Scott v. Sanford case? The ...
The Civil War Begins - Johnston County Schools
... On March 4th the new president said he had not had plans to end slavery in those states where it already existed, but he also said he would not accept secession. He hoped to resolve the national crisis without warfare ...
... On March 4th the new president said he had not had plans to end slavery in those states where it already existed, but he also said he would not accept secession. He hoped to resolve the national crisis without warfare ...
Civil War Begins
... much of a fight Lincoln did not defend nor abandon Fort Sumter, he just sent food for the hungry men ...
... much of a fight Lincoln did not defend nor abandon Fort Sumter, he just sent food for the hungry men ...
Key Figures of the Civil War
... • General in the Union Army • Won the battle of Vicksburg (splitting the Confederacy in two at the Mississippi River) • Named as the commander of the Army of the Potomac • Strategy was total war • Changed the Union Army from a weak one into a strong one • Accepted the surrender of Confederate troops ...
... • General in the Union Army • Won the battle of Vicksburg (splitting the Confederacy in two at the Mississippi River) • Named as the commander of the Army of the Potomac • Strategy was total war • Changed the Union Army from a weak one into a strong one • Accepted the surrender of Confederate troops ...
CW Study Guide Ans.
... 4. The North believed that the nation was a Union and could not be divided. 5. The South was afraid that the North would take control of Congress and began to proclaim States Rights’ as self - protection. 6. Following Lincoln’s election, the southern states seceded from the union. ...
... 4. The North believed that the nation was a Union and could not be divided. 5. The South was afraid that the North would take control of Congress and began to proclaim States Rights’ as self - protection. 6. Following Lincoln’s election, the southern states seceded from the union. ...
People of the Civil War - Mrs. Pollnow`s US History and Western
... the Union Army • Future (18th) President • Battle of Vicksburg • Accepts surrender of Confederates ...
... the Union Army • Future (18th) President • Battle of Vicksburg • Accepts surrender of Confederates ...
Jefferson Davis
... Appomattox Courthouse, April 1865 Lee’s army is surrounded on three sides. The Confederates surrender. The Union wins. ...
... Appomattox Courthouse, April 1865 Lee’s army is surrounded on three sides. The Confederates surrender. The Union wins. ...
Jefferson Davis - Steele
... Appomattox Courthouse, April 1865 Lee’s army is surrounded on three sides. The Confederates surrender. The Union wins. ...
... Appomattox Courthouse, April 1865 Lee’s army is surrounded on three sides. The Confederates surrender. The Union wins. ...
Chapter 16 Study Guide - Liberty Hill Junior High
... Robert E. Lee – a talented military officer who resigned from the US Army and became the commanding general of the Confederate Army of Northern Virginia New Orleans – capturing of this city advanced the Union’s goal of dividing the Confederacy in two Antietam – the bloodiest one-day battle in Americ ...
... Robert E. Lee – a talented military officer who resigned from the US Army and became the commanding general of the Confederate Army of Northern Virginia New Orleans – capturing of this city advanced the Union’s goal of dividing the Confederacy in two Antietam – the bloodiest one-day battle in Americ ...
Study Guide
... A. After the American Revolution, our founding fathers got together to write: 1. __________ - created on ______________. It defines the _______ major branches of government and how it should rule. The Constitution is also a ______ of the _______ and ________ that we have in the U.S. 2. The _________ ...
... A. After the American Revolution, our founding fathers got together to write: 1. __________ - created on ______________. It defines the _______ major branches of government and how it should rule. The Constitution is also a ______ of the _______ and ________ that we have in the U.S. 2. The _________ ...
Confederate privateer

The Confederate privateers were privately owned ships that were authorized by the government of the Confederate States of America to attack the shipping of the United States. Although the appeal was to profit by capturing merchant vessels and seizing their cargoes, the government was most interested in diverting the efforts of the Union Navy away from the blockade of Southern ports, and perhaps to encourage European intervention in the conflict.At the beginning of the American Civil War, the Confederate government sought to counter the United States Navy in part by appealing to private enterprise world-wide to engage in privateering against United States Shipping. [[