Sample Take-home Final Exam
... (8 pts) For each sensory system, please name and describe the sensory receptor cell(s) that transduce the stimulus into a neural signal. Indicate whether this cell is a neuron or is not a neuron. Indicate what type of receptor it is: photoreceptor, mechanoreceptor, free nerve ending, thermoreceptor, ...
... (8 pts) For each sensory system, please name and describe the sensory receptor cell(s) that transduce the stimulus into a neural signal. Indicate whether this cell is a neuron or is not a neuron. Indicate what type of receptor it is: photoreceptor, mechanoreceptor, free nerve ending, thermoreceptor, ...
Lecture
... Representation with neurons and populations of neurons II. Do we really have a certain nerve cell for recognising the concatenation of features representing our grandmother(s)? Population (ensemble) code: Perception depends on the combined output of a group (ensemble) of cells not on the ouput of an ...
... Representation with neurons and populations of neurons II. Do we really have a certain nerve cell for recognising the concatenation of features representing our grandmother(s)? Population (ensemble) code: Perception depends on the combined output of a group (ensemble) of cells not on the ouput of an ...
Graphic Organizer for Chapter 2 Review
... Thompson, a social studies teacher, would be able to complete a similar problem! ...
... Thompson, a social studies teacher, would be able to complete a similar problem! ...
Unit V - Sensation and Perception
... ● Visual cortex neurons rapidly learn to associate different views of an object ● Size constancy: we perceive objects as having a constant size even while our distance from them varies ● Perception is not merely a projection of the world onto our brains. Rather, our sensations are disambled into inf ...
... ● Visual cortex neurons rapidly learn to associate different views of an object ● Size constancy: we perceive objects as having a constant size even while our distance from them varies ● Perception is not merely a projection of the world onto our brains. Rather, our sensations are disambled into inf ...
consciousness
... consciousness; cortical activity provides the contents of consciousness. The reticular activating system connects lower brain stem neurons to the thalamus (and hence on to the cortex); it is responsible for cortical EEG readings (‘brain waves’). It used (1960s) to be thought that this was the seat o ...
... consciousness; cortical activity provides the contents of consciousness. The reticular activating system connects lower brain stem neurons to the thalamus (and hence on to the cortex); it is responsible for cortical EEG readings (‘brain waves’). It used (1960s) to be thought that this was the seat o ...
Using the State-Space Paradigm to Analyze Information Representation in Neural Systems
... dynamic and stochastic. Even though the signal is often continuous, its representation in the nervous systems is as a high-dimensional point process time-series. Because neural spike trains are point processes, standard signal processing techniques for continuous-valued data will have limited utilit ...
... dynamic and stochastic. Even though the signal is often continuous, its representation in the nervous systems is as a high-dimensional point process time-series. Because neural spike trains are point processes, standard signal processing techniques for continuous-valued data will have limited utilit ...
Kein Folientitel - Institut für Grundlagen der Informationsverarbeitung
... sensory cortex • then draws conclusions from that in the association cortices („inference“) • then initiates motor outputs on the basis of these conclusions in the motor cortex ...
... sensory cortex • then draws conclusions from that in the association cortices („inference“) • then initiates motor outputs on the basis of these conclusions in the motor cortex ...
669790507205MyersMod_LG_12
... Visual Information Processing 2. Discuss the different levels of visual information processing. We process information at progressively more abstract levels. The information from the retina’s 130 million rods and cones is received and transmitted by the million or so ganglion cells whose fibers make ...
... Visual Information Processing 2. Discuss the different levels of visual information processing. We process information at progressively more abstract levels. The information from the retina’s 130 million rods and cones is received and transmitted by the million or so ganglion cells whose fibers make ...
Dendritic organization of sensory input to cortical neurons in vivo
... dendritic organization of sensory inputs to neurons of the visual cortex in vivo. • Identified discrete dendritic hotspots as synaptic entry sites for specific sensory features • Afferent sensory inputs with the same orientation preference are widely dispersed over thedendritic tree and do not conve ...
... dendritic organization of sensory inputs to neurons of the visual cortex in vivo. • Identified discrete dendritic hotspots as synaptic entry sites for specific sensory features • Afferent sensory inputs with the same orientation preference are widely dispersed over thedendritic tree and do not conve ...
A Dualistic Theory of Consciousness
... goes together well with Rumelhart and McClelland’s ideas of Parallel Distributed Processing (Rumelhart & McClelland, 1986, and McClelland & Rumelhart, 1986) and, for instance, with the fact that different aspects such as motion, depth, and form are abstracted from visual information in different bra ...
... goes together well with Rumelhart and McClelland’s ideas of Parallel Distributed Processing (Rumelhart & McClelland, 1986, and McClelland & Rumelhart, 1986) and, for instance, with the fact that different aspects such as motion, depth, and form are abstracted from visual information in different bra ...
Neurons - Transcript - the Cassiopeia Project
... on the fly in order to improve the flow. It is written in a manner that suggests to the narrator where emphasis and pauses might go, so it is not intended to be grammatically correct. The Scene numbers are left in this transcript although they are not necessarily observable by watching the video. Th ...
... on the fly in order to improve the flow. It is written in a manner that suggests to the narrator where emphasis and pauses might go, so it is not intended to be grammatically correct. The Scene numbers are left in this transcript although they are not necessarily observable by watching the video. Th ...
Reflex Arc - Point Loma High School
... relatively quickly by activating spinal motor neurons without the delay of steering signals through the brain, although the brain will receive sensory input while the reflex action occurs. ...
... relatively quickly by activating spinal motor neurons without the delay of steering signals through the brain, although the brain will receive sensory input while the reflex action occurs. ...
A true science of consciousness explains
... context in which they are presented. Even though the surfaces in A and B emit light with identical wavelengths, they have very different perceptual properties. Conversely, the apples seem to have the same color, whereas in fact apple B is much darker than apple A. During the Ponzo illusion (stimulus ...
... context in which they are presented. Even though the surfaces in A and B emit light with identical wavelengths, they have very different perceptual properties. Conversely, the apples seem to have the same color, whereas in fact apple B is much darker than apple A. During the Ponzo illusion (stimulus ...
Computational Theory of Mind
... Original Goal A. To formally describe the meanings humans make of their worlds & then hypothesize what meaning-making processes might be involved Key Feature 2. Faith that central to any understanding of the human mind is the computer ...
... Original Goal A. To formally describe the meanings humans make of their worlds & then hypothesize what meaning-making processes might be involved Key Feature 2. Faith that central to any understanding of the human mind is the computer ...
Mind, Brain & Behavior
... sense the missing limb. Originally thought to be caused by signals coming from the spinal cord from scar tissue. Now thought to originate from representation areas as they are remapped (other functions expand into the area for the lost limb). ...
... sense the missing limb. Originally thought to be caused by signals coming from the spinal cord from scar tissue. Now thought to originate from representation areas as they are remapped (other functions expand into the area for the lost limb). ...
Neuroscience Journal Club
... electrical signals (spikes) propogate between synapses •Once a circuit is stimulated, under certain circumstances it is easier to stimulate again ...
... electrical signals (spikes) propogate between synapses •Once a circuit is stimulated, under certain circumstances it is easier to stimulate again ...
LSU Seminar Neuroscience Center of Excellence
... early critical period. Visual deprivation (VD) during the critical period has atastrophic effects on visual function, including loss of visual responsiveness to the deprived eye, reduced visual acuity, and loss of tuning to many stimulus characteristics. These changes occur faster than remodeling of ...
... early critical period. Visual deprivation (VD) during the critical period has atastrophic effects on visual function, including loss of visual responsiveness to the deprived eye, reduced visual acuity, and loss of tuning to many stimulus characteristics. These changes occur faster than remodeling of ...
Slide ()
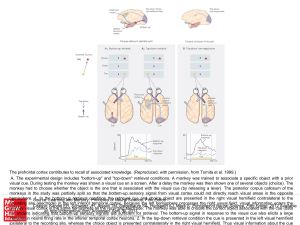
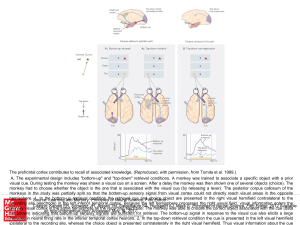
... A. The experimental design includes "bottom-up" and "top-down" retrieval conditions. A monkey was trained to associate a specific object with a prior visual cue. During testing the monkey was shown a visual cue on a screen. After a delay the monkey was then shown one of several objects (choice). The ...
... A. The experimental design includes "bottom-up" and "top-down" retrieval conditions. A monkey was trained to associate a specific object with a prior visual cue. During testing the monkey was shown a visual cue on a screen. After a delay the monkey was then shown one of several objects (choice). The ...
Slide ()
... A. The experimental design includes "bottom-up" and "top-down" retrieval conditions. A monkey was trained to associate a specific object with a prior visual cue. During testing the monkey was shown a visual cue on a screen. After a delay the monkey was then shown one of several objects (choice). The ...
... A. The experimental design includes "bottom-up" and "top-down" retrieval conditions. A monkey was trained to associate a specific object with a prior visual cue. During testing the monkey was shown a visual cue on a screen. After a delay the monkey was then shown one of several objects (choice). The ...
Project 4: Quadratic programming of tuning curves: a theory for
... Firing rate tuning curves come in many shapes and sizes, from bumpshaped to sigmoidal, from sharply peaked to broad. What are the functional roles of these many shapes? This question has been central to neuroscience since the first firing rate recordings of Lord Adrian in 1928. In this project, we w ...
... Firing rate tuning curves come in many shapes and sizes, from bumpshaped to sigmoidal, from sharply peaked to broad. What are the functional roles of these many shapes? This question has been central to neuroscience since the first firing rate recordings of Lord Adrian in 1928. In this project, we w ...