Lecture 3.1: Human Vision: Colour.
... photoreceptors in the retina • The information leaves the eye by way of the optic nerve • There is a partial crossing of axons at the optic chiasm. • After the chiasm, the axons are called the optic tract. • The optic tract wraps around the midbrain to get to the lateral ...
... photoreceptors in the retina • The information leaves the eye by way of the optic nerve • There is a partial crossing of axons at the optic chiasm. • After the chiasm, the axons are called the optic tract. • The optic tract wraps around the midbrain to get to the lateral ...
Lecture notes - University of Sussex
... composite message in many nerve fibres.” Lord Adrian, Nobel Acceptance Speech, 1932. ...
... composite message in many nerve fibres.” Lord Adrian, Nobel Acceptance Speech, 1932. ...
2.2 Electrical Communication Study Guide by Hisrich
... membrane + and inside – by pumping positive ions out of the membrane, priming the membrane to carry charges During an action potential, there’s a sudden reversal of charge, carrying a message down the axis ...
... membrane + and inside – by pumping positive ions out of the membrane, priming the membrane to carry charges During an action potential, there’s a sudden reversal of charge, carrying a message down the axis ...
Paper I
... 4. If the two structures are both on the left side of the body, they are If one is on the left and the other is on the right, they are ...
... 4. If the two structures are both on the left side of the body, they are If one is on the left and the other is on the right, they are ...
Title: Development of a novel class of hyper-multi
... approaches, can play a key role as hit compounds. Multivalency is a design principle that can convert inhibitors with low affinity to ones with high avidity and/or biological "activity" gauged by some relevant parameter: (for example, values of IC50 the concentration of free ligand, often approximat ...
... approaches, can play a key role as hit compounds. Multivalency is a design principle that can convert inhibitors with low affinity to ones with high avidity and/or biological "activity" gauged by some relevant parameter: (for example, values of IC50 the concentration of free ligand, often approximat ...
PsychScich04
... into a perception of a whole object? – Bottom-up processing: Data are relayed in the brain from lower to higher levels of processing – Top-down processing: Information at higher levels of mental processing can influence lower, “earlier” levels in the processing hierarchy • The flight crew of New Zea ...
... into a perception of a whole object? – Bottom-up processing: Data are relayed in the brain from lower to higher levels of processing – Top-down processing: Information at higher levels of mental processing can influence lower, “earlier” levels in the processing hierarchy • The flight crew of New Zea ...
The effect of visual experience on the development of the mirror
... cortex and called mirror neurons, discharges both when subjects perform a goal-directed action and when they observe another individual performing a similar action. Furthermore, several pieces of evidence support the existence of a particular subclass of mirror neurons, defined auditory-visual mirro ...
... cortex and called mirror neurons, discharges both when subjects perform a goal-directed action and when they observe another individual performing a similar action. Furthermore, several pieces of evidence support the existence of a particular subclass of mirror neurons, defined auditory-visual mirro ...
Slide ()
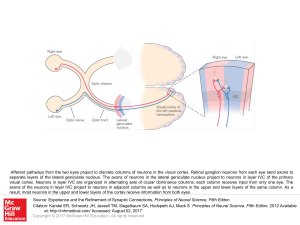
... Afferent pathways from the two eyes project to discrete columns of neurons in the visual cortex. Retinal ganglion neurons from each eye send axons to separate layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus. The axons of neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus project to neurons in layer IVC of the prima ...
... Afferent pathways from the two eyes project to discrete columns of neurons in the visual cortex. Retinal ganglion neurons from each eye send axons to separate layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus. The axons of neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus project to neurons in layer IVC of the prima ...
Lecture 5
... prefrontal cortex, showed enhanced beta rhythm synchrony during stimulus processing. • the synchronicity between regions in beta frequency predicted the subjects’ perception of the stimulus even on a single-trial level! • when beta frequency synchronization was enhanced, subjects were more likely to ...
... prefrontal cortex, showed enhanced beta rhythm synchrony during stimulus processing. • the synchronicity between regions in beta frequency predicted the subjects’ perception of the stimulus even on a single-trial level! • when beta frequency synchronization was enhanced, subjects were more likely to ...
Sensation and Perception
... Fovea – center of retina with densely packed cones; visual acquity (picture sharpness) is the greatest here Optic Nerve – carries neural impulses to the brain Occipital Lobe – neural impulses are than sent to the primary visual cortex within the occipital lobe ...
... Fovea – center of retina with densely packed cones; visual acquity (picture sharpness) is the greatest here Optic Nerve – carries neural impulses to the brain Occipital Lobe – neural impulses are than sent to the primary visual cortex within the occipital lobe ...
Cognitive Psychology
... complex computations. (opponent processes, how feature detectors are calculated). • Computational modeling - Neural networks are computer models of how groups of neurons behave. Use these models to try and better understand cognitive processing in the brain. ...
... complex computations. (opponent processes, how feature detectors are calculated). • Computational modeling - Neural networks are computer models of how groups of neurons behave. Use these models to try and better understand cognitive processing in the brain. ...
Slide 1
... a. Anatomy. We know a lot about what is where. But be careful about labels: neurons in motor cortex sometimes respond to color. Connectivity. We know (more or less) which area is connected to which. We don’t know the wiring diagram at the microscopic level. wij ...
... a. Anatomy. We know a lot about what is where. But be careful about labels: neurons in motor cortex sometimes respond to color. Connectivity. We know (more or less) which area is connected to which. We don’t know the wiring diagram at the microscopic level. wij ...
Nervous System
... Strange perceptions Which one of these, if any, is the right color for this letter? ...
... Strange perceptions Which one of these, if any, is the right color for this letter? ...
What we*ll sense and perceive* in this chapter:
... Difference threshold: the minimum difference (in color, pitch, weight, temperature, etc) for a person to be able to detect the difference half the time. Weber’s law refers to the principle that for two stimuli to be perceived as different, they must differ by a minimum percentage: 2 percent of ...
... Difference threshold: the minimum difference (in color, pitch, weight, temperature, etc) for a person to be able to detect the difference half the time. Weber’s law refers to the principle that for two stimuli to be perceived as different, they must differ by a minimum percentage: 2 percent of ...
Introduction to Neural Networks
... Definition of Neural Networks • An information processing system that has been developed as a generalization of mathematical models of human cognition or neurobiology, based on the assumptions that – Information processing occurs at many simple elements called neurons. – Signals are passed between ...
... Definition of Neural Networks • An information processing system that has been developed as a generalization of mathematical models of human cognition or neurobiology, based on the assumptions that – Information processing occurs at many simple elements called neurons. – Signals are passed between ...
Vision
... Parallel processing – the processing of many aspects of a problem simultaneously; the brain’s natural mode of information processing for many functions including vision. Contrasts conscious problem solving ...
... Parallel processing – the processing of many aspects of a problem simultaneously; the brain’s natural mode of information processing for many functions including vision. Contrasts conscious problem solving ...
Artificial Intelligence and Artificial Consciousness: Continuum or
... having its own intrinsic experiential point of view, and hence an intrinsic moral worth; • i.e. it would deserve consideration for its own sake; • this would be in contrast with purely cognitive systems, even ones with highly complex features – (No one ever suggested that we should care for the well ...
... having its own intrinsic experiential point of view, and hence an intrinsic moral worth; • i.e. it would deserve consideration for its own sake; • this would be in contrast with purely cognitive systems, even ones with highly complex features – (No one ever suggested that we should care for the well ...
Ch. 11: Machine Learning: Connectionist
... do take people less than a second. So any brain “program” can’t be longer than 100 neural “instructions.” ...
... do take people less than a second. So any brain “program” can’t be longer than 100 neural “instructions.” ...
Accumulative evidence indicates that microglial cells influence the
... with electrophysiological recordings. Neurons in the visual cortex have a receptive field like a keyhole through which they look at the scenery in front of the eyes. Visual input from the area surrounding the receptive field fails to induce neuronal firing but can modulate the neuronal responses to ...
... with electrophysiological recordings. Neurons in the visual cortex have a receptive field like a keyhole through which they look at the scenery in front of the eyes. Visual input from the area surrounding the receptive field fails to induce neuronal firing but can modulate the neuronal responses to ...
feedback-poster
... Chunshui Cao , Xianming Liu ,Yi Yang , Yinan Yu, Jiang Wang ,Zilei Wang, Yongzhen Huang ,Liang Wang , Chang Huang, Wei Xu ,Deva Ramanan ,Thomas S. Huang ...
... Chunshui Cao , Xianming Liu ,Yi Yang , Yinan Yu, Jiang Wang ,Zilei Wang, Yongzhen Huang ,Liang Wang , Chang Huang, Wei Xu ,Deva Ramanan ,Thomas S. Huang ...
Vision - Ms. Fahey
... 18-2. Discuss the different levels of processing that occur as information travels from the retina to the brain’s cortex. We process information at progressively more abstract levels. The information from the retina’s 130 million rods and cones travels to our bipolar cells, then to our million or so ...
... 18-2. Discuss the different levels of processing that occur as information travels from the retina to the brain’s cortex. We process information at progressively more abstract levels. The information from the retina’s 130 million rods and cones travels to our bipolar cells, then to our million or so ...
Paul Churchland`s Call for a Paradigm Shift in Cognitive Science
... only one among a great variety of learned manipulative skills; and it is mastered by a brain that evolution has shaped for a great many functions, language use being only the very latest and perhaps the least of them […]. Why accept, then, a theory of cognitive activity that models its elements on t ...
... only one among a great variety of learned manipulative skills; and it is mastered by a brain that evolution has shaped for a great many functions, language use being only the very latest and perhaps the least of them […]. Why accept, then, a theory of cognitive activity that models its elements on t ...