Local Copy - Synthetic Neurobiology Group
... Our brains mediate everything we perceive, feel, decide, and do. This is accomplished by an incredibly densely packed network of hundreds of billions of neurons, which fall into perhaps hundreds of different classes, defined by their shape and the molecules they contain. Each computes in concert wit ...
... Our brains mediate everything we perceive, feel, decide, and do. This is accomplished by an incredibly densely packed network of hundreds of billions of neurons, which fall into perhaps hundreds of different classes, defined by their shape and the molecules they contain. Each computes in concert wit ...
Perspectives on Cognitive Neuroscience
... the perception of color involved complex spatial and temporal effects. As Goethe pointed out in Zur Farbenlehre, dark shadows often appear blue. The physical description of color and the psychological description of color perception are at two different levels: The link between them is at the heart ...
... the perception of color involved complex spatial and temporal effects. As Goethe pointed out in Zur Farbenlehre, dark shadows often appear blue. The physical description of color and the psychological description of color perception are at two different levels: The link between them is at the heart ...
the summary and précis of the conference
... itself that gives rise to the peaks. This tells us that we really should think of ERPs as being not separate from, but rather a property of, the on-going background EEG, the continuous, spontaneous activity. The modulation of the EEG with state of arousal and attention suggest that it might reflect ...
... itself that gives rise to the peaks. This tells us that we really should think of ERPs as being not separate from, but rather a property of, the on-going background EEG, the continuous, spontaneous activity. The modulation of the EEG with state of arousal and attention suggest that it might reflect ...
Lecture slides
... •Neurons are not isolated. They are part of circuits. A typical cortical neuron receives input from ~104 other neurons. •It is not always trivial to predict circuit-level properties from single neuron properties. There could be interesting properties emerging at the network level. ...
... •Neurons are not isolated. They are part of circuits. A typical cortical neuron receives input from ~104 other neurons. •It is not always trivial to predict circuit-level properties from single neuron properties. There could be interesting properties emerging at the network level. ...
PowerPoint
... organization in the visual system, based on unsupervised Hebbian learning – Input is random dots (does not need to be structured) – Layers as in the visual cortex, with FF connections only (no lateral connections) – Each neuron receives inputs from a well defined area in the previous layer (“recepti ...
... organization in the visual system, based on unsupervised Hebbian learning – Input is random dots (does not need to be structured) – Layers as in the visual cortex, with FF connections only (no lateral connections) – Each neuron receives inputs from a well defined area in the previous layer (“recepti ...
ppt file
... Specify world space constraints that one or more parts of the skeleton must achieve Solve for joint angles to achieve these Good for meeting world space constraints, but movement flow can be a problem Most skeletons are highly redundant, so problem is underconstrained ...
... Specify world space constraints that one or more parts of the skeleton must achieve Solve for joint angles to achieve these Good for meeting world space constraints, but movement flow can be a problem Most skeletons are highly redundant, so problem is underconstrained ...
A1981LQ21400002
... But there was no reason to expect the receptor to be present in the neuronal cells of brain tissue. "To support the hypothesis that the colchicine-binding receptor was important in cell division, we attempted to correlate colchicine-binding activity with mitotic index. What a surprise, then, to find ...
... But there was no reason to expect the receptor to be present in the neuronal cells of brain tissue. "To support the hypothesis that the colchicine-binding receptor was important in cell division, we attempted to correlate colchicine-binding activity with mitotic index. What a surprise, then, to find ...
Sermon Presentation
... • Sensory information that is picked up by the optic system is in the form of Light waves enter retina detected and transduced into neural signals. The light passes through the pupil, and cornea. Rods and cones send signals to the brain by activating bipolar and ganglion cells. The Signal exits eye ...
... • Sensory information that is picked up by the optic system is in the form of Light waves enter retina detected and transduced into neural signals. The light passes through the pupil, and cornea. Rods and cones send signals to the brain by activating bipolar and ganglion cells. The Signal exits eye ...
UNIT 4: Sensation and Perception I. Overview A. Sensation
... Misfiring: rubbing right eyelid; brain reads this as light on the left ...
... Misfiring: rubbing right eyelid; brain reads this as light on the left ...
PSy420: Sensation and Perception (Dr. Hajnal) March 22, 2010
... A major problem with template theories of object recognition is that a) we cannot possibly store enough templates in memory to match every object we might encounter. b) template theories predict that object recognition should usually be viewpoint-invariant, but in fact recognition has been shown to ...
... A major problem with template theories of object recognition is that a) we cannot possibly store enough templates in memory to match every object we might encounter. b) template theories predict that object recognition should usually be viewpoint-invariant, but in fact recognition has been shown to ...
Chapter 5 - Novell Open Enterprise Server 2
... (3) The trichromatic theory explains the most common form of color blindness, red–green color blindness, in which people cannot discriminate between red and green. b. The opponent-process theory (1) An afterimage is a visual experience that occurs after the original source of stimulation is no longe ...
... (3) The trichromatic theory explains the most common form of color blindness, red–green color blindness, in which people cannot discriminate between red and green. b. The opponent-process theory (1) An afterimage is a visual experience that occurs after the original source of stimulation is no longe ...
Neural Decoding www.AssignmentPoint.com Neural decoding is a
... we find to be the most salient aspects of the input stimulus. As these images hit the back of our retina, these stimuli are converted from varying wavelengths to a series of neural spikes called action potentials. These pattern of action potentials are different for different objects and different c ...
... we find to be the most salient aspects of the input stimulus. As these images hit the back of our retina, these stimuli are converted from varying wavelengths to a series of neural spikes called action potentials. These pattern of action potentials are different for different objects and different c ...
Cybernetics, AI, Cognitive Science and Computational
... • Self-replicating automaton: the machine and its description • Reliable calculation with unreliable elements • Analog vs. digital machines • Specialized memory unit • Language of the brain: ”Thus the outward forms of our mathematics are not absolutely relevant from the point of view of evaluating w ...
... • Self-replicating automaton: the machine and its description • Reliable calculation with unreliable elements • Analog vs. digital machines • Specialized memory unit • Language of the brain: ”Thus the outward forms of our mathematics are not absolutely relevant from the point of view of evaluating w ...
Neuron death - UBC Psychology`s Research Labs
... By the end of today’s class, you should be able to: 1. discuss the mechanisms involved in neuron death. 2. discuss the process and goals of synaptic rearrangement. 3. discuss neurodevelopment in infancy through to adolescence. ...
... By the end of today’s class, you should be able to: 1. discuss the mechanisms involved in neuron death. 2. discuss the process and goals of synaptic rearrangement. 3. discuss neurodevelopment in infancy through to adolescence. ...
Where does breathing start?
... spinal nerve (C3 - C5) and the intercostals by the thoracic spinal nerve (T1 - T11). We can move skeletal muscle voluntarily, we have, in part, conscious control over it. The signals that neurons send to the diaphragm and the intercostals function as if they were autonomic, even though the respirato ...
... spinal nerve (C3 - C5) and the intercostals by the thoracic spinal nerve (T1 - T11). We can move skeletal muscle voluntarily, we have, in part, conscious control over it. The signals that neurons send to the diaphragm and the intercostals function as if they were autonomic, even though the respirato ...
Information Theoretic Approach to the Study of Auditory Coding
... Finally, a method to identify relevant features, by filtering out the effects of lower processing stations is developed. This approach is shown to have numerous applications in domains extending far beyond neural coding. These three components are summarized below. The problem of the neural code of ...
... Finally, a method to identify relevant features, by filtering out the effects of lower processing stations is developed. This approach is shown to have numerous applications in domains extending far beyond neural coding. These three components are summarized below. The problem of the neural code of ...
Theory of Vision: What We Can Easily See
... also arrows that bring direction and motion to the poster. This keeps the eyes moving back an forth across the page. The bold black text boxes keep your eyes centered on the page. The dark irregular shape of the monkey then attracts the viewer. Color, motion, then shape. POSTED BY BAILEY KIMA ...
... also arrows that bring direction and motion to the poster. This keeps the eyes moving back an forth across the page. The bold black text boxes keep your eyes centered on the page. The dark irregular shape of the monkey then attracts the viewer. Color, motion, then shape. POSTED BY BAILEY KIMA ...
Self-Organization in the Nervous System
... remains the only piece of information left. This position alone has to be sufficient for the cortex to conclude which part of the body initiated the stimulus in the first place. This type of connectivity pattern is called topographic map. The mapping process is slightly divergent. Neighboring stimul ...
... remains the only piece of information left. This position alone has to be sufficient for the cortex to conclude which part of the body initiated the stimulus in the first place. This type of connectivity pattern is called topographic map. The mapping process is slightly divergent. Neighboring stimul ...
EASTERN MICHIGAN UNIVERSITY Chemistry Department Seminar Wednesday December 3, 2014 2:00 p.m.
... paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy. We proposed a novel model of transport that described previously unidentified inward-facing and substrate-occluded conformations. Also, this work revealed specific shifts in conformational equilibria associated with Na+ and substrate binding, which form the basis ...
... paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy. We proposed a novel model of transport that described previously unidentified inward-facing and substrate-occluded conformations. Also, this work revealed specific shifts in conformational equilibria associated with Na+ and substrate binding, which form the basis ...
Policy Evaluation Primer
... goal; clear dominant means to achieve that goal • Many ways to describe problem, complex goal state, values matter, no one clear best goalstate, etc. • Structuring ill-structured problems complicated, but necessary ...
... goal; clear dominant means to achieve that goal • Many ways to describe problem, complex goal state, values matter, no one clear best goalstate, etc. • Structuring ill-structured problems complicated, but necessary ...
Brainfunction - Oakton Community College
... Brains exposed to enriched and challenging environments become smarter due to the growth of new extensive neural networks. Neuroplasticity or the ability to establish new neural networks occurs throughout life but does require more time and effort during adulthood. ...
... Brains exposed to enriched and challenging environments become smarter due to the growth of new extensive neural networks. Neuroplasticity or the ability to establish new neural networks occurs throughout life but does require more time and effort during adulthood. ...
read more
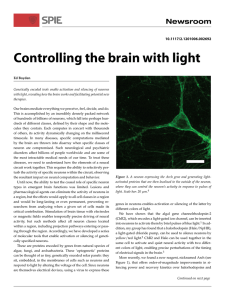
... techniques, which allow us to instantaneously perturb neural activity and record the response. We do not yet have a theoretical framework to adequately describe the neural response to such optogenetic perturbations, nor do we understand how neural networks can perform computations amid a background ...
... techniques, which allow us to instantaneously perturb neural activity and record the response. We do not yet have a theoretical framework to adequately describe the neural response to such optogenetic perturbations, nor do we understand how neural networks can perform computations amid a background ...