Asexual and Sexual Reproduction
... results in two daughter cells from a single parent cell. • The daughter cells are identical to each other and to the parent cell. • It is asexual reproduction. ...
... results in two daughter cells from a single parent cell. • The daughter cells are identical to each other and to the parent cell. • It is asexual reproduction. ...
What is Biology?
... Biology: Organisms: 1. Organization cells -> ___ ___ ___ specialization 2. Reproduction ...
... Biology: Organisms: 1. Organization cells -> ___ ___ ___ specialization 2. Reproduction ...
Genetic notes
... Sexual vs. Asexual Reproduction • Organisms reproduce two different ways: – Sexual reproduction requires two parents (one male and one female) to make a genetically similar offspring. • Gametes are an organism’s reproductive cells – Males have sperm – Females have eggs ...
... Sexual vs. Asexual Reproduction • Organisms reproduce two different ways: – Sexual reproduction requires two parents (one male and one female) to make a genetically similar offspring. • Gametes are an organism’s reproductive cells – Males have sperm – Females have eggs ...
What have these animals got in common? - pams
... Asexual reproduction only needs one parent. All the offspring are genetically identical to each other, and their parent. They are clones. ...
... Asexual reproduction only needs one parent. All the offspring are genetically identical to each other, and their parent. They are clones. ...
File
... -the growing tips of roots and stems contain areas of rapidly reproducing cells called meristem -when a plant is damaged, these meristem cells can create copies of the damaged cells and the plant continues to grow ...
... -the growing tips of roots and stems contain areas of rapidly reproducing cells called meristem -when a plant is damaged, these meristem cells can create copies of the damaged cells and the plant continues to grow ...
6.2 Sexual Reproduction
... Many gametes will not survive. Many eggs will not be fertilized. Offspring are often not protected by parents, so many ...
... Many gametes will not survive. Many eggs will not be fertilized. Offspring are often not protected by parents, so many ...
Lesson: Mitosis and Meiosis Lab
... • Mitosis is used by single celled organisms to reproduce; it is also used for the organic growth of body cells, tissues, and fibers. • Mitosis creates cells identical the original cell. ...
... • Mitosis is used by single celled organisms to reproduce; it is also used for the organic growth of body cells, tissues, and fibers. • Mitosis creates cells identical the original cell. ...
File - Wake Acceleration Academy
... (of gametes) Somatic Cells Diploid Haploid Key Questions: 1. Classify the following statements as either asexual or sexual reproduction Statement Asexual or Sexual Reproduction? can reproduce by itself requires a mate produces an offspring that is not identical to the parent produces an offspring th ...
... (of gametes) Somatic Cells Diploid Haploid Key Questions: 1. Classify the following statements as either asexual or sexual reproduction Statement Asexual or Sexual Reproduction? can reproduce by itself requires a mate produces an offspring that is not identical to the parent produces an offspring th ...
Selecting Desirable Traits
... male, the eggs are removed from the female. In a laboratory petri dish the eggs are fertilized with the male sperm producing embryo's • Advantages many embryo's can be fertilized at one time, and implanted into a number of females • The result will be all the offspring being brother and sister ...
... male, the eggs are removed from the female. In a laboratory petri dish the eggs are fertilized with the male sperm producing embryo's • Advantages many embryo's can be fertilized at one time, and implanted into a number of females • The result will be all the offspring being brother and sister ...
File
... _______________________________________ When these two gametes unite, it is called _______________________________ This combination of the two gametes is called a ____________________________. The zygote splits through a process called ___________________________ and more cells are made Continued ce ...
... _______________________________________ When these two gametes unite, it is called _______________________________ This combination of the two gametes is called a ____________________________. The zygote splits through a process called ___________________________ and more cells are made Continued ce ...
Quarter 4 Final Review ANSWERS Mitosis is a cell process in which
... Adenine and Thymine are paired together, Guanine and Cytosine are paired together. 5. A diploid cell all chromosomes are found in a pair. For example, a human diploid cell has 46 chromosomes, found in 23 pairs. 6. A haploid cell has half the number of chromosomes as body cells. This are always sex c ...
... Adenine and Thymine are paired together, Guanine and Cytosine are paired together. 5. A diploid cell all chromosomes are found in a pair. For example, a human diploid cell has 46 chromosomes, found in 23 pairs. 6. A haploid cell has half the number of chromosomes as body cells. This are always sex c ...
Sexual reproduction
... •All of the organs that work together for sexual reproduction to take place are collectively called the reproductive systems. •Let’s take a look at the reproductive systems in human females and males... ...
... •All of the organs that work together for sexual reproduction to take place are collectively called the reproductive systems. •Let’s take a look at the reproductive systems in human females and males... ...
Notes 7-8
... Isogamy vs. aniogamy: isogamous species produce gametes of the same size and form; anisogamous species produce gametes that differ in size and form. Some fungi and algae are isogamous. All other sexually reproducing species are anisogamous. The sex that produces the larger gamete is defined to be th ...
... Isogamy vs. aniogamy: isogamous species produce gametes of the same size and form; anisogamous species produce gametes that differ in size and form. Some fungi and algae are isogamous. All other sexually reproducing species are anisogamous. The sex that produces the larger gamete is defined to be th ...
Mitosis - benanbiology
... individuals exchange genetic material with each other. Most of the time DNA is not exchanged , instead plasmid which is a small part of DNA found in cytoplasm is exchanged. In that way organisms can gain new traits from the other organism. ...
... individuals exchange genetic material with each other. Most of the time DNA is not exchanged , instead plasmid which is a small part of DNA found in cytoplasm is exchanged. In that way organisms can gain new traits from the other organism. ...
Asexual Reproduction
... Mitosis - cell division that makes two identical daughter cells If an organism has 24 chromosomes, each new cell will also have 24 chromosomes. The new cells are called daughter cells and are identical to the original cell. It happens in every cell and makes body cells with same # of chromosomes It ...
... Mitosis - cell division that makes two identical daughter cells If an organism has 24 chromosomes, each new cell will also have 24 chromosomes. The new cells are called daughter cells and are identical to the original cell. It happens in every cell and makes body cells with same # of chromosomes It ...
Topic Three - Jordan Bilozir Science 9
... Sexual reproduction usually involves two individual organisms. The offspring that are produced from this union have a mix of characteristics, half from one parent and the other half from the other parent. Sexual reproduction does not always involve male and female parents, but can have specialized g ...
... Sexual reproduction usually involves two individual organisms. The offspring that are produced from this union have a mix of characteristics, half from one parent and the other half from the other parent. Sexual reproduction does not always involve male and female parents, but can have specialized g ...
how do organisms reproduce
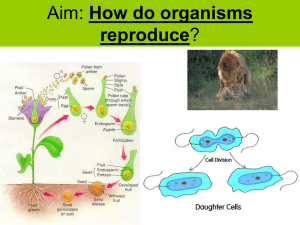
... 1. Sexual reproduction in flowering plants. The reproductive parts of angiosperms are located in the flower. Stamens (in male) and carpels (in female) are the reproductive parts of a flower which contain the germ-cells. Pollination is a process by which the pollen grains are transferred from t ...
... 1. Sexual reproduction in flowering plants. The reproductive parts of angiosperms are located in the flower. Stamens (in male) and carpels (in female) are the reproductive parts of a flower which contain the germ-cells. Pollination is a process by which the pollen grains are transferred from t ...
Chromosomes
... Meiosis A special process of cell division that results in haploid sex cells The total number of chromosomes decreases to half the original number ...
... Meiosis A special process of cell division that results in haploid sex cells The total number of chromosomes decreases to half the original number ...
Mitosis/Meiosis PPT - Boone County Schools
... gametes with half as many chromosomes. • In sexual reproduction, two parents provide an offspring with an unique gene combination. Each parent gives 1/2 of his/her genes (Chromosomes) to the offspring. ...
... gametes with half as many chromosomes. • In sexual reproduction, two parents provide an offspring with an unique gene combination. Each parent gives 1/2 of his/her genes (Chromosomes) to the offspring. ...
Booklet #3 - Science 9 Homework Page
... Sexual reproduction usually involves two individual organisms. The offspring that are produced from this union have a mix of characteristics, half from one parent and the other half from the other parent. Sexual reproduction does not always involve male and female parents, but can have specialized g ...
... Sexual reproduction usually involves two individual organisms. The offspring that are produced from this union have a mix of characteristics, half from one parent and the other half from the other parent. Sexual reproduction does not always involve male and female parents, but can have specialized g ...
Sexual Reproduction in Animals involves specialized sex cells
... – self pollination (plant pollinates its own eggs) ...
... – self pollination (plant pollinates its own eggs) ...
Notes 8-9
... Isogamy vs. anisogamy: isogamous species produce gametes of the same size and form; anisogamous species produce gametes that differ in size and form. Some fungi and algae are isogamous. All other sexually reproducing species are anisogamous. The sex that produces the larger gamete is defined to be t ...
... Isogamy vs. anisogamy: isogamous species produce gametes of the same size and form; anisogamous species produce gametes that differ in size and form. Some fungi and algae are isogamous. All other sexually reproducing species are anisogamous. The sex that produces the larger gamete is defined to be t ...
Notes 7-8
... Isogamy vs. anisogamy: isogamous species produce gametes of the same size and form; anisogamous species produce gametes that differ in size and form. Some fungi and algae are isogamous. All other sexually reproducing species are anisogamous. The sex that produces the larger gamete is defined to be t ...
... Isogamy vs. anisogamy: isogamous species produce gametes of the same size and form; anisogamous species produce gametes that differ in size and form. Some fungi and algae are isogamous. All other sexually reproducing species are anisogamous. The sex that produces the larger gamete is defined to be t ...
Sex

Organisms of many species are specialized into male and female varieties, each known as a sex. Sexual reproduction involves the combining and mixing of genetic traits: specialized cells known as gametes combine to form offspring that inherit traits from each parent. Gametes can be identical in form and function (known as isogamy), but in many cases an asymmetry has evolved such that two sex-specific types of gametes (heterogametes) exist (known as anisogamy). By definition, male gametes are small, motile, and optimized to transport their genetic information over a distance, while female gametes are large, non-motile and contain the nutrients necessary for the early development of the young organism. Among humans and other mammals, males typically carry XY chromosomes, whereas females typically carry XX chromosomes, which are a part of the XY sex-determination system. Other animals have a sex-determination system as well, such as the ZW sex-determination system in birds, and the X0 sex-determination system in insects. The gametes produced by an organism are determined by its sex: males produce male gametes (spermatozoa, or sperm, in animals; pollen in plants) while females produce female gametes (ova, or egg cells); individual organisms which produce both male and female gametes are termed hermaphroditic. Frequently, physical differences are associated with the different sexes of an organism; these sexual dimorphisms can reflect the different reproductive pressures the sexes experience.