* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Selecting Desirable Traits
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
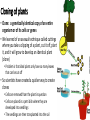
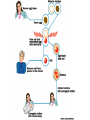
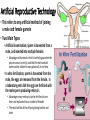
Selecting Desirable Traits Section 4.2 p. 66 Learning Outcomes • I can describe examples of genetic technology • I can identify examples of natural selection, and artificial selection • I can describe methods being used with biotechnology to better environmental issues such as agriculture, and forestry Artificial Selection • Remember that Natural Selection is when the environment “selects” which individuals will survive long enough to reproduce • Artificial Selection • Is the process of selecting and breeding individuals with desirable traits to produce offspring that have these desired traits • Animal breeders have practiced this method for a long time, such as horses, cows, dogs, and many other types of animals (this is where the idea of Purebred comes into play) • Agriculture is another example of where humans have practiced Artificial Selection as long a 10,000 years ago. The plants no longer resemble the wild species from which they came from • Teosinte produced much smaller cobs and far fewer seeds than modern day corn Bio Technology • Biotechnology is the use of living things to make agricultural, industrial, or medicinal products • Natural means of artificial selection tends to occur quite slowly, so scientist and breeders have developed to techniques to speed these process’s up • These technologies can range from “low tech” to extremely “high tech” Cloning of plants • Clone: a genetically identical copy of an entire organism or of its cells or genes • We learned of an asexual technique called cuttings where you take a clipping of a plant, cut it off, plant it, and it will grow to develop an identical plant (clone) • Problem is that ideal plants only have so many leaves that can be cut off • So scientists have created a quicker way to create clones • Cells are removed from the plant in question • Cells are placed in a petri dish where they are developed into seedlings • The seedlings are then transplanted into the soil Cloning of Animals • Animals have been cloned for a variety of reasons • To help with research programs (alter the DNA) • To help create the necessary amount of livestock needed to produce meat and animal product demands • This is a highly controversial subject, and the cloning that has been done has proved to have many problems • Unsuccessful preganecies • Birth Defects • Death among the clones Artificial Reproductive Technology • This refers to any artificial method of joining a male and female gamete • Two Main Types • Artificial insemination; Sperm is harvested from a male, and inserted into multiple females • Advantage with animals is that it can help guarantee the process occurs correctly, and that the male animals sperm can be utilized in many places all at one time • In vitro fertilization; sperm is harvested from the male, the eggs are removed from the female. In a laboratory petri dish the eggs are fertilized with the male sperm producing embryo's • Advantages many embryo's can be fertilized at one time, and implanted into a number of females • The result will be all the offspring being brother and sister Genetic Engineering • Refers to any technology that directly alters the DNA of an organism • This science is rapidly developing to try and control the characteristics of an organism to better mankind • This had led to many different types of GMO’s (Genetically Modified Organism) • Inserting the gene for insulin production into bacteria which reproduce very quickly to produce enough insulin for Diabetics • Trying to cut down on pesticides used by farmers by inserting genes from insect resistive strains of plants into those that are normally affected • This has a very negative affect on the overall variation of the plants and animals that have been developed Summary