Exam 1 Review - Iowa State University
... A) each cell will develop into a full-sized, normal embryo B) each cell may develop into a smaller than average, but normal embryo C) each cell may continue to develop, but only into an embryo that lacks many parts D) all 4 cells will die 34. If you separate 4 cells that are indeterminate, what will ...
... A) each cell will develop into a full-sized, normal embryo B) each cell may develop into a smaller than average, but normal embryo C) each cell may continue to develop, but only into an embryo that lacks many parts D) all 4 cells will die 34. If you separate 4 cells that are indeterminate, what will ...
Unit 2 Biology Test Chapter 31.2
... easier for phagocytes to engulf and destroy. Other antibodies activate complement proteins that weaken the pathogen’s cell membrane. ...
... easier for phagocytes to engulf and destroy. Other antibodies activate complement proteins that weaken the pathogen’s cell membrane. ...
Y8_Cells_Summary - Ralph Thoresby School
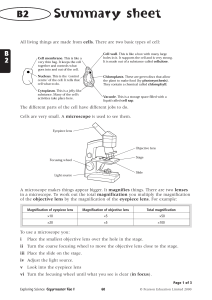
... The object you want to look at using a microscope is called the specimen. It has to be thin to let light get through it. It is placed, with a drop of water, onto a slide. A coverslip is put on top. The coverslip stops the specimen from drying out, holds it flat and stops it moving. A stain might be ...
... The object you want to look at using a microscope is called the specimen. It has to be thin to let light get through it. It is placed, with a drop of water, onto a slide. A coverslip is put on top. The coverslip stops the specimen from drying out, holds it flat and stops it moving. A stain might be ...
Chapter 4 - Living Systems: Human Systems
... Life Science Standards: 5, 6 1. The numbered drawings below show the organization within a multicellular organism from simple to complex. ...
... Life Science Standards: 5, 6 1. The numbered drawings below show the organization within a multicellular organism from simple to complex. ...
Introduction to Cells, Tissues, Organs and Systems
... muscles, and state that one is the "strongest". 1. lifting a weight - the jaw muscle is the strongest. 2. If "strength" refers to the force exerted by the muscle itself - the quadriceps femoris or the gluteus maximus. 3. A shorter muscle will be stronger "pound for pound" (i.e., by weight) than a lo ...
... muscles, and state that one is the "strongest". 1. lifting a weight - the jaw muscle is the strongest. 2. If "strength" refers to the force exerted by the muscle itself - the quadriceps femoris or the gluteus maximus. 3. A shorter muscle will be stronger "pound for pound" (i.e., by weight) than a lo ...
Microbiology/Cells/Nutrition Vocabulary 1 Abiotic
... dioxide & water vapor into the air 77. Ribosomes- organelle that makes protein 78. Slime mold- creeping jelly; fungus like 79. Tissue- a group of biological cells that preform a specific function 80. Toxin- harmful to the body 81. Unicellular- organism that consists of only one cell 82. Vaccination- ...
... dioxide & water vapor into the air 77. Ribosomes- organelle that makes protein 78. Slime mold- creeping jelly; fungus like 79. Tissue- a group of biological cells that preform a specific function 80. Toxin- harmful to the body 81. Unicellular- organism that consists of only one cell 82. Vaccination- ...
How does the food you eat provide energy to cells in
... Imagine von are a microSCopiC, unicellular organism. lour whole body is one cell. This one cell must carry out all the functions needed to keep you alive. It must be able to move, obtain food, reproduce, and respond to the environment. "There are many living organisms that consist of only one cell. ...
... Imagine von are a microSCopiC, unicellular organism. lour whole body is one cell. This one cell must carry out all the functions needed to keep you alive. It must be able to move, obtain food, reproduce, and respond to the environment. "There are many living organisms that consist of only one cell. ...
Body System Organization Overview
... UEQ: How is the body organized? • LEQ: What are the major organ systems of the human body? • Warm up: How many organ systems can you name in the human body? ...
... UEQ: How is the body organized? • LEQ: What are the major organ systems of the human body? • Warm up: How many organ systems can you name in the human body? ...
specialized cells - Bremen High School District 228
... constantly traveling through the body delivering oxygen and removing waste • RBCs are red because they contain a protein called hemoglobin (bright red in color) • Hemoglobin contains iron, an excellent vehicle for transporting oxygen and carbon dioxide ...
... constantly traveling through the body delivering oxygen and removing waste • RBCs are red because they contain a protein called hemoglobin (bright red in color) • Hemoglobin contains iron, an excellent vehicle for transporting oxygen and carbon dioxide ...
Cells to Body Systems
... • Plant cells also form tissues, such as the bark of a tree. And plant cells work together, forming organs, such as roots and leaves. ...
... • Plant cells also form tissues, such as the bark of a tree. And plant cells work together, forming organs, such as roots and leaves. ...
Cells - Livingstone High School
... • Plant cells also form tissues, such as the bark of a tree. And plant cells work together, forming organs, such as roots and leaves. ...
... • Plant cells also form tissues, such as the bark of a tree. And plant cells work together, forming organs, such as roots and leaves. ...
Animal Systems and Specialized Cells Scavenger Hunt
... Carries oxygen from the lungs to the cells in the body. Also carries the carbon dioxide back to the lungs to exhale. ...
... Carries oxygen from the lungs to the cells in the body. Also carries the carbon dioxide back to the lungs to exhale. ...
1 - WordPress.com
... 12. There is a bacterium on the laboratory bench beside you. What do you think limits the number of times the bacterium will divide? If there is food, moisture, low radiation (darker conditions), and the right temperature 13. Why are most multicellular organisms unable to reproduce by budding? Buddi ...
... 12. There is a bacterium on the laboratory bench beside you. What do you think limits the number of times the bacterium will divide? If there is food, moisture, low radiation (darker conditions), and the right temperature 13. Why are most multicellular organisms unable to reproduce by budding? Buddi ...
Unit 2: Multi-cellular organisms
... The genotype of an organism with identical alleles of a gene is described as HOMOZYGOUS; the genotype of an organism with two different alleles of a gene is described as HETEROZYGOUS. ...
... The genotype of an organism with identical alleles of a gene is described as HOMOZYGOUS; the genotype of an organism with two different alleles of a gene is described as HETEROZYGOUS. ...
From cell to an organism
... ___________ signals. • Some neurons have very long fibres extending from the cell, called ________, which allow the cell to carry messages over long distances. ...
... ___________ signals. • Some neurons have very long fibres extending from the cell, called ________, which allow the cell to carry messages over long distances. ...
File
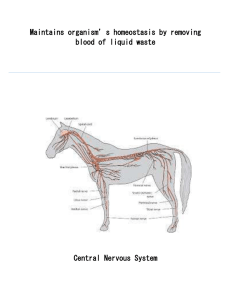
... fluid, which is called the internal environment. As long as normal conditions are maintained in this internal environment, the cells of the body continue to live and function properly. Each cell benefits from homeostasis, and in turn, each cell contributes its share toward the maintenance of homeost ...
... fluid, which is called the internal environment. As long as normal conditions are maintained in this internal environment, the cells of the body continue to live and function properly. Each cell benefits from homeostasis, and in turn, each cell contributes its share toward the maintenance of homeost ...
Multicellular Organisms live in & get Energy from a variety of
... buds, from another. • Asexual reproduction can occur quicker & more often, but limits diversity (have same genetic material as parents). • In sexual reproduction, there is a chance for a new combination of characteristics in offspring, which may help it in some way. ...
... buds, from another. • Asexual reproduction can occur quicker & more often, but limits diversity (have same genetic material as parents). • In sexual reproduction, there is a chance for a new combination of characteristics in offspring, which may help it in some way. ...
BIO 101 Chapter 1 Lecture Notes * WHAT IS LIFE?
... BIO 101 Chapter 1 Lecture Notes – WHAT IS LIFE? I. ...
... BIO 101 Chapter 1 Lecture Notes – WHAT IS LIFE? I. ...
Cell Specialization Powerpoint
... Nerve Cell Job: Send messages throughout the body Shape allows the dendrites to receive message, axon allows message to travel along it, axon endings transmits the message to the next nerve cell. They are lined up end to end in the body in a network (almost like telephone lines) ...
... Nerve Cell Job: Send messages throughout the body Shape allows the dendrites to receive message, axon allows message to travel along it, axon endings transmits the message to the next nerve cell. They are lined up end to end in the body in a network (almost like telephone lines) ...
Dictyostelium discoideum
Dictyostelium discoideum is a species of soil-living amoeba belonging to the phylum Amoebozoa, infraphylum Mycetozoa. Commonly referred to as slime mold, D. discoideum is a eukaryote that transitions from a collection of unicellular amoebae into a multicellular slug and then into a fruiting body within its lifetime. Its unique asexual lifecycle consists of four stages: vegetative, aggregation, migration, and culmination. The lifecycle of D. discoideum is relatively short, which allows for timely viewing of all stages. The cells involved in the lifecycle undergo movement, chemical signaling, and development, which are applicable to human cancer research. The simplicity of its lifecycle makes D. discoideum a valuable model organism to study genetic, cellular, and biochemical processes in other organisms.