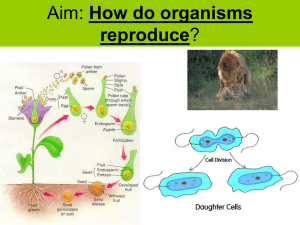
How do organisms reproduce
... Structures found in the nucleus of our cells that determine our physical characteristics (traits). They have the genetic information(DNA) Chromosomes need to be passed onto the offspring. They are the “instructions” for the cell. ...
... Structures found in the nucleus of our cells that determine our physical characteristics (traits). They have the genetic information(DNA) Chromosomes need to be passed onto the offspring. They are the “instructions” for the cell. ...
Chromosomes
... c. Long bridge of protein forms between and connects two bacterial cells. d. Part of genetic info of one cell, called the donor, transferred to the other cell, called the recipient. e. The recipient cell has a different set of genes from those it had before conjugation occurred. f. This increases ge ...
... c. Long bridge of protein forms between and connects two bacterial cells. d. Part of genetic info of one cell, called the donor, transferred to the other cell, called the recipient. e. The recipient cell has a different set of genes from those it had before conjugation occurred. f. This increases ge ...
Click Here for Science Words in Word DOC format
... Equilibrium – occurs when molecules of one substance are spread evenly throughout another substance. Esophagus – muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach; moves food by peristalsis. Exocytosis – process by which vesicles release their contents outside the cell. Fission – simplest form of ...
... Equilibrium – occurs when molecules of one substance are spread evenly throughout another substance. Esophagus – muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach; moves food by peristalsis. Exocytosis – process by which vesicles release their contents outside the cell. Fission – simplest form of ...
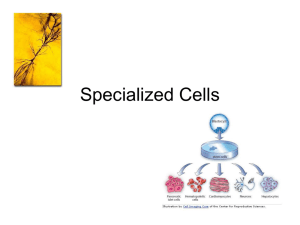
Specialized Cells
... -are made up of several tissue types that work together to perform one or more functions. *exs. -heart beating -eating -walking -running ...
... -are made up of several tissue types that work together to perform one or more functions. *exs. -heart beating -eating -walking -running ...
Science Words in Adobe Reader PDF format
... Equilibrium – occurs when molecules of one substance are spread evenly throughout another substance. Esophagus – muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach; moves food by peristalsis. Exocytosis – process by which vesicles release their contents outside the cell. Fission – simplest form of ...
... Equilibrium – occurs when molecules of one substance are spread evenly throughout another substance. Esophagus – muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach; moves food by peristalsis. Exocytosis – process by which vesicles release their contents outside the cell. Fission – simplest form of ...
Exam 3
... next to the question. Please feel free to ask me to clarify any question. (2 pts. each - 70 total) ____ 1. How are adaptations beneficial to organisms? A. Adaptations help organisms survive and reproduce in any environment, such that organisms can easily move into different environments. B. Adaptati ...
... next to the question. Please feel free to ask me to clarify any question. (2 pts. each - 70 total) ____ 1. How are adaptations beneficial to organisms? A. Adaptations help organisms survive and reproduce in any environment, such that organisms can easily move into different environments. B. Adaptati ...
Anatomy and Physiology Defined
... They are indicated in your text by a RULER BALANCED ON A PYRAMID Find 2 in your book now, give page number and explanation ...
... They are indicated in your text by a RULER BALANCED ON A PYRAMID Find 2 in your book now, give page number and explanation ...
Communicable Diseases
... Macrophage- Bite virus and send antigen to Tcells Helper T cells – act as messenger calling B cells B Cells – create antibody to help kill pathogens and remove pathogens (interlocking parts) Virus can no longer invade body’s cells Kept on file – body has immunity Killer T Cells – destroy v ...
... Macrophage- Bite virus and send antigen to Tcells Helper T cells – act as messenger calling B cells B Cells – create antibody to help kill pathogens and remove pathogens (interlocking parts) Virus can no longer invade body’s cells Kept on file – body has immunity Killer T Cells – destroy v ...
Section 4- Microscopes, Cells and Reproduction: Summary Sheets
... produces individuals which are identical to the parent. This can be a disadvantage as all individuals have the same weaknesses e.g. prone to the same illnesses. Sexual reproduction involves two parents (one male, one female) producing sex cells which join together to make a new individual take ...
... produces individuals which are identical to the parent. This can be a disadvantage as all individuals have the same weaknesses e.g. prone to the same illnesses. Sexual reproduction involves two parents (one male, one female) producing sex cells which join together to make a new individual take ...
Cells to Body Systems
... Most cells can only be seen under a microscope; they are microscopic. All organisms (any living thing that maintain life) are made up of cells. Some organisms have only one cell. Most plants and animals are made of many cells. Different types of cells have different jobs. Cells work together to carr ...
... Most cells can only be seen under a microscope; they are microscopic. All organisms (any living thing that maintain life) are made up of cells. Some organisms have only one cell. Most plants and animals are made of many cells. Different types of cells have different jobs. Cells work together to carr ...
Document
... protective barrier that can reduce the pathogen’s attack speed. In hand-to-hand combat with the pathogens, complements can attach themselves to the pathogens and accelerate their demise. When the fist two lines fail to stop the pathogens, then is time for the third and last line to intervene. The h ...
... protective barrier that can reduce the pathogen’s attack speed. In hand-to-hand combat with the pathogens, complements can attach themselves to the pathogens and accelerate their demise. When the fist two lines fail to stop the pathogens, then is time for the third and last line to intervene. The h ...
A3. Describe, in general terms, the role of genetic materials in the
... is a process in which the environment helps the species to survive. It is a process in nature that results in the fittest organism producing offspring. The species that is able to adapt by showing variability in traits becomes the fittest. Nature selects this individual to produce new offspring. ...
... is a process in which the environment helps the species to survive. It is a process in nature that results in the fittest organism producing offspring. The species that is able to adapt by showing variability in traits becomes the fittest. Nature selects this individual to produce new offspring. ...
Exam 7 Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice
... It is important to distinguish between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria in diagnosing a bacterial infection because a. Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria differ in their response to different antibiotics. b. Gram-positive bacteria never cause fatal diseases. c. Gram-positive bacteria d ...
... It is important to distinguish between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria in diagnosing a bacterial infection because a. Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria differ in their response to different antibiotics. b. Gram-positive bacteria never cause fatal diseases. c. Gram-positive bacteria d ...
6.1.01a - UC CEAS
... Describe a malfunction that can occur in the system chosen. Your answer must include at least: The name of the system and a malfunction that can occur in this system. A description of a possible cause of the malfunction identified. An effect this malfunction may have on any other body systems. ...
... Describe a malfunction that can occur in the system chosen. Your answer must include at least: The name of the system and a malfunction that can occur in this system. A description of a possible cause of the malfunction identified. An effect this malfunction may have on any other body systems. ...
unit 1: the organisation of the human body
... When different types of tissue join together and form organs, their functions complement each other and produce more complex functions. Some examples of organs in our body are the heart, stomach, lung, kidney, liver, etc. Systems.They are formed by organs, and they are responsible for carrying out ...
... When different types of tissue join together and form organs, their functions complement each other and produce more complex functions. Some examples of organs in our body are the heart, stomach, lung, kidney, liver, etc. Systems.They are formed by organs, and they are responsible for carrying out ...
Session 2 Presentation
... particular job for a particular system. Blood cells are moved by the circulatory system to carry oxygen to cells. Muscle cells contract to move the body. Liver cells play a role in digestion and filtering toxins from the blood. Explain how the job of the mitochondria relates to the number of mitocho ...
... particular job for a particular system. Blood cells are moved by the circulatory system to carry oxygen to cells. Muscle cells contract to move the body. Liver cells play a role in digestion and filtering toxins from the blood. Explain how the job of the mitochondria relates to the number of mitocho ...
4-1 outline answers
... 2. Body cells are diploid; they have pairs of chromosomes. 3. If a zygote has too many or too few chromosomes, it will not develop properly. 4. Different organisms have different numbers of chromosomes. 5. Homologous chromosomes are pairs of chromosomes that have genes for the same traits arranged i ...
... 2. Body cells are diploid; they have pairs of chromosomes. 3. If a zygote has too many or too few chromosomes, it will not develop properly. 4. Different organisms have different numbers of chromosomes. 5. Homologous chromosomes are pairs of chromosomes that have genes for the same traits arranged i ...
Compendium 1-3
... - Cells are the basic units of all living things, they are the smallest part of the organism that has the characteristics of life Cell metabolism and energy use - Chemical reactions that occur in cells are metabolic processes - The energy released by these reactions, fuels cell activity- synthesis o ...
... - Cells are the basic units of all living things, they are the smallest part of the organism that has the characteristics of life Cell metabolism and energy use - Chemical reactions that occur in cells are metabolic processes - The energy released by these reactions, fuels cell activity- synthesis o ...
UNIT ONE - Cells and Heredity
... -include information on the difference between plant and animal cells. ...
... -include information on the difference between plant and animal cells. ...
Chapter 24 – The Body`s Defenses against Pathogens State
... People who share contaminated needles to inject themselves with drugs are at a high risk for contracting HIV. People who have sex with IV drug abusers are also at high risk. ...
... People who share contaminated needles to inject themselves with drugs are at a high risk for contracting HIV. People who have sex with IV drug abusers are also at high risk. ...
Module A-1 (Principles of Biology)
... 15. As a human red blood cell matures, it loses its nucleus. After losing its nucleus, what ability does a mature red blood cell lack? A) B) C) D) ...
... 15. As a human red blood cell matures, it loses its nucleus. After losing its nucleus, what ability does a mature red blood cell lack? A) B) C) D) ...
Dictyostelium discoideum
Dictyostelium discoideum is a species of soil-living amoeba belonging to the phylum Amoebozoa, infraphylum Mycetozoa. Commonly referred to as slime mold, D. discoideum is a eukaryote that transitions from a collection of unicellular amoebae into a multicellular slug and then into a fruiting body within its lifetime. Its unique asexual lifecycle consists of four stages: vegetative, aggregation, migration, and culmination. The lifecycle of D. discoideum is relatively short, which allows for timely viewing of all stages. The cells involved in the lifecycle undergo movement, chemical signaling, and development, which are applicable to human cancer research. The simplicity of its lifecycle makes D. discoideum a valuable model organism to study genetic, cellular, and biochemical processes in other organisms.