Sponges
... • Other sponges have a material called spongin which is similar to foam rubber and makes them soft and flexible • Some have both ...
... • Other sponges have a material called spongin which is similar to foam rubber and makes them soft and flexible • Some have both ...
Chapter 9 – Multicellular and Tissue Levels of Organization
... I. Intro - Origins of Multicellularity A. Multicellular life has been on earth for 550 million years, B. The evolutionary explosion that occurred in the 100 million yrs. prior to the Cambrian/Precambrian C. colonial hypothesis D. syncytial hypothesis E. Are animals polyphyletic or monophyletic? The ...
... I. Intro - Origins of Multicellularity A. Multicellular life has been on earth for 550 million years, B. The evolutionary explosion that occurred in the 100 million yrs. prior to the Cambrian/Precambrian C. colonial hypothesis D. syncytial hypothesis E. Are animals polyphyletic or monophyletic? The ...
phylum porifera and cnidaria
... A. loosely organized groups of cells B. no true tissues or organs C. 3 layers: 1. endoderm: inner layer of cells (choanocytes) a. choanocytes (collar cells) whip flagella to create a current inside the sponge (make own current) and food is also trapped in their stickiness and nutrients are passed on ...
... A. loosely organized groups of cells B. no true tissues or organs C. 3 layers: 1. endoderm: inner layer of cells (choanocytes) a. choanocytes (collar cells) whip flagella to create a current inside the sponge (make own current) and food is also trapped in their stickiness and nutrients are passed on ...
Cnidaria - Raleigh Charter High School
... dependent on one another for survival. The float (pneumatophore) is a single individual and supports the rest of the colony. The tentacles (dactylozooids) are polyps concerned with the detection and capture of food and convey their prey to the digestive polyps (gastrozooids). Reproduction is carried ...
... dependent on one another for survival. The float (pneumatophore) is a single individual and supports the rest of the colony. The tentacles (dactylozooids) are polyps concerned with the detection and capture of food and convey their prey to the digestive polyps (gastrozooids). Reproduction is carried ...
Chapter 1
... • Cell – Basic unit of structure and function in living things • Group of cells – tissue – organ • Groups of structures that perform the broadest functions of an animal are systems. ...
... • Cell – Basic unit of structure and function in living things • Group of cells – tissue – organ • Groups of structures that perform the broadest functions of an animal are systems. ...
Marine Animals Without a Backbone
... 3. Compare and contrast body structures between gastropods, bivalves, and ...
... 3. Compare and contrast body structures between gastropods, bivalves, and ...
evolution / taxonomy study guide
... 1. homologous – organisms are similar in structure, but may look slightly different and or have a different function a. whale flipper, human arm, bat wing 2. vestigial – organ that is no longer used, but was used at some point in the organisms ancestry a. human appendix 3. analogous – organisms stru ...
... 1. homologous – organisms are similar in structure, but may look slightly different and or have a different function a. whale flipper, human arm, bat wing 2. vestigial – organ that is no longer used, but was used at some point in the organisms ancestry a. human appendix 3. analogous – organisms stru ...
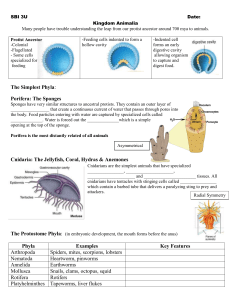
Kingdom Animalia
... Sponges have very similar structures to ancestral protists. They contain an outer layer of _________________ that create a continuous current of water that passes through pores into the body. Food particles entering with water are captured by specialized cells called ______________. Water is forced ...
... Sponges have very similar structures to ancestral protists. They contain an outer layer of _________________ that create a continuous current of water that passes through pores into the body. Food particles entering with water are captured by specialized cells called ______________. Water is forced ...
Biology II – Chapter 1 Study Guide
... 10. ____________________________________________ is the process of generating a generalization based on many specific observations that support the theory and cannot be contradicted. 11. A condition that is the cause of a single observation – subject to change – is _____________________________. 12. ...
... 10. ____________________________________________ is the process of generating a generalization based on many specific observations that support the theory and cannot be contradicted. 11. A condition that is the cause of a single observation – subject to change – is _____________________________. 12. ...
Biology Study Guide 2nd Semester Exam
... group are both modifications of the _______________. What does molting enable arthropods to do? Arthropods are classified based on the # and structure of their _______________ & _______________. The easiest way to tell whether an arthropod is an insect of a spider is to _______________. The respirat ...
... group are both modifications of the _______________. What does molting enable arthropods to do? Arthropods are classified based on the # and structure of their _______________ & _______________. The easiest way to tell whether an arthropod is an insect of a spider is to _______________. The respirat ...
Chapter 26
... the digestive tract and much of the respiratory system. The Mesoderm will develop into muscles and most of the circulatory, reproductive, and excretory organ systems Three types of body symmetry exist. They are Radial symmetry, Bilateral symmetry, and asymmetry. Most animals develop a body cavity wh ...
... the digestive tract and much of the respiratory system. The Mesoderm will develop into muscles and most of the circulatory, reproductive, and excretory organ systems Three types of body symmetry exist. They are Radial symmetry, Bilateral symmetry, and asymmetry. Most animals develop a body cavity wh ...
Fact you need to know to pass the Living Environment Regents
... 49. _____________________ -the process that transforms developing cells into specialized cells with different structures and functions. 50. females –ovaries, hormones p_____________________, e_____________________, uterus, placenta and egg 51. males hormone : t_____________________, and sex cell = s ...
... 49. _____________________ -the process that transforms developing cells into specialized cells with different structures and functions. 50. females –ovaries, hormones p_____________________, e_____________________, uterus, placenta and egg 51. males hormone : t_____________________, and sex cell = s ...
Living Organisms unit test study guide - Answer Key - Parkway C-2
... -An animal is made of many complex cells, and must eat other organisms to survive. -A bacteria is made of individual simple cells, and can reproduce on its own. -A fungus can be made of either one or many complex cells with cell walls, and must consume other organisms for energy --A plant is made of ...
... -An animal is made of many complex cells, and must eat other organisms to survive. -A bacteria is made of individual simple cells, and can reproduce on its own. -A fungus can be made of either one or many complex cells with cell walls, and must consume other organisms for energy --A plant is made of ...
Cells and Systems
... Fluid Movement in Cells • diffusion - spreading out of particles from an area of more concentration to areas of ...
... Fluid Movement in Cells • diffusion - spreading out of particles from an area of more concentration to areas of ...
11.1 Evidence for Evolution
... • Analogous structures serve the same function but come from different origins. • Homologous structures have a common origin, but do not necessarily perform the same function. ...
... • Analogous structures serve the same function but come from different origins. • Homologous structures have a common origin, but do not necessarily perform the same function. ...
Evolution Notes - Spring Branch ISD
... the “Origin of Species” he explained his theory of Evolution. It had four main points: 1. Individuals in a species are varied (no two individuals are identical) 2. Organism that produce the most offspring that survive to maturity have better successes. 3. In an ecosystem in equilibrium, a population ...
... the “Origin of Species” he explained his theory of Evolution. It had four main points: 1. Individuals in a species are varied (no two individuals are identical) 2. Organism that produce the most offspring that survive to maturity have better successes. 3. In an ecosystem in equilibrium, a population ...
Chapter 17 The History of Life Section 17
... 1. Studies of fossils or of living organisms show that a single species or a small group of species has evolved, through natural selection and other processes, into diverse forms that live in different ways 2. Dinosaurs were the products of adaptive radiation among ancient reptiles and this allowed ...
... 1. Studies of fossils or of living organisms show that a single species or a small group of species has evolved, through natural selection and other processes, into diverse forms that live in different ways 2. Dinosaurs were the products of adaptive radiation among ancient reptiles and this allowed ...
Fossils – Evidence?
... What Scientists Agree On • Scientists believe they can explain the diversity of species on Earth given the following three statements: – Earth is about 4.6 billion years old – Organisms have inhabited Earth for most of its history – All organisms living today have evolved from earlier, simpler orga ...
... What Scientists Agree On • Scientists believe they can explain the diversity of species on Earth given the following three statements: – Earth is about 4.6 billion years old – Organisms have inhabited Earth for most of its history – All organisms living today have evolved from earlier, simpler orga ...
Chapter 25 outline
... Sedimentary rocks are the richest source of fossils Fossils are the preserved remnants or impressions left by organisms that lived in the past. Sedimentary rocks form from layers of sand and silt that are carried by rivers to seas and swamps, where the minerals settle to the bottom along with t ...
... Sedimentary rocks are the richest source of fossils Fossils are the preserved remnants or impressions left by organisms that lived in the past. Sedimentary rocks form from layers of sand and silt that are carried by rivers to seas and swamps, where the minerals settle to the bottom along with t ...
Porifera - Perth Beachcombers Education Kit
... microscopic holes or pores, as well as one or more larger round openings or vents. Because they are sedentary (fixed in one place), colourful and simple in structure, sponges are often mistaken for plants. Sponges are in fact the simplest form of multicellular animal. They have no mouth, internal or ...
... microscopic holes or pores, as well as one or more larger round openings or vents. Because they are sedentary (fixed in one place), colourful and simple in structure, sponges are often mistaken for plants. Sponges are in fact the simplest form of multicellular animal. They have no mouth, internal or ...
Evolution Practice Questions
... 9. Any structure that is reduced in function in a living organism but may have been used in an ancestor. 10. The concept that evolution occurs over long periods of stability that are interrupted by geologically brief periods of change. 11. The mechanism for change in a population in which organisms ...
... 9. Any structure that is reduced in function in a living organism but may have been used in an ancestor. 10. The concept that evolution occurs over long periods of stability that are interrupted by geologically brief periods of change. 11. The mechanism for change in a population in which organisms ...
Precambrian body plans

Until the late 1950’s, the Precambrian era was not believed to have hosted multicellular organisms. However, with radiometric dating techniques, it has been found that fossils initially found in the Ediacara Hills in Southern Australia date back to the late Precambrian era. These fossils are body impressions of organisms shaped like disks, fronds and some with ribbon patterns that were most likely tentacles.These are the earliest multicellular organisms in Earth’s history, despite the fact that unicellularity had been around for a long time before that. The requirements for multicellularity were embedded in the genes of some of these cells, specifically choanoflagellates. These are thought to be the precursors for all multicellular organisms. They are highly related to sponges (Porifera), which are the simplest multicellular organisms.In order to understand the transition to multicellularity during the Precambrian, it is important to look at the requirements for multicellularity—both biological and environmental.