Unit 5 – Reproduction and Development Review Sheet Vocabulary
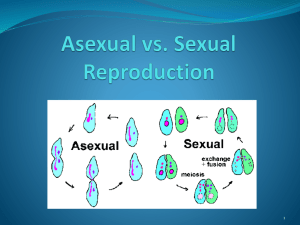
... - What is the difference between asexual and sexual reproduction? What kinds of organisms reproduce sexually and asexually? Sexual Reproduction - requires 2 parents; sexual reproduction starts with meiosis to form haploid gametes that unite to form a diploid cell; offspring are genetically different ...
... - What is the difference between asexual and sexual reproduction? What kinds of organisms reproduce sexually and asexually? Sexual Reproduction - requires 2 parents; sexual reproduction starts with meiosis to form haploid gametes that unite to form a diploid cell; offspring are genetically different ...
Ch 04 Origins of Life/ Natural Selection
... selection is limited by its existing genes and how fast it can reproduce. a) Humans have a relatively slow generation time (decades) and output (# of young) versus bacteria which can reproduce millions in hours! ...
... selection is limited by its existing genes and how fast it can reproduce. a) Humans have a relatively slow generation time (decades) and output (# of young) versus bacteria which can reproduce millions in hours! ...
Agricultural Importance of Autopolyploidy
... genetically unbalanced gametes with odd numbers of chromosomes, tetraploids are more likely to produce balanced gametes when involved in sexual reproduction. The Significance of Autopolyploidy in Agriculture In many organisms, cell volume is correlated with nuclear volume, which, in turn, is determi ...
... genetically unbalanced gametes with odd numbers of chromosomes, tetraploids are more likely to produce balanced gametes when involved in sexual reproduction. The Significance of Autopolyploidy in Agriculture In many organisms, cell volume is correlated with nuclear volume, which, in turn, is determi ...
Unit 6 Review The major evolutionary trend among plants is a
... A structure called the antheridia produce a flagellated swimming sperm in the gametophyte stage. For this reason moss needs moisture (water) to allow for fertilization. During this stage the egg is also produced. In mosses the haploid gametophyte generation is dominant Mosses do not produce windblow ...
... A structure called the antheridia produce a flagellated swimming sperm in the gametophyte stage. For this reason moss needs moisture (water) to allow for fertilization. During this stage the egg is also produced. In mosses the haploid gametophyte generation is dominant Mosses do not produce windblow ...
SEVENTH GRADE LIFE SCIENCES THEME: LIFE AROUND US
... 1. Science Processes and Inquiry – The student will engage in investigations that lead to the discovery of science concepts. a. Use appropriate tools and technology to perform tests, collect and display data. b. Use a variety of resources to collect information for research. c. Select the most logic ...
... 1. Science Processes and Inquiry – The student will engage in investigations that lead to the discovery of science concepts. a. Use appropriate tools and technology to perform tests, collect and display data. b. Use a variety of resources to collect information for research. c. Select the most logic ...
Plants! - AP Biology with Ms. Costigan
... because offspring will have all of the genes that are successful in that area ...
... because offspring will have all of the genes that are successful in that area ...
Facts you need to know to pass the Living Environment
... 44.Gene splicingexample: moving a human insulin-producing gene into a bacterial cell, the bacterium, and all of its offspring- will produce human insulin. This provides a way to produce large quantities of a hormone at low cost. 45._________ is a group of closely related organisms that share certain ...
... 44.Gene splicingexample: moving a human insulin-producing gene into a bacterial cell, the bacterium, and all of its offspring- will produce human insulin. This provides a way to produce large quantities of a hormone at low cost. 45._________ is a group of closely related organisms that share certain ...
Reproduction of Organisms
... might expose individuals to predators, diseases, or harsh environmental conditions. ...
... might expose individuals to predators, diseases, or harsh environmental conditions. ...
Unit XVII: Reproduction
... 1. Advantages for Sexual Reproduction - __________ allows for adaptation to new environments - ____________ - __________________ 2. ____________________ - _______ _________ ___________________ 3. _____________ - __________________________ - ________________________ - formation of a ________ ...
... 1. Advantages for Sexual Reproduction - __________ allows for adaptation to new environments - ____________ - __________________ 2. ____________________ - _______ _________ ___________________ 3. _____________ - __________________________ - ________________________ - formation of a ________ ...
Sexual and Asexual Reproduction
... • When an egg is fertilized by a sperm cell, a new cell, called a zygote, is formed. It has a full set of genetic material (DNA). - half from the mother - half from the father • The zygote develops into a new organism. ...
... • When an egg is fertilized by a sperm cell, a new cell, called a zygote, is formed. It has a full set of genetic material (DNA). - half from the mother - half from the father • The zygote develops into a new organism. ...
File
... Waste like carbon dioxide is carried by blood and filtered through exhaling, perspiration and urinating. ...
... Waste like carbon dioxide is carried by blood and filtered through exhaling, perspiration and urinating. ...
Asexual & Sexual Reproduction
... Previously, you learned that cells make more cells through the process of … ...
... Previously, you learned that cells make more cells through the process of … ...
Reproduction Unit Review
... 1. List the parts of the animal and plant cell. (Know what each of these parts do and be able to label them on a diagram.) 2. What is the function of a) The cell membrane of a cell? b) The cytoplasm? 3. Where is the genetic information found in the cell? 4. How does the structure of a plant cell dif ...
... 1. List the parts of the animal and plant cell. (Know what each of these parts do and be able to label them on a diagram.) 2. What is the function of a) The cell membrane of a cell? b) The cytoplasm? 3. Where is the genetic information found in the cell? 4. How does the structure of a plant cell dif ...
Reproduction
... Desirable traits can be restored due to offspring are genetically identical to parents. ...
... Desirable traits can be restored due to offspring are genetically identical to parents. ...
Diversity Notes
... describe physical characteristics of different organisms. 2. Simplifies classification. 3. Lab on page 462-63. III. Reproduction A. Sexual reproduction – two cells from different parents unite to produce the first cell of the new organism. 1. Ex: sperm + egg = zygote B. Asexual reproduction – new or ...
... describe physical characteristics of different organisms. 2. Simplifies classification. 3. Lab on page 462-63. III. Reproduction A. Sexual reproduction – two cells from different parents unite to produce the first cell of the new organism. 1. Ex: sperm + egg = zygote B. Asexual reproduction – new or ...
Protist Homework
... The following vocabulary terms comprise a partial list for which you should have more than a passing familiarity. photoautotroph tertiary symbiosis plasmodium trichocyst pseudoplasmodium holozoic feeder cytopyge autoheterotroph ...
... The following vocabulary terms comprise a partial list for which you should have more than a passing familiarity. photoautotroph tertiary symbiosis plasmodium trichocyst pseudoplasmodium holozoic feeder cytopyge autoheterotroph ...
Sexual Selection
... (2) more gametes increases chances of fertilization As resources for reproduction become limiting, these 2 pressures oppose one another – the compromise solution is the evolution of 2 different sexes, one producing few, large gametes the other many, small gametes. ...
... (2) more gametes increases chances of fertilization As resources for reproduction become limiting, these 2 pressures oppose one another – the compromise solution is the evolution of 2 different sexes, one producing few, large gametes the other many, small gametes. ...
Reproduction and Meiosis
... offspring. A key part of sexual reproduction is meiosis, which produces gametes (reproductive cells) with half the usual number of chromosomes. During fertilization, a male gamete joins with a female gamete to form an offspring cell containing genes from both parents. ...
... offspring. A key part of sexual reproduction is meiosis, which produces gametes (reproductive cells) with half the usual number of chromosomes. During fertilization, a male gamete joins with a female gamete to form an offspring cell containing genes from both parents. ...
Unit XVII: Reproduction
... - basically another name for mitosis - used by many one celled organisms ...
... - basically another name for mitosis - used by many one celled organisms ...
File - Ms. Ippolito
... 1. The characteristics of arthropods are listed below. Memorize them. Explain what each term means. 1- exoskeleton: external skeleton that supports and protects and animals body. 2- molting: the shedding of the exoskeleton, which allows an animal to grow and then it is replaced with a new exoskeleto ...
... 1. The characteristics of arthropods are listed below. Memorize them. Explain what each term means. 1- exoskeleton: external skeleton that supports and protects and animals body. 2- molting: the shedding of the exoskeleton, which allows an animal to grow and then it is replaced with a new exoskeleto ...
Back to Reality: Reproduction Quiz Name: score : /40 1. The ovaries
... A) cilia B) estrogens C) sperm D) eggs 2. An embryo develops inside the ___________________. A) vagina B) uterus C) cervix D) ovary 3. The vagina is the passageway through which a baby moves during ____________________ . A) fertilization B) contraception C) birth D) menstruation 4. The _____________ ...
... A) cilia B) estrogens C) sperm D) eggs 2. An embryo develops inside the ___________________. A) vagina B) uterus C) cervix D) ovary 3. The vagina is the passageway through which a baby moves during ____________________ . A) fertilization B) contraception C) birth D) menstruation 4. The _____________ ...
Structure of mating systems
... reproduction (e.g. in plants, by runners (strawberries) or horizontal rhizomes (in many goldenrods). Here every offspring is genetically identical to its parent. The offspring form a clone. 2) It may occur with partial meiosis. The first meiotic division, with crossing over and recombination, produc ...
... reproduction (e.g. in plants, by runners (strawberries) or horizontal rhizomes (in many goldenrods). Here every offspring is genetically identical to its parent. The offspring form a clone. 2) It may occur with partial meiosis. The first meiotic division, with crossing over and recombination, produc ...
Sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a form of reproduction where two morphologically distinct types of specialized reproductive cells called gametes fuse together, involving a female's large ovum (or egg) and a male's smaller sperm. Each gamete contains half the number of chromosomes of normal cells. They are created by a specialized type of cell division, which only occurs in eukaryotic cells, known as meiosis. The two gametes fuse during fertilization to produce DNA replication and the creation of a single-celled zygote which includes genetic material from both gametes. In a process called genetic recombination, genetic material (DNA) joins up so that homologous chromosome sequences are aligned with each other, and this is followed by exchange of genetic information. Two rounds of cell division then produce four daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes from each original parent cell, and the same number of chromosomes as both parents, though self-fertilization can occur. For instance, in human reproduction each human cell contains 46 chromosomes, 23 pairs, except gamete cells, which only contain 23 chromosomes, so the child will have 23 chromosomes from each parent genetically recombined into 23 pairs. Cell division initiates the development of a new individual organism in multicellular organisms, including animals and plants, for the vast majority of whom this is the primary method of reproduction. A species is defined as a taxonomic rank. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms where two hybrids are capable of reproducing fertile offspring, typically using sexual reproduction, although the species problem encompasses a series of difficult related questions that often come up when biologists define the word species. The evolution of sexual reproduction is a major puzzle because asexual reproduction should be able to outcompete it as every young organism created can bear its own young. This implies that an asexual population has an intrinsic capacity to grow more rapidly with each generation. This 50% cost is a fitness disadvantage of sexual reproduction. The two-fold cost of sex includes this cost and the fact that any organism can only pass on 50% of its own genes to its offspring. One definite advantage of sexual reproduction is that it prevents the accumulation of genetic mutations.Sexual selection is a mode of natural selection in which some individuals out-reproduce others of a population because they are better at securing mates for sexual reproduction. It has been described as ""a powerful evolutionary force that does not exist in asexual populations""Prokaryotes reproduce through asexual reproduction but may display processes similar to sexual reproduction (mechanisms for lateral gene transfer such as bacterial conjugation, transformation and transduction), but they do not lead to reproduction. In prokaryotes, the initial cell has additional or transformed genetic material.