Human Sexuality - Northwest Missouri State University
... a. the sexual behaviors of humans are quite similar to those of other animals b. instincts become increasingly more important in determining sexual behavior c. experience and learning play increasingly more important roles in sexual behavior * d. the social behavior of animals and human becomes rema ...
... a. the sexual behaviors of humans are quite similar to those of other animals b. instincts become increasingly more important in determining sexual behavior c. experience and learning play increasingly more important roles in sexual behavior * d. the social behavior of animals and human becomes rema ...
Strand 3 - Biological Sciences
... 13. Organisms that have traits that make them better able to survive will live long enough to reproduce and pass on these traits to the next generation. This is called A. homologous structures B. co-evolution C. natural selection D. vestigial 14. Type of reproduction that involves only one cell is c ...
... 13. Organisms that have traits that make them better able to survive will live long enough to reproduce and pass on these traits to the next generation. This is called A. homologous structures B. co-evolution C. natural selection D. vestigial 14. Type of reproduction that involves only one cell is c ...
Asexual & Sexual Reproduction
... Binary Fission – used by bacteria, an organism whose cells do not contain a nucleus copy then divide into two identical organisms ...
... Binary Fission – used by bacteria, an organism whose cells do not contain a nucleus copy then divide into two identical organisms ...
Strand 3 - Biological Sciences
... 13. Organisms that have traits that make them better able to survive will live long enough to reproduce and pass on these traits to the next generation. This is called A. homologous structures B. co-evolution C. natural selection D. vestigial 14. Type of reproduction that involves only one cell is c ...
... 13. Organisms that have traits that make them better able to survive will live long enough to reproduce and pass on these traits to the next generation. This is called A. homologous structures B. co-evolution C. natural selection D. vestigial 14. Type of reproduction that involves only one cell is c ...
Year 9 Reproduction – Vocabulary list
... When two sex cells join together to form a fertilised egg cell. ...
... When two sex cells join together to form a fertilised egg cell. ...
Asexual Reproduction
... Disadvantages: Asexual Reproduction Because their offspring are identical, there is no genetic variation that can give an organism a better chance for survival Example: If a weed killer can kill the parent, it will also kill the offspring A whole species can be wiped out from a ...
... Disadvantages: Asexual Reproduction Because their offspring are identical, there is no genetic variation that can give an organism a better chance for survival Example: If a weed killer can kill the parent, it will also kill the offspring A whole species can be wiped out from a ...
CH 8 Review - Haiku Learning
... chromosomes/other traits Explain the difference between diploid and haploid cells and give example (short answer) Diploid: 2 sets of chromosomes (2n) (skin, muscle, nerve cells) ...
... chromosomes/other traits Explain the difference between diploid and haploid cells and give example (short answer) Diploid: 2 sets of chromosomes (2n) (skin, muscle, nerve cells) ...
Bigsby - Bio S - 5 - Reproduction and Development
... produce unique haploid cells. Their young come from eggs, but the offspring are genetically identical to the parents. This is clearly asexual reproduction and is called parthenogenesis. A similar process called apomixis occurs in plants. Haploid eggs develop into haploid seeds and haploid adults. In ...
... produce unique haploid cells. Their young come from eggs, but the offspring are genetically identical to the parents. This is clearly asexual reproduction and is called parthenogenesis. A similar process called apomixis occurs in plants. Haploid eggs develop into haploid seeds and haploid adults. In ...
Final Review - Iowa State University
... semelparity- produce all offspring in a single reproductive event. Reproduce once and die. Live for many years without reproducing iteroparity- reproduce throughout the lifecycle (seasonal or continuous) 63) A species interaction in which one species benefits but the other species in unharmed is ...
... semelparity- produce all offspring in a single reproductive event. Reproduce once and die. Live for many years without reproducing iteroparity- reproduce throughout the lifecycle (seasonal or continuous) 63) A species interaction in which one species benefits but the other species in unharmed is ...
102. animals 103. daphnia 104. hydra 105. planaria
... - nervous system with a simple brain and nerve cord - has blood and blood vessels with multiple (5) hearts - no respiratory organ = takes in oxygen directly through its skin and gives off CO2 - Its skin is always moist, able to regenerate - reproduction = sexual: eggs must be fertilized by the sperm ...
... - nervous system with a simple brain and nerve cord - has blood and blood vessels with multiple (5) hearts - no respiratory organ = takes in oxygen directly through its skin and gives off CO2 - Its skin is always moist, able to regenerate - reproduction = sexual: eggs must be fertilized by the sperm ...
Week 12 - CMS - Cerritos College
... A. SYMMETRY: Think "balance" – plane(s) by which an organism can be divided to give similar pieces. RADIAL - _________________________________________________________________________ BILATERAL - ______________________________________________________________________ ASYMMETRY - ______________________ ...
... A. SYMMETRY: Think "balance" – plane(s) by which an organism can be divided to give similar pieces. RADIAL - _________________________________________________________________________ BILATERAL - ______________________________________________________________________ ASYMMETRY - ______________________ ...
Print Preview - D:\Temp\e3temp_3492\.aptcache\aea03492/tfa03492
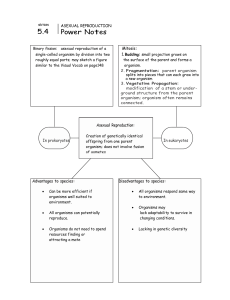
... splits into pieces that can each grow into a new organism 3. Vegetative Propagation: modification of a stem or underground structure from the parent organism; organism often remains connected. ...
... splits into pieces that can each grow into a new organism 3. Vegetative Propagation: modification of a stem or underground structure from the parent organism; organism often remains connected. ...
Biology Chp 1 Notes (The Science of Life)
... a. Cell Division: the formation of two new cells from one existing cell 1. all living things grow this way b. Development: the process by which an organism becomes a mature adult 1. achieved by cell division and differentiation 2. an adult organism is composed of many different cells 6. Reproductio ...
... a. Cell Division: the formation of two new cells from one existing cell 1. all living things grow this way b. Development: the process by which an organism becomes a mature adult 1. achieved by cell division and differentiation 2. an adult organism is composed of many different cells 6. Reproductio ...
Sexual reproduction
... organisms by mitosis. • Only in single celled organisms like bacteria and protists. ...
... organisms by mitosis. • Only in single celled organisms like bacteria and protists. ...
Human Reproduction
... with a female sex cell, called an egg, during a process called fertilization (fur-tuh-lih-ZAY-shun). These sex cells contained half of the normal amount of information in a human body cell, so that when they combined, the full amount of information was present in the offspring. The new cell formed b ...
... with a female sex cell, called an egg, during a process called fertilization (fur-tuh-lih-ZAY-shun). These sex cells contained half of the normal amount of information in a human body cell, so that when they combined, the full amount of information was present in the offspring. The new cell formed b ...
Recent research reveals
... disease. As evolutionary biologist Jonathan Howard put it: if sex causes disease, then it might also be true that disease causes sex. (Nature (Nature 296296-299 (2000) ...
... disease. As evolutionary biologist Jonathan Howard put it: if sex causes disease, then it might also be true that disease causes sex. (Nature (Nature 296296-299 (2000) ...
Asexual & Sexual Reproduction
... Binary Fission – used by bacteria, an organism whose cells do not contain a nucleus copy then divide into two identical organisms ...
... Binary Fission – used by bacteria, an organism whose cells do not contain a nucleus copy then divide into two identical organisms ...
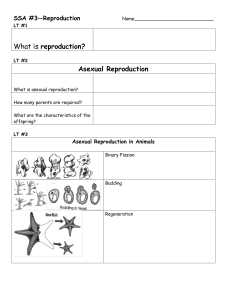
What is reproduction? Asexual Reproduction
... normally be present in the sex cell produced by this chimpanzee? A) 48 B) 36 C) 96 D) 24 ____6. The cellular process that produces sperm or egg cells with half the number of chromosomes as regular body cells is called: A) Meiosis B) Mutation C) Mitosis D) Binary fission _____7. Which of the followin ...
... normally be present in the sex cell produced by this chimpanzee? A) 48 B) 36 C) 96 D) 24 ____6. The cellular process that produces sperm or egg cells with half the number of chromosomes as regular body cells is called: A) Meiosis B) Mutation C) Mitosis D) Binary fission _____7. Which of the followin ...
2017 General externally set tasks Unit 3 content
... main reproductive structures and their functions mechanisms of pollination ...
... main reproductive structures and their functions mechanisms of pollination ...
Class Notes - North Star Academy
... Vascular (with tubes{stems, roots}): grass, fern, dandelion, celery, trees Nonvascular (without tubes): moss, hornworts, liverworts - They make seeds but do not have flowers ...
... Vascular (with tubes{stems, roots}): grass, fern, dandelion, celery, trees Nonvascular (without tubes): moss, hornworts, liverworts - They make seeds but do not have flowers ...
Biology Final Jeopary 2
... A: The condition in which a cell has only half the number of chromosomes; there are no homologous pairs. ...
... A: The condition in which a cell has only half the number of chromosomes; there are no homologous pairs. ...
Sexual Reproduction
... - zygote – fertilized egg egg + sperm = zygote - meiosis – process by which sex cells develop ...
... - zygote – fertilized egg egg + sperm = zygote - meiosis – process by which sex cells develop ...
Sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a form of reproduction where two morphologically distinct types of specialized reproductive cells called gametes fuse together, involving a female's large ovum (or egg) and a male's smaller sperm. Each gamete contains half the number of chromosomes of normal cells. They are created by a specialized type of cell division, which only occurs in eukaryotic cells, known as meiosis. The two gametes fuse during fertilization to produce DNA replication and the creation of a single-celled zygote which includes genetic material from both gametes. In a process called genetic recombination, genetic material (DNA) joins up so that homologous chromosome sequences are aligned with each other, and this is followed by exchange of genetic information. Two rounds of cell division then produce four daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes from each original parent cell, and the same number of chromosomes as both parents, though self-fertilization can occur. For instance, in human reproduction each human cell contains 46 chromosomes, 23 pairs, except gamete cells, which only contain 23 chromosomes, so the child will have 23 chromosomes from each parent genetically recombined into 23 pairs. Cell division initiates the development of a new individual organism in multicellular organisms, including animals and plants, for the vast majority of whom this is the primary method of reproduction. A species is defined as a taxonomic rank. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms where two hybrids are capable of reproducing fertile offspring, typically using sexual reproduction, although the species problem encompasses a series of difficult related questions that often come up when biologists define the word species. The evolution of sexual reproduction is a major puzzle because asexual reproduction should be able to outcompete it as every young organism created can bear its own young. This implies that an asexual population has an intrinsic capacity to grow more rapidly with each generation. This 50% cost is a fitness disadvantage of sexual reproduction. The two-fold cost of sex includes this cost and the fact that any organism can only pass on 50% of its own genes to its offspring. One definite advantage of sexual reproduction is that it prevents the accumulation of genetic mutations.Sexual selection is a mode of natural selection in which some individuals out-reproduce others of a population because they are better at securing mates for sexual reproduction. It has been described as ""a powerful evolutionary force that does not exist in asexual populations""Prokaryotes reproduce through asexual reproduction but may display processes similar to sexual reproduction (mechanisms for lateral gene transfer such as bacterial conjugation, transformation and transduction), but they do not lead to reproduction. In prokaryotes, the initial cell has additional or transformed genetic material.