* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sexual reproduction
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
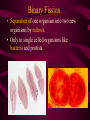
Reproduction Introduction Asexual reproduction: 1. The prefix “A” comes from the Greek language and means without. 2. The term asexual means without to cross which really doesn’t make sense but it is also defined as without crossing. 3. Asexual organisms make an exact copy of themselves, like a photocopy. 4. Is there much variation (different genes) in a group of paramecia ? No. Paramecia offspring are all identical to the parent (cell that divides) genetically because there is no combination of traits or genes. Reproduction Introduction Sexual reproduction: 1. Sexual reproduction means to “to cross”. 2. Sexual reproduction means that two parents combine parts of their genetic material (DNA).The male contributes a copy of half his genetic material and the female contributes a copy of half of her genetic material. 3. The “baby” that is born is called the offspring. 4. In a very basic way, the offspring get half their traits from each parent. 5. Because of the way the male and female copy their own genetic material and the way they are combined each offspring is different. Reproduction Introduction Circle the correct type of reproduction: 1. Mammal Sexual Asexual Both 2. Insect Sexual Asexual Both 3. Fish Sexual Asexual Both 4. Plants Sexual Asexual Both 5. Bacteria Sexual Asexual Both mixing DNA Types of Reproduction Sexual vs. Asexual Reproduction Reproduction In order to be considered alive, organisms must be able to reproduce Reproduction is the ability to produce offspring that are similar to the parents. Offspring - the product of reproduction. The “child” or “baby”. There are two possible ways the organisms can reproduce: Asexual reproduction Sexual reproduction Asexual Reproduction Asexual reproduction: reproduction where an organism makes an exact copy of itself and splits to become two separate organisms Asexual reproduction is characterized by: Only 1 parent Parent and offspring are identical genetic copies Copying mistake (genetic mutations) can occur A small, limited gene pool (little variation) Requires less energy Asexual reproducers: Bacteria Hydra (simple sea animals) Microscopic organisms (paramecium, amoeba) Types of Asexual Reproduction • • • • • • Budding Fragmentation Propagation Regeneration Binary Fission Others… Budding • Process by which a new, duplicate plant or animal begins to form at the side of the parent and enlarges until an individual is created. • Common in some plants and hydra Fragmentation • In this type of reproduction, the body of the parent breaks into distinct pieces, each of which can produce an offspring. • Common in some types worms like Planaria Propagation • Part of the parent cell is cut off and can grow into a new individual. • Common in certain plants. Regeneration • If a piece of a parent is detached, it can grow and develop into a completely new individual. • It is a common feature in invertebrates like starfish. Binary Fission • Separation of one organism into two new organisms by mitosis. • Only in single celled organisms like bacteria and protists. Sexual Reproduction Sexual reproduction: reproduction where two organisms’ genetic information (DNA) combines in a single, new offspring Sexual reproduction is characterized by: Two parents (male and female) Combination of egg and sperm cells Genetic information gets mixed Large gene pool (lots of variation in traits) Sexual reproducers Mammals, Fish, Reptiles, Birds, Most Insects Most Plants Large, complex organisms BOTH Asexual and Sexual Reproduction • Some organisms can use both types of reproduction. There are advantages to each method. • Most organism switch to the type of reproduction that is best for their current situation. • Examples: – organisms that can regenerate - star fish, newts, worms – Some plants – Daffodil, Cactus – Fungi – Mushrooms Advantages and Disadvantages of Asexual Reproduction ADVANTAGES • Less energy required • Don’t need to find a partner • Very Quick (Have several offspring in a short amount of time) • Less resources required DISADVANTAGES • Need a stable environment • Sensitive to their environment • Limited amount of traits available • No mixing of DNA Advantages and Disadvantages of Sexual Reproduction ADVANTAGES • Don’t need a stable environment • Varied genetically (Many traits to choose from) • Mixing of DNA; endless possibilities of traits. DISADVANTAGES • Need to find a partner • Requires more energy • Smaller amount of offspring • More resources needed.




















![Chapter 3 - Cell_Division_Test_Study_Guide[1].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009683824_1-add56d75145939ff28543ed83f830e06-150x150.png)





