Monomers and Polymers I
... genetic code used in the production of proteins. The genetic code is the same in all living organisms, this also provides evidence for evolution. As different cells are specialised to perform different functions, the proteins and carbohydrates of cells from different tissues can be different. Due to ...
... genetic code used in the production of proteins. The genetic code is the same in all living organisms, this also provides evidence for evolution. As different cells are specialised to perform different functions, the proteins and carbohydrates of cells from different tissues can be different. Due to ...
Bacterial enzymes that can deglycate glucose
... products could be an important energy source for this bacterium. By analogy with FN3K and FN3K-RP, whose phosphorylating action destabilizes the Amadori product, another speculative role for these enzymes is protein repair. In that regard, GfrF and GfrE are true deglycating enzymes, but it is yet un ...
... products could be an important energy source for this bacterium. By analogy with FN3K and FN3K-RP, whose phosphorylating action destabilizes the Amadori product, another speculative role for these enzymes is protein repair. In that regard, GfrF and GfrE are true deglycating enzymes, but it is yet un ...
H - Liberty Public Schools
... • Similar to amylose but not recognized by the same enzymes. Resistant. Compare in Fig. 3.7. • A water-tight, structural molecule. ...
... • Similar to amylose but not recognized by the same enzymes. Resistant. Compare in Fig. 3.7. • A water-tight, structural molecule. ...
Characterization and transcriptional analysis of
... Schneider, Derived amino acids sequences of the nosZ gene (respiratory N2 O reductase) from Acaligenes eutrophus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Pseudomonas stutzeri reveal potential copper-binding residues, Eur. J. Biochem. 208 (1992) 31^40. [11] K. Inatomi, Analysis of the nitrous oxide reduction gene ...
... Schneider, Derived amino acids sequences of the nosZ gene (respiratory N2 O reductase) from Acaligenes eutrophus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Pseudomonas stutzeri reveal potential copper-binding residues, Eur. J. Biochem. 208 (1992) 31^40. [11] K. Inatomi, Analysis of the nitrous oxide reduction gene ...
Liver- integrated lecture
... • Blood cortisol, glucagon, catecholamines increase. Basal metabolic rate, blood glucose, and free fatty acids level are elvated. Ketogenesis is not accelerated as in fasting, glutamine pool in muscle is reduced, protein breakdown is increased. • It has been proposed that the negative nitrogen balan ...
... • Blood cortisol, glucagon, catecholamines increase. Basal metabolic rate, blood glucose, and free fatty acids level are elvated. Ketogenesis is not accelerated as in fasting, glutamine pool in muscle is reduced, protein breakdown is increased. • It has been proposed that the negative nitrogen balan ...
article.
... vitamins aid in oxygen transport, metabolism, and help the body use carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. The major minerals, potassium (K), calcium (Ca), and phosphorus (P), also have important roles, including enzyme function and bone development. Whey protein — 0.6 percent of milk’s volume ...
... vitamins aid in oxygen transport, metabolism, and help the body use carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. The major minerals, potassium (K), calcium (Ca), and phosphorus (P), also have important roles, including enzyme function and bone development. Whey protein — 0.6 percent of milk’s volume ...
Organ Integration and Control
... In this mode glucose can be made from a number of sources including: 1. Glycerol from fat breakdown 2. Alanine from protein breakdown – alanine cycle 3. Lactate (Red blood cells, Muscle) – Cori Cycle ...
... In this mode glucose can be made from a number of sources including: 1. Glycerol from fat breakdown 2. Alanine from protein breakdown – alanine cycle 3. Lactate (Red blood cells, Muscle) – Cori Cycle ...
Genetic Techniques for Biological Research Chapter11
... The Cdc28 protein is a cyclin-dependent protein kinase and binding of proteins called cyclins is necessary to activate the kinase activity of Cdc28p. Cdc28p kinase is an essential protein needed for the progress from GI to S and G2 to M in the cell cycle. Cyclin proteins are present in limiting amou ...
... The Cdc28 protein is a cyclin-dependent protein kinase and binding of proteins called cyclins is necessary to activate the kinase activity of Cdc28p. Cdc28p kinase is an essential protein needed for the progress from GI to S and G2 to M in the cell cycle. Cyclin proteins are present in limiting amou ...
07 PLASMID, PLANT DEV, GENETICS 2009
... Other mutations include insertions, inversions, translocations. Mutagens- chemical, x-ray, UV, sloppy polymerase. ...
... Other mutations include insertions, inversions, translocations. Mutagens- chemical, x-ray, UV, sloppy polymerase. ...
Chapter 25: Metabolism
... – Peptide bonds broken amino acids (AAs) – Free AAs used in new proteins ...
... – Peptide bonds broken amino acids (AAs) – Free AAs used in new proteins ...
GI Digest - Douglas Labs
... GI Digest provides a unique proprietary blend of proteases with DPP-IV (dipeptidyl peptidase IV) enzyme activity targeting proline bonds. Gluten contains numerous proline-rich peptides that the human body has difficulty breaking down. In vitro studies show DPP-IV aids in the breakdown of gluten and ...
... GI Digest provides a unique proprietary blend of proteases with DPP-IV (dipeptidyl peptidase IV) enzyme activity targeting proline bonds. Gluten contains numerous proline-rich peptides that the human body has difficulty breaking down. In vitro studies show DPP-IV aids in the breakdown of gluten and ...
Section 2.5
... 2. (a) In animals, starch is used for energy and glycogen is used for energy storage. The orientation of the glucose–glucose linkages favours intrachain hydrogen bonds between hydroxyl groups and results in a helical structure. These chains are sufficiently small to make these polysaccharides solubl ...
... 2. (a) In animals, starch is used for energy and glycogen is used for energy storage. The orientation of the glucose–glucose linkages favours intrachain hydrogen bonds between hydroxyl groups and results in a helical structure. These chains are sufficiently small to make these polysaccharides solubl ...
Glucose
... Glycogen is stored hydrated with water; thus the water makes glycogen large, cumbersome, and unsuitable for long-term energy storage. The 70-kg "average" man stores only an IS-hour fuel supply as glycogen, compared with a 2-month supply stored as fat. If all human energy stores were glycogen, humans ...
... Glycogen is stored hydrated with water; thus the water makes glycogen large, cumbersome, and unsuitable for long-term energy storage. The 70-kg "average" man stores only an IS-hour fuel supply as glycogen, compared with a 2-month supply stored as fat. If all human energy stores were glycogen, humans ...
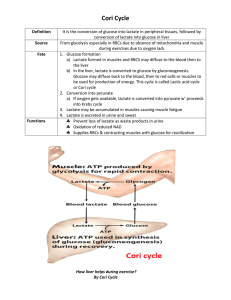
Cori Cycle - COFFEE BREAK CORNER
... From glycolysis especially in RBCs due to absence of mitochondria and muscle during exercises due to oxygen lack 1. Glucose formation a) Lactate formed in muscles and RBCS may diffuse to the blood ...
... From glycolysis especially in RBCs due to absence of mitochondria and muscle during exercises due to oxygen lack 1. Glucose formation a) Lactate formed in muscles and RBCS may diffuse to the blood ...
Macromolecules
... The deadly venoms of cobras, scorpions, and puffer fish contain small proteins that act as nerve toxins. Some sea snails stun their prey (and occasionally, unlucky humans) with up to 50 such toxins. One of these toxins has been developed into a drug called Prialt®, which is used to ...
... The deadly venoms of cobras, scorpions, and puffer fish contain small proteins that act as nerve toxins. Some sea snails stun their prey (and occasionally, unlucky humans) with up to 50 such toxins. One of these toxins has been developed into a drug called Prialt®, which is used to ...
First Pass Comments from Eric Stavney 10/29/03
... - Remove all stops between animations. - The image is of a table showing ß Galactosidase Activity and the title “Comparison of Gene Activity….” - Scroll the text of just this page: “This chart compares the gene activity…” from the bottom to the top of the text window, stopping when the top line reac ...
... - Remove all stops between animations. - The image is of a table showing ß Galactosidase Activity and the title “Comparison of Gene Activity….” - Scroll the text of just this page: “This chart compares the gene activity…” from the bottom to the top of the text window, stopping when the top line reac ...
Cell Respiration and Metabolism
... • 1- One guanosin triphosphate (GTP) is produced, which gives a phosphate group to ADP to produce one ATP. 2ATP/glucose • 2- Three molecules of NAD are reduced to NADH • 3- One molecule of FAD is reduced to FADH2. ...
... • 1- One guanosin triphosphate (GTP) is produced, which gives a phosphate group to ADP to produce one ATP. 2ATP/glucose • 2- Three molecules of NAD are reduced to NADH • 3- One molecule of FAD is reduced to FADH2. ...
RPQP05 - cucet 2017
... of optimum concentration of gratuitous inducer IPTG. Both the cultures are now used to inoculate fresh medium containing sub-optimal concentrations of IPTG. It was observed that the culture B was unable to utilize lactose, while culture A did so efficiently. The reason behind this is A) Pretreatment ...
... of optimum concentration of gratuitous inducer IPTG. Both the cultures are now used to inoculate fresh medium containing sub-optimal concentrations of IPTG. It was observed that the culture B was unable to utilize lactose, while culture A did so efficiently. The reason behind this is A) Pretreatment ...
Genetic backgrounds of each Escherichia coli strain used
... ompT: Mutation in outer-membrane protease that Improves yield of some recombinant proteins. gal: Mutation in galactose metabolism. Blocks galactose utilization. dcm: Cytosine methylation blocked (it makes DNA susceptible to cleavage at CC(A/T)GG sequences by some restriction enzymes). lon: This stra ...
... ompT: Mutation in outer-membrane protease that Improves yield of some recombinant proteins. gal: Mutation in galactose metabolism. Blocks galactose utilization. dcm: Cytosine methylation blocked (it makes DNA susceptible to cleavage at CC(A/T)GG sequences by some restriction enzymes). lon: This stra ...
Biomacromolecules ppt
... • Secondary structures bent and folded into a more complex 3-D arrangement of linked polypeptides • Bonds: Hydrogen-bonds, ionic, disulfide bridges (S-S) • Called a “subunit”. This subunit is made of 3 chains of polypeptide ...
... • Secondary structures bent and folded into a more complex 3-D arrangement of linked polypeptides • Bonds: Hydrogen-bonds, ionic, disulfide bridges (S-S) • Called a “subunit”. This subunit is made of 3 chains of polypeptide ...
Problem Set Four
... You make a version of the bla gene that has one of your SS mutations included in it. The strain of E. coli containing this bla SS mutation is no longer resistant to Ampicillin, while a bla+ strain grows well on nutrient agar + 200 μg/ml Ampicillin at 37°C. How would you isolate a mutation that would ...
... You make a version of the bla gene that has one of your SS mutations included in it. The strain of E. coli containing this bla SS mutation is no longer resistant to Ampicillin, while a bla+ strain grows well on nutrient agar + 200 μg/ml Ampicillin at 37°C. How would you isolate a mutation that would ...
Carbohydrates Structure
... Signaling Sugars associated with proteins or lipids are involved in cell signaling. Sugars are involved in cell-cell interactions, immunological responses and determine the metabolic role of many proteins. Carbohydrates are polyalcohols of ketones or aldehydes and simple derivatives (like carboxylic ...
... Signaling Sugars associated with proteins or lipids are involved in cell signaling. Sugars are involved in cell-cell interactions, immunological responses and determine the metabolic role of many proteins. Carbohydrates are polyalcohols of ketones or aldehydes and simple derivatives (like carboxylic ...
Carbohydrates (CHO)
... glycogen glucose and released – 80-100g, but reduced to <20g after overnight fast – Also produces glucose via gluconeogenesis fom ...
... glycogen glucose and released – 80-100g, but reduced to <20g after overnight fast – Also produces glucose via gluconeogenesis fom ...
Date: Period
... A scientist is using an ampicillin-sensitive strain of bacteria that cannot use lactose because it has a nonfunctional gene in the lac operon. She has two plasmids. One contains a functional copy of the affected gene of the lac operon, and the other contains the gene for ampicillin resistance. Using ...
... A scientist is using an ampicillin-sensitive strain of bacteria that cannot use lactose because it has a nonfunctional gene in the lac operon. She has two plasmids. One contains a functional copy of the affected gene of the lac operon, and the other contains the gene for ampicillin resistance. Using ...
Loss-of-Function Mutation in a Repressor Module of Human
... in HACNS1 that harbors 13 human-specific GC-biased substitutions. One, HACNS1-full, has an intact human HACNS1 sequence that is combined with heat shock protein 68 promoter (hsp68p) and lacZ reporter gene with SV40 polyA signal sequence. Another construct, HACNS1-D81bp, is basically the same as HACN ...
... in HACNS1 that harbors 13 human-specific GC-biased substitutions. One, HACNS1-full, has an intact human HACNS1 sequence that is combined with heat shock protein 68 promoter (hsp68p) and lacZ reporter gene with SV40 polyA signal sequence. Another construct, HACNS1-D81bp, is basically the same as HACN ...
Lac operon

lac operon (lactose operon) is an operon required for the transport and metabolism of lactose in Escherichia coli and many other enteric bacteria. Although glucose is the preferred carbon source for most bacteria, the lac operon allows for the effective digestion of lactose when glucose is not available. Gene regulation of the lac operon was the first genetic regulatory mechanism to be understood clearly, so it has become a foremost example of prokaryotic gene regulation. It is often discussed in introductory molecular and cellular biology classes at universities for this reason.Bacterial operons are polycistronic transcripts that are able to produce multiple proteins from one mRNA transcript. In this case, when lactose is required as a sugar source for the bacterium, the three genes of the lac operon can be expressed and their subsequent proteins translated: lacZ, lacY, and lacA. The gene product of lacZ is β-galactosidase which cleaves lactose, a disaccharide, into glucose and galactose. LacY encodes lactose permease, a protein which becomes embedded in the cytoplasmic membrane to enable transport of lactose into the cell. Finally, lacA encodes galactoside O-acetyltransferase. Layout of the lac operon.It would be wasteful to produce the enzymes when there is no lactose available or if there is a more preferable energy source available, such as glucose. The lac operon uses a two-part control mechanism to ensure that the cell expends energy producing the enzymes encoded by the lac operon only when necessary. In the absence of lactose, the lac repressor halts production of the enzymes encoded by the lac operon. In the presence of glucose, the catabolite activator protein (CAP), required for production of the enzymes, remains inactive, and EIIAGlc shuts down lactose permease to prevent transport of lactose into the cell. This dual control mechanism causes the sequential utilization of glucose and lactose in two distinct growth phases, known as diauxie.