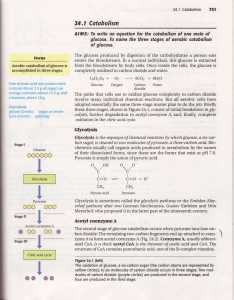
30 Synthesis of Glycosides, Lactose, Glycoproteins and Glycolipids
... derivatives use activated sugars attached to nucleotides. Both UDP-glucose and UDP-galactose are used for glycosyltransferase reactions in many systems. Lactose, for example, is synthesized from UDP-galactose and glucose in the mammary gland. UDP-glucose also can be oxidized to form UDP-glucuronate, ...
... derivatives use activated sugars attached to nucleotides. Both UDP-glucose and UDP-galactose are used for glycosyltransferase reactions in many systems. Lactose, for example, is synthesized from UDP-galactose and glucose in the mammary gland. UDP-glucose also can be oxidized to form UDP-glucuronate, ...
Chapter 16 solutions
... Chapter 16 Solutions to Selected problems 2007 2. Tracing carbon atoms I. Glucose labeled with 14C at C-1 is incubated with the glycolytic enzymes and necessary cofactors. (a) What is the distribution of 14C in the pyruvate that is formed? (Assume that the interconversion of glyceraldehyde 3-phospha ...
... Chapter 16 Solutions to Selected problems 2007 2. Tracing carbon atoms I. Glucose labeled with 14C at C-1 is incubated with the glycolytic enzymes and necessary cofactors. (a) What is the distribution of 14C in the pyruvate that is formed? (Assume that the interconversion of glyceraldehyde 3-phospha ...
Molecular Plant Microbe Interactions
... a potential promoter (Fig. 2B). This potential promoter overlaps the rmrA upstream sequence between the ATG start codon and putative promoter of rmrA. This organization is similar to that of the qacA gene (encoding an efflux transporter of quaternary ammonium antiseptics and some basic dyes in Staph ...
... a potential promoter (Fig. 2B). This potential promoter overlaps the rmrA upstream sequence between the ATG start codon and putative promoter of rmrA. This organization is similar to that of the qacA gene (encoding an efflux transporter of quaternary ammonium antiseptics and some basic dyes in Staph ...
Summary of Metabolism
... • Allows pathway to be rapidly up or down regulated by small amounts of triggering signal (HORMONES) • Last longer than do allosteric regulation (seconds to minutes) • Functions at whole body level ...
... • Allows pathway to be rapidly up or down regulated by small amounts of triggering signal (HORMONES) • Last longer than do allosteric regulation (seconds to minutes) • Functions at whole body level ...
Analysis of a ribose transport operon from Bacillus
... these systems have a protein homologous to the periplasmic substrate-binding protein, even though this bacterium does not have a periplasm. Nevertheless, Perego e t al. (1991) have demonstrated that the periplasmic oligopeptide binding protein OppA is cell wall associated in exponentially growing ce ...
... these systems have a protein homologous to the periplasmic substrate-binding protein, even though this bacterium does not have a periplasm. Nevertheless, Perego e t al. (1991) have demonstrated that the periplasmic oligopeptide binding protein OppA is cell wall associated in exponentially growing ce ...
Properties of the Major Biological Molecules
... made from just one monomer (called monosaccharides) are fructose and galactose. Examples of simple sugars made from two monomers (called disaccharides) are lactose and sucrose (table sugar). What is a complex sugar? Give other examples of complex sugars. A complex sugar is a long chain of simple s ...
... made from just one monomer (called monosaccharides) are fructose and galactose. Examples of simple sugars made from two monomers (called disaccharides) are lactose and sucrose (table sugar). What is a complex sugar? Give other examples of complex sugars. A complex sugar is a long chain of simple s ...
1 - u.arizona.edu
... Activation of PFK-1 by AMP/inhibition of PFK-1 by ATP - energy low in muscle glycolysis increases - AMP regulates PFK-1; it signal this need for energy in the muscle cell - ATP declines [AMP] increases 100-fold signal that energy availability is low - muscle in resting state [AMP] is low - A ...
... Activation of PFK-1 by AMP/inhibition of PFK-1 by ATP - energy low in muscle glycolysis increases - AMP regulates PFK-1; it signal this need for energy in the muscle cell - ATP declines [AMP] increases 100-fold signal that energy availability is low - muscle in resting state [AMP] is low - A ...
CHO PPT
... MUSCLE:the heart muscle mainly uses glucose as source of energy SYNTHESIS OF RIBOSE TO GLUCOSE:it is formed in the body from glucose by ...
... MUSCLE:the heart muscle mainly uses glucose as source of energy SYNTHESIS OF RIBOSE TO GLUCOSE:it is formed in the body from glucose by ...
Topic 3.2: Carbohydrates, Lipids, and Proteins
... serve many functions. • Triglyceride lipids – Solid form as fats – Liquid form as oils ...
... serve many functions. • Triglyceride lipids – Solid form as fats – Liquid form as oils ...
H &
... The phosphoryl group of glucose 6-phosphate comes from ATP This may seem a little surprising. Since glycolysisis a pathway of catabolism, we might expect it to produce NlP,not to zseit!The important point here is that the cell is investingAlB just asyou might invest money in the stock market. Your i ...
... The phosphoryl group of glucose 6-phosphate comes from ATP This may seem a little surprising. Since glycolysisis a pathway of catabolism, we might expect it to produce NlP,not to zseit!The important point here is that the cell is investingAlB just asyou might invest money in the stock market. Your i ...
Lect 1 (Metabolic Pathways) Lect 2 (Enzymes) Lect 3 (Glucose
... Hexokinase converts glucose to G6P. Hexokinase I and II play a major role in muscle. Hexokinase I has a high affinity for glucose. This is important for muscle as it converts glucose to G6P quickly, so there’ll always be low [free glucose], travelling down the concentration gradient. G6P also won’t ...
... Hexokinase converts glucose to G6P. Hexokinase I and II play a major role in muscle. Hexokinase I has a high affinity for glucose. This is important for muscle as it converts glucose to G6P quickly, so there’ll always be low [free glucose], travelling down the concentration gradient. G6P also won’t ...
Mammalian Expression Vectors Mammalian Stable Expression
... Electra vectors, vector configurations for expression of multiple genes and other customized configurations of the Licensed Vectors, and ProteinPaintbox genes or CUSTOMER genes cloned into the Licensed Vectors) is subject to a limited, non-transferable license pursuant to which CUSTOMER acknowledges ...
... Electra vectors, vector configurations for expression of multiple genes and other customized configurations of the Licensed Vectors, and ProteinPaintbox genes or CUSTOMER genes cloned into the Licensed Vectors) is subject to a limited, non-transferable license pursuant to which CUSTOMER acknowledges ...
Successful Longevity - SENS Research Foundation
... Offspring inherit longevity traits from their parents, and these may be a platform for longevityassociated traits. ...
... Offspring inherit longevity traits from their parents, and these may be a platform for longevityassociated traits. ...
REVIEW: Bio 139 Lab Practical #1 All labs from beginning of the
... General guidelines for preparation: Especially regarding the many biochemical tests, focus your effort on understanding each test, and how it relates to other tests. You should be able to summarize what type of metabolism or biochemical reaction is tested, what the significance of the test result is ...
... General guidelines for preparation: Especially regarding the many biochemical tests, focus your effort on understanding each test, and how it relates to other tests. You should be able to summarize what type of metabolism or biochemical reaction is tested, what the significance of the test result is ...
LacZ Reporter Gene Expression in 81 KOMP Heterozygous Mutants
... sections has a similar anatomical distribution and is observed less frequently than that found with whole-mounts. ...
... sections has a similar anatomical distribution and is observed less frequently than that found with whole-mounts. ...
Cell density-dependent gene expression controls luminescence in
... coli. Fortunately, the genes for autoinduction are linked to the luminescence structural genes (Fig. l), and E. coli cells containing this lux gene cluster produce light in a cell density-dependent fashion. Thus, quorum sensing could be analyzed with the tools of E. coli genetics. It was found that ...
... coli. Fortunately, the genes for autoinduction are linked to the luminescence structural genes (Fig. l), and E. coli cells containing this lux gene cluster produce light in a cell density-dependent fashion. Thus, quorum sensing could be analyzed with the tools of E. coli genetics. It was found that ...
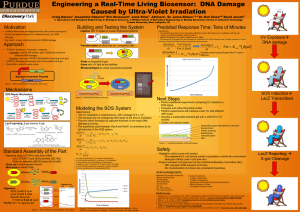
Jamboree Poster
... -Promoter: recA of SOS system, part J22106 (activated for extreme DNA damage) -Reporter: lacZ, part I732017 (blue/white screening on X-gal) • If DNA is damaged extensively, then transcription of β-gal • Essentially a reporter-gene assay ...
... -Promoter: recA of SOS system, part J22106 (activated for extreme DNA damage) -Reporter: lacZ, part I732017 (blue/white screening on X-gal) • If DNA is damaged extensively, then transcription of β-gal • Essentially a reporter-gene assay ...
Homeostatic Control of Metabolism
... – Increased plasma amino acids – Feedforward effects of GI hormones • Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) • Gastric inhibitory peptide (GIP) • Anticipatory release of insulin ...
... – Increased plasma amino acids – Feedforward effects of GI hormones • Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) • Gastric inhibitory peptide (GIP) • Anticipatory release of insulin ...
Gene Expression - Bioinformatics and Genomics Department at CIPF
... • Selection of differentially expressed genes among the phenotypes / experiments. Did I select the relevant genes, all the relevant genes and nothing but the relevant genes? (specificity) • Biological roles the genes are carrying out in the cell. What general biological roles are really represented ...
... • Selection of differentially expressed genes among the phenotypes / experiments. Did I select the relevant genes, all the relevant genes and nothing but the relevant genes? (specificity) • Biological roles the genes are carrying out in the cell. What general biological roles are really represented ...
Reassembled Biosynthetic Pathway for Large
... containing one plasmid harboring an artificial gene cluster encoding all the five enzymes in the biosynthetic pathway of Gala1,3Lac through galactose metabolism has been developed. The plasmid contains a l promoter, a cI857 repressor gene, an ampicillin resistance gene, and a T7 terminator. Each gen ...
... containing one plasmid harboring an artificial gene cluster encoding all the five enzymes in the biosynthetic pathway of Gala1,3Lac through galactose metabolism has been developed. The plasmid contains a l promoter, a cI857 repressor gene, an ampicillin resistance gene, and a T7 terminator. Each gen ...
Computational Geometry of Molecular Structure
... (mutant – wt) topological score difference = TSmut – TSwt (empirical measure of relative structural change due to mutation) • Vector “Residual Profile” of a mutant: R = Qmut – Qwt = (mutant – wt) 3D-1D potential profile difference (environmental perturbation score at every position in structure) ...
... (mutant – wt) topological score difference = TSmut – TSwt (empirical measure of relative structural change due to mutation) • Vector “Residual Profile” of a mutant: R = Qmut – Qwt = (mutant – wt) 3D-1D potential profile difference (environmental perturbation score at every position in structure) ...
The Enterobacteriaceae
... NAD is reduced to NADH2 by accepting electrons during glycolytic conversion of glucose to pyruvate NADH2 in turn reduces pyruvate with oxidation of NADH2 to NAD which supports continued anaerobic glycolysis, and generation from pyruvate of alcohols, carboxylic acids, and CO2 gas End products of gluc ...
... NAD is reduced to NADH2 by accepting electrons during glycolytic conversion of glucose to pyruvate NADH2 in turn reduces pyruvate with oxidation of NADH2 to NAD which supports continued anaerobic glycolysis, and generation from pyruvate of alcohols, carboxylic acids, and CO2 gas End products of gluc ...
CHAPTER 2 The Chemistry of Living Things
... • What are the electron carrying coenzymes that are modified during glycolysis and what is their relevance to cellular respiration? • In the presence of oxygen how many of each of the reduced coenzymes are produced (per glucose)? • With oxygen the carbons from the original glucose exit glycolysis a ...
... • What are the electron carrying coenzymes that are modified during glycolysis and what is their relevance to cellular respiration? • In the presence of oxygen how many of each of the reduced coenzymes are produced (per glucose)? • With oxygen the carbons from the original glucose exit glycolysis a ...
Chem 356 Structure and Function in Biochemistry
... (b) The value of this ratio in the cell (>100:1) indicates that [glucose 1-P] is far below the equilibrium value. The rate at which glucose 1-P is removed (through entry into glycolysis) is greater than its rate of production (by the glycogen phosphorylase reaction). This indicates that metabolic f ...
... (b) The value of this ratio in the cell (>100:1) indicates that [glucose 1-P] is far below the equilibrium value. The rate at which glucose 1-P is removed (through entry into glycolysis) is greater than its rate of production (by the glycogen phosphorylase reaction). This indicates that metabolic f ...
Lac operon

lac operon (lactose operon) is an operon required for the transport and metabolism of lactose in Escherichia coli and many other enteric bacteria. Although glucose is the preferred carbon source for most bacteria, the lac operon allows for the effective digestion of lactose when glucose is not available. Gene regulation of the lac operon was the first genetic regulatory mechanism to be understood clearly, so it has become a foremost example of prokaryotic gene regulation. It is often discussed in introductory molecular and cellular biology classes at universities for this reason.Bacterial operons are polycistronic transcripts that are able to produce multiple proteins from one mRNA transcript. In this case, when lactose is required as a sugar source for the bacterium, the three genes of the lac operon can be expressed and their subsequent proteins translated: lacZ, lacY, and lacA. The gene product of lacZ is β-galactosidase which cleaves lactose, a disaccharide, into glucose and galactose. LacY encodes lactose permease, a protein which becomes embedded in the cytoplasmic membrane to enable transport of lactose into the cell. Finally, lacA encodes galactoside O-acetyltransferase. Layout of the lac operon.It would be wasteful to produce the enzymes when there is no lactose available or if there is a more preferable energy source available, such as glucose. The lac operon uses a two-part control mechanism to ensure that the cell expends energy producing the enzymes encoded by the lac operon only when necessary. In the absence of lactose, the lac repressor halts production of the enzymes encoded by the lac operon. In the presence of glucose, the catabolite activator protein (CAP), required for production of the enzymes, remains inactive, and EIIAGlc shuts down lactose permease to prevent transport of lactose into the cell. This dual control mechanism causes the sequential utilization of glucose and lactose in two distinct growth phases, known as diauxie.