Chapter 3
... molecules and the breakdown of molecules. Cell structure includes the following three major parts: (1) cell membrane, (2) nucleus, and (3) cytoplasm (called sarcoplasm in muscle). The cell membrane provides a protective barrier between the interior of the cell and the extracellular fluid. Gene ...
... molecules and the breakdown of molecules. Cell structure includes the following three major parts: (1) cell membrane, (2) nucleus, and (3) cytoplasm (called sarcoplasm in muscle). The cell membrane provides a protective barrier between the interior of the cell and the extracellular fluid. Gene ...
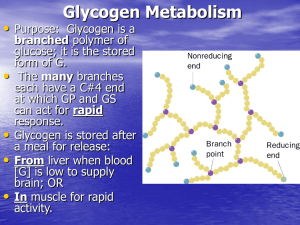
Glycogen Metabolism - http://www.utm.edu
... So, these C’s of xs AA intake (in relation to need for protein synth) are used as fuel, just like dietary CH2O’s, fats. 2. Part (or all) of the C’s of 18 of the AAs can be converted to TCA intermediates, which can be converted to G (TCA int oxac PEP G). These are referred to as the “glucogenic ...
... So, these C’s of xs AA intake (in relation to need for protein synth) are used as fuel, just like dietary CH2O’s, fats. 2. Part (or all) of the C’s of 18 of the AAs can be converted to TCA intermediates, which can be converted to G (TCA int oxac PEP G). These are referred to as the “glucogenic ...
mechanism of photosynthesis
... 5. Electron transport and the production of assimilatory power (NADPH + H+ and ATP) : The electron expels from P 680 and P 700 after travelling through Electron Transport System (E.T.S) of photosynthesis, are either assumed in reducing ...
... 5. Electron transport and the production of assimilatory power (NADPH + H+ and ATP) : The electron expels from P 680 and P 700 after travelling through Electron Transport System (E.T.S) of photosynthesis, are either assumed in reducing ...
Chapter 9
... • Electrons are transferred from NADH or FADH2 to the electron transport chain • Electrons are passed through a number of proteins including cytochromes (each with an iron atom) to O2 • The electron transport chain generates no ATP • The chain’s function is to break the large freeenergy drop from f ...
... • Electrons are transferred from NADH or FADH2 to the electron transport chain • Electrons are passed through a number of proteins including cytochromes (each with an iron atom) to O2 • The electron transport chain generates no ATP • The chain’s function is to break the large freeenergy drop from f ...
09_Lecture_Presentation
... • Electrons are transferred from NADH or FADH2 to the electron transport chain • Electrons are passed through a number of proteins including cytochromes (each with an iron atom) to O2 • The electron transport chain generates no ATP • The chain’s function is to break the large freeenergy drop from f ...
... • Electrons are transferred from NADH or FADH2 to the electron transport chain • Electrons are passed through a number of proteins including cytochromes (each with an iron atom) to O2 • The electron transport chain generates no ATP • The chain’s function is to break the large freeenergy drop from f ...
Chapter 9
... • Electrons are transferred from NADH or FADH2 to the electron transport chain • Electrons are passed through a number of proteins including cytochromes (each with an iron atom) to O2 • The electron transport chain generates no ATP • The chain’s function is to break the large freeenergy drop from f ...
... • Electrons are transferred from NADH or FADH2 to the electron transport chain • Electrons are passed through a number of proteins including cytochromes (each with an iron atom) to O2 • The electron transport chain generates no ATP • The chain’s function is to break the large freeenergy drop from f ...
Gluconeogenesis
... starvation is mainly amino acid catabolism. Some amino acids are catabolized to pyruvate, oxaloacetate, or precursors of these. Muscle proteins may break down to supply amino acids. These are transported to liver where they are deaminated and converted to gluconeogenesis inputs. Glycerol, derived fr ...
... starvation is mainly amino acid catabolism. Some amino acids are catabolized to pyruvate, oxaloacetate, or precursors of these. Muscle proteins may break down to supply amino acids. These are transported to liver where they are deaminated and converted to gluconeogenesis inputs. Glycerol, derived fr ...
Mitochondrial Fatty Acid ß-Oxidation in the Human Eye and
... with mitochondrial fatty acid -oxidation (A–D and H) and control antibodies (E–G and I) without counterstain. Sections A–G are from one and sections H and I from another adult eye specimen. (A) VLCAD antibodies label strongly the RPE. Labeling of the nerve fiber layer (nfl), ganglion cell layer (gc ...
... with mitochondrial fatty acid -oxidation (A–D and H) and control antibodies (E–G and I) without counterstain. Sections A–G are from one and sections H and I from another adult eye specimen. (A) VLCAD antibodies label strongly the RPE. Labeling of the nerve fiber layer (nfl), ganglion cell layer (gc ...
26_Catabolism of tryacylglycerols oxidation of fatty acids a
... Storage and Mobilization of Fatty Acids (FA) • TGs are delivered to adipose tissue in the form of chylomicrones and VLDL, hydrolyzed by lipoprotein lipase into fatty acids and glycerol, which are taken up by adipocytes. • Then fatty acids are reesterified to TGs. • TGs are stored in adipocytes. • T ...
... Storage and Mobilization of Fatty Acids (FA) • TGs are delivered to adipose tissue in the form of chylomicrones and VLDL, hydrolyzed by lipoprotein lipase into fatty acids and glycerol, which are taken up by adipocytes. • Then fatty acids are reesterified to TGs. • TGs are stored in adipocytes. • T ...
Cytochromes P450 – importance of tissue specificity
... the liver, kidney, lung, adrenal, gonads, brain, and most others. For cytochromes P450 that are expressed in many tissues or cell types, the tissue/cell type-specific expression might be associated with their special physiological roles. Several cytochrome P450 enzymes are found not only in differen ...
... the liver, kidney, lung, adrenal, gonads, brain, and most others. For cytochromes P450 that are expressed in many tissues or cell types, the tissue/cell type-specific expression might be associated with their special physiological roles. Several cytochrome P450 enzymes are found not only in differen ...
Acetyl CoA - WordPress.com
... Fermentation is an anaeorbic process and does not require oxygen. In humans, pyruvate is reduced to lactic acid during fermentation. ...
... Fermentation is an anaeorbic process and does not require oxygen. In humans, pyruvate is reduced to lactic acid during fermentation. ...
Biosynthesis of glucose – gluconeogenesis
... G°' = -9 kcal mol-1 Six nucleotide triphosphate molecules are hydrolyzed to synthesize glucose from pyruvate in gluconeogenesis, whereas only two molecules of ATP are generated in glycolysis in the conversion of glucose into pyruvate. The extra cost of gluconeogenesis is four high phosphoryl-transf ...
... G°' = -9 kcal mol-1 Six nucleotide triphosphate molecules are hydrolyzed to synthesize glucose from pyruvate in gluconeogenesis, whereas only two molecules of ATP are generated in glycolysis in the conversion of glucose into pyruvate. The extra cost of gluconeogenesis is four high phosphoryl-transf ...
Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy
... • The chain’s function is to break the large freeenergy drop from food to O2 into smaller steps that release energy in manageable amounts ...
... • The chain’s function is to break the large freeenergy drop from food to O2 into smaller steps that release energy in manageable amounts ...
Polynucleotide Phosphorylase and Mitochondrial
... We have demonstrated that phosphorolytic-arsenolytic enzymes can promote reduction of arsenate (AsV) into the more toxic arsenite (AsIII) because they convert AsV into an arsenylated product in which the arsenic is more reducible by glutathione (GSH) or other thiols to AsIII than in inorganic AsV. W ...
... We have demonstrated that phosphorolytic-arsenolytic enzymes can promote reduction of arsenate (AsV) into the more toxic arsenite (AsIII) because they convert AsV into an arsenylated product in which the arsenic is more reducible by glutathione (GSH) or other thiols to AsIII than in inorganic AsV. W ...
Karbohidrat Metabolizması
... Oxaloacetate is first decarboxylated to yield a pyruvate enolate anion intermediate. This is phosphorylated by phosphate transfer from GTP. A metal ion such as Mn++ is required, in addition to Mg++ associated with the nucleotide substrate. ...
... Oxaloacetate is first decarboxylated to yield a pyruvate enolate anion intermediate. This is phosphorylated by phosphate transfer from GTP. A metal ion such as Mn++ is required, in addition to Mg++ associated with the nucleotide substrate. ...
The mitochondrial carnitine/acylcarnitine carrier: Function
... of the carnitine-palmitoyl-transferase 1 (CPT1) which is located on the external surface of the outer mitochondrial membrane (Lee et al., 2011; Rufer et al., 2009); the formed acylcarnitines cross the outer membrane, which is permeable to small molecules (Zeth and Thein, 2010) and are translocated t ...
... of the carnitine-palmitoyl-transferase 1 (CPT1) which is located on the external surface of the outer mitochondrial membrane (Lee et al., 2011; Rufer et al., 2009); the formed acylcarnitines cross the outer membrane, which is permeable to small molecules (Zeth and Thein, 2010) and are translocated t ...
An acetate-sensitive mutant of Neurospora crassa deficient in acetyl
... tively defective in isocitrate lyase and acetyl-CoA synthetase, were also inhibited by acetate when grown on glycerol as carbon source. As shown in Table 2, they differed from acu-8 in showing no growth on acetate alone at any concentration. NMR analysis showed that acu-8 mycelium did not accumulate ...
... tively defective in isocitrate lyase and acetyl-CoA synthetase, were also inhibited by acetate when grown on glycerol as carbon source. As shown in Table 2, they differed from acu-8 in showing no growth on acetate alone at any concentration. NMR analysis showed that acu-8 mycelium did not accumulate ...
biochem ch 23 [2-9
... o Fatty acid levels rise because of decreased β-oxidation; because of this, ω-oxidation increases, and dicarboxylic acids excreted in urine o Diminished capacity to oxidize fatty acids in liver mitochondria results in decreased levels of acetyl-CoA (substrate for ketone body synthesis) Fatty acids ...
... o Fatty acid levels rise because of decreased β-oxidation; because of this, ω-oxidation increases, and dicarboxylic acids excreted in urine o Diminished capacity to oxidize fatty acids in liver mitochondria results in decreased levels of acetyl-CoA (substrate for ketone body synthesis) Fatty acids ...
Dr. V. Main Powerpoint
... • Electrons are transferred from NADH or FADH2 to the electron transport chain • Electrons are passed through a number of proteins including cytochromes (each with an iron atom) to O2 • The electron transport chain generates no ATP • The chain’s function is to break the large freeenergy drop from f ...
... • Electrons are transferred from NADH or FADH2 to the electron transport chain • Electrons are passed through a number of proteins including cytochromes (each with an iron atom) to O2 • The electron transport chain generates no ATP • The chain’s function is to break the large freeenergy drop from f ...
Chapter 9 Powerpoint
... – Oxidative phosphorylation (accounts for most of the ATP synthesis) For each molecule of glucose, between about 3638 ATP, although 36 is most widely used. Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
... – Oxidative phosphorylation (accounts for most of the ATP synthesis) For each molecule of glucose, between about 3638 ATP, although 36 is most widely used. Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
Stress Induction of Mitochondrial Formate Dehydrogenase in Potato
... formaldehyde dehydrogenase, in providing NADH to the respiratory chain (Van Dijken et al., 1976). Aside from formate, it is possible that S-formylglutathione might also be a substrate for FDH, as was suggested for yeasts (Van Dijken et al., 1976), pea (Uotila and Koivusalo, 1979), and Pseudomonas sp ...
... formaldehyde dehydrogenase, in providing NADH to the respiratory chain (Van Dijken et al., 1976). Aside from formate, it is possible that S-formylglutathione might also be a substrate for FDH, as was suggested for yeasts (Van Dijken et al., 1976), pea (Uotila and Koivusalo, 1979), and Pseudomonas sp ...
Computational Biology
... (2) generate initial multiple sequence alignment (MSA) with ClustalW. Delete fragments < 80% of length of query sequence. From these refined MSA, apply 6 different % identity criteria, 6 final MSAs for each test protein. ...
... (2) generate initial multiple sequence alignment (MSA) with ClustalW. Delete fragments < 80% of length of query sequence. From these refined MSA, apply 6 different % identity criteria, 6 final MSAs for each test protein. ...
Glucose
... glucose, galactose and fructose. They are absorbed from the jejunum to portal veins to the liver, where fructose and galactose are transformed into glucose. B.Two mechanisms are responsible for absorption of monosaccharides: active transport (against concentration gradient i.e. from low to high conc ...
... glucose, galactose and fructose. They are absorbed from the jejunum to portal veins to the liver, where fructose and galactose are transformed into glucose. B.Two mechanisms are responsible for absorption of monosaccharides: active transport (against concentration gradient i.e. from low to high conc ...
NAD Malic Enzyme and the Control of
... It is well established that the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle functions universally in plant mitochondria in the breakdown of pyruvate derived from various metabolic processes to produce ATP, reducing equivalents, and biosynthetic precursors. There are three ways in which carbon can enter the cycle ...
... It is well established that the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle functions universally in plant mitochondria in the breakdown of pyruvate derived from various metabolic processes to produce ATP, reducing equivalents, and biosynthetic precursors. There are three ways in which carbon can enter the cycle ...
Enzyme Redundancy and the Importance of 2
... plants, only partially purified IDH has been characterized. Etiolated pea plants show two biochemically distinct forms associated with the mitochondrial soluble matrix and membrane fractions (McIntosh, 1997). These IDH forms show similar enzymatic properties and, like all TCA cycle dehydrogenases, a ...
... plants, only partially purified IDH has been characterized. Etiolated pea plants show two biochemically distinct forms associated with the mitochondrial soluble matrix and membrane fractions (McIntosh, 1997). These IDH forms show similar enzymatic properties and, like all TCA cycle dehydrogenases, a ...
Mitochondrion

The mitochondrion (plural mitochondria) is a double membrane-bound organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. The word mitochondrion comes from the Greek μίτος, mitos, i.e. ""thread"", and χονδρίον, chondrion, i.e. ""granule"" or ""grain-like"".Mitochondria range from 0.5 to 1.0 μm in diameter. A considerable variation can be seen in the structure and size of this organelle. Unless specifically stained, they are not visible. These structures are described as ""the powerhouse of the cell"" because they generate most of the cell's supply of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), used as a source of chemical energy. In addition to supplying cellular energy, mitochondria are involved in other tasks, such as signaling, cellular differentiation, and cell death, as well as maintaining control of the cell cycle and cell growth. Mitochondria have been implicated in several human diseases, including mitochondrial disorders, cardiac dysfunction, and heart failure. A recent University of California study including ten children diagnosed with severe autism suggests that autism may be correlated with mitochondrial defects as well.Several characteristics make mitochondria unique. The number of mitochondria in a cell can vary widely by organism, tissue, and cell type. For instance, red blood cells have no mitochondria, whereas liver cells can have more than 2000. The organelle is composed of compartments that carry out specialized functions. These compartments or regions include the outer membrane, the intermembrane space, the inner membrane, and the cristae and matrix. Mitochondrial proteins vary depending on the tissue and the species. In humans, 615 distinct types of protein have been identified from cardiac mitochondria, whereas in rats, 940 proteins have been reported. The mitochondrial proteome is thought to be dynamically regulated. Although most of a cell's DNA is contained in the cell nucleus, the mitochondrion has its own independent genome. Further, its DNA shows substantial similarity to bacterial genomes.