cellular respiration
... Indicate if each of the following characteristics / descriptions is true of Substratelevel and Oxidative phosphorylation. ______ Produce ATP by adding a phosphate to ADP ______ Involves the direct transfer of a phosphate from an intermediate to ADP ______ Couples the addition of a phosphate to ADP w ...
... Indicate if each of the following characteristics / descriptions is true of Substratelevel and Oxidative phosphorylation. ______ Produce ATP by adding a phosphate to ADP ______ Involves the direct transfer of a phosphate from an intermediate to ADP ______ Couples the addition of a phosphate to ADP w ...
The Calcium-Binding Activity of a Vacuole
... A vacuole membrane-associated calcium-binding protein with an apparent mass of 45 kD was purified from celery (Apium graveolens). This protein, VCaB45, is enriched in highly vacuolate tissues and is located within the lumen of vacuoles. Antigenically related proteins are present in many dicotyledono ...
... A vacuole membrane-associated calcium-binding protein with an apparent mass of 45 kD was purified from celery (Apium graveolens). This protein, VCaB45, is enriched in highly vacuolate tissues and is located within the lumen of vacuoles. Antigenically related proteins are present in many dicotyledono ...
01 Signal transduction
... Toll-like Receptors. Whether the expression of inflammatory cytokines or type I interferons are regulated by the TLR – IRF5 pathway is discussed controversially. Consistently is the finding that IRF5 is involved in the MyD88 dependent signaling pathway: it coimmunoprecipitates with MyD88 and TRAF6, ...
... Toll-like Receptors. Whether the expression of inflammatory cytokines or type I interferons are regulated by the TLR – IRF5 pathway is discussed controversially. Consistently is the finding that IRF5 is involved in the MyD88 dependent signaling pathway: it coimmunoprecipitates with MyD88 and TRAF6, ...
hanan abas
... Oxalate :Chemical compounds such as Na2CO3 ,NH4CO3 ,Li2CO3 are inhibit blood coagulation by forming insolulube complexes for Ca++ ( salts) .Potassium Oxalate is always used as anticoagulants, by most ...
... Oxalate :Chemical compounds such as Na2CO3 ,NH4CO3 ,Li2CO3 are inhibit blood coagulation by forming insolulube complexes for Ca++ ( salts) .Potassium Oxalate is always used as anticoagulants, by most ...
PDF
... pathways that regulate many aspects of eukaryotic biology (1, 2). The protein kinase gene family is one of the largest in eukaryotic organisms and typically constitutes almost 2% of all protein-encoding genes (3, 4). In general, these enzymes catalyze the transfer of the terminal phosphate from ATP ...
... pathways that regulate many aspects of eukaryotic biology (1, 2). The protein kinase gene family is one of the largest in eukaryotic organisms and typically constitutes almost 2% of all protein-encoding genes (3, 4). In general, these enzymes catalyze the transfer of the terminal phosphate from ATP ...
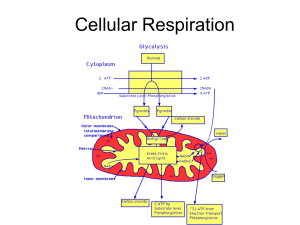
Cellular Respiration
... 1. I n which organelle does cell respiration occur? 2. Photosynthesis occurs in what types of organisms? Cell respiration occurs in what type? 3. Write the equation for photosynthesis. 4. Write the equation for cell respiration…notice they are opposites! 5. Which step of cell respiration breaks down ...
... 1. I n which organelle does cell respiration occur? 2. Photosynthesis occurs in what types of organisms? Cell respiration occurs in what type? 3. Write the equation for photosynthesis. 4. Write the equation for cell respiration…notice they are opposites! 5. Which step of cell respiration breaks down ...
Chem464 Abrol Spring2017 FlippedReview4
... carrying a gene for a protein similar to the chemokine receptors CXCR1 and CXCR2. Chemokines are cell-specific growth factors. C. Adenovirus, a tumor virus, carries a gene for the protein E1A, which binds to the retinoblastoma protein, pRb. (Hint: See Fig. 12–49.) D. An important feature of many onc ...
... carrying a gene for a protein similar to the chemokine receptors CXCR1 and CXCR2. Chemokines are cell-specific growth factors. C. Adenovirus, a tumor virus, carries a gene for the protein E1A, which binds to the retinoblastoma protein, pRb. (Hint: See Fig. 12–49.) D. An important feature of many onc ...
AP Biology Discussion Notes Thursday 121516
... • Following glycolysis and the citric acid cycle, NADH and FADH2 account for most of the energy extracted from food • These two electron carriers donate electrons to the electron transport chain, which powers ATP synthesis via oxidative phosphorylation ...
... • Following glycolysis and the citric acid cycle, NADH and FADH2 account for most of the energy extracted from food • These two electron carriers donate electrons to the electron transport chain, which powers ATP synthesis via oxidative phosphorylation ...
09_Lecture_Presentation
... phosphorylation, chemiosmosis couples electron transport to ATP synthesis • Following glycolysis and the citric acid cycle, NADH and FADH2 account for most of the energy extracted from food • These two electron carriers donate electrons to the electron transport chain, which powers ATP synthesis via ...
... phosphorylation, chemiosmosis couples electron transport to ATP synthesis • Following glycolysis and the citric acid cycle, NADH and FADH2 account for most of the energy extracted from food • These two electron carriers donate electrons to the electron transport chain, which powers ATP synthesis via ...
H 2 O 2
... on protons, but also on concentrations of other ions, ΔG = – nFΔ The proton motive force Δ p is the quantity expressed in the term of potential (milivolts per mole of H+ transferred): Δ p = – ΔG / nF = Δ + 60 Δ pH . Utilization of proton motive force • synthesis of ATP = aerobic phosphorylation • ...
... on protons, but also on concentrations of other ions, ΔG = – nFΔ The proton motive force Δ p is the quantity expressed in the term of potential (milivolts per mole of H+ transferred): Δ p = – ΔG / nF = Δ + 60 Δ pH . Utilization of proton motive force • synthesis of ATP = aerobic phosphorylation • ...
Studies of focal adhesion assembly
... composed of three different domain types: Fn1, Fn2 and Fn3. High-resolution structures of many of these component domains and domain combinations have been available for some time [6]; the main remaining uncertainties are associated with how Fn forms complexes with its various partners. Fn has confo ...
... composed of three different domain types: Fn1, Fn2 and Fn3. High-resolution structures of many of these component domains and domain combinations have been available for some time [6]; the main remaining uncertainties are associated with how Fn forms complexes with its various partners. Fn has confo ...
Carbohydrates - REVISION-IB2
... Building block molecules = sugars sugar - sugar - sugar - sugar - sugar sugar sugar sugar sugar sugar sugar sugar sugar ...
... Building block molecules = sugars sugar - sugar - sugar - sugar - sugar sugar sugar sugar sugar sugar sugar sugar sugar ...
Chapter 9: Glycolysis & Krebs Cycle
... broken down and energy is released Mitochondria in a Liver Cell!! ...
... broken down and energy is released Mitochondria in a Liver Cell!! ...
electron transport chain
... phosphorylation, chemiosmosis couples electron transport to ATP synthesis • Following glycolysis and the citric acid cycle, NADH and FADH2 account for most of the energy extracted from food • These two electron carriers donate electrons to the electron transport chain, which powers ATP synthesis via ...
... phosphorylation, chemiosmosis couples electron transport to ATP synthesis • Following glycolysis and the citric acid cycle, NADH and FADH2 account for most of the energy extracted from food • These two electron carriers donate electrons to the electron transport chain, which powers ATP synthesis via ...
Functions of the liver Assessment and interpretation of liver function
... Proteins & peptides Albumin • Most abundant protein • Normal plasma conc- 3 - 5 g% • Daily production -12-15 g/d • Plasma half life – 15-20 days • Functions – • maintains plasma oncotic pressure (80% by albumin) • binds ions, bilirubin, hormones & drugs ...
... Proteins & peptides Albumin • Most abundant protein • Normal plasma conc- 3 - 5 g% • Daily production -12-15 g/d • Plasma half life – 15-20 days • Functions – • maintains plasma oncotic pressure (80% by albumin) • binds ions, bilirubin, hormones & drugs ...
Ch 9 Homework Plan - Dublin City Schools
... Complete the Cellular Respiration Review Activity #1 Thursday (Oct. 15th) – Read p. 166-167 (from the “Stages of Cellular Respiration”) and take notes Read p. 170-172 (The Citric Acid cycle completes…”) and take notes Understand the following figures: 9.7 - 9.11 Answer the following questi ...
... Complete the Cellular Respiration Review Activity #1 Thursday (Oct. 15th) – Read p. 166-167 (from the “Stages of Cellular Respiration”) and take notes Read p. 170-172 (The Citric Acid cycle completes…”) and take notes Understand the following figures: 9.7 - 9.11 Answer the following questi ...
electron transport chain.
... • These small molecules may come directly from food, from glycolysis, or from the citric acid cycle. • They can be converted by cells to other types of molecules. • If we eat more food than we need, we store excess fat. ...
... • These small molecules may come directly from food, from glycolysis, or from the citric acid cycle. • They can be converted by cells to other types of molecules. • If we eat more food than we need, we store excess fat. ...
ATP/NADH Ledger
... be converted into glucose, a cell can produce ATP. Continual production creates NADH accumulation and NAD+ depletion. NADH must be recycled into NAD+. • Aerobic respiration - oxygen as electron acceptor • Fermentation - organic molecule ...
... be converted into glucose, a cell can produce ATP. Continual production creates NADH accumulation and NAD+ depletion. NADH must be recycled into NAD+. • Aerobic respiration - oxygen as electron acceptor • Fermentation - organic molecule ...
Nutrition
... Cellulose is a polysaccharide. What is it formed from? State a role for cellulose in living organisms. ...
... Cellulose is a polysaccharide. What is it formed from? State a role for cellulose in living organisms. ...
normal myocardial metabolism: fueling cardiac contraction
... Optimal cardiac function depends on the efficient matching of energy generation to energetic demands and the orchestrated metabolism of multiple substrate oxidation to generate sufficient ATP under varied physiologic conditions. In the actively pumping heart, the rate of ATP hydrolysis must match th ...
... Optimal cardiac function depends on the efficient matching of energy generation to energetic demands and the orchestrated metabolism of multiple substrate oxidation to generate sufficient ATP under varied physiologic conditions. In the actively pumping heart, the rate of ATP hydrolysis must match th ...
Energy Cycle in Vertebrates - Jean
... reserves at the appropriate times and rates to meet their life requirements. The building blocks of triacylglycerol and glycogen must be separated before they can be utilized or transported to other tissues. Therefore, fuel mobilization is controlled by complex neural and hormonal mechanisms designe ...
... reserves at the appropriate times and rates to meet their life requirements. The building blocks of triacylglycerol and glycogen must be separated before they can be utilized or transported to other tissues. Therefore, fuel mobilization is controlled by complex neural and hormonal mechanisms designe ...
Area 4: Molecular recognition in biomolecules Computational
... There is a wide interest in designing peptides able to bind to a specific region of a protein with the aim of interfering with a known interaction or as starting point for the design of inhibitors. We plan to develop and implement a tool for the computational design of peptides binding to a protein ...
... There is a wide interest in designing peptides able to bind to a specific region of a protein with the aim of interfering with a known interaction or as starting point for the design of inhibitors. We plan to develop and implement a tool for the computational design of peptides binding to a protein ...
Lecture # 7 Pentose Phosphate Pathway
... The pentose pathway is a shunt. • The pathway begins with the glycolytic intermediate glucose 6-P. • It reconnects with glycolysis because two of the end products of the pentose pathway are glyceraldehyde 3-P and fructose 6-P; two intermediates further down in the glycolytic pathway. • It is for th ...
... The pentose pathway is a shunt. • The pathway begins with the glycolytic intermediate glucose 6-P. • It reconnects with glycolysis because two of the end products of the pentose pathway are glyceraldehyde 3-P and fructose 6-P; two intermediates further down in the glycolytic pathway. • It is for th ...
03-232 Exam III 2013 Name:__________________________
... metabolic pathways the carbons flow through, and provide the names of key molecules, such as the input to the pathway, output from the pathway, and any intermediate molecules between the pathways. Feel free to draw a well labeled diagram for your answer. Choice A: Outline the flow of carbon atoms fr ...
... metabolic pathways the carbons flow through, and provide the names of key molecules, such as the input to the pathway, output from the pathway, and any intermediate molecules between the pathways. Feel free to draw a well labeled diagram for your answer. Choice A: Outline the flow of carbon atoms fr ...
Phosphorylation

Phosphorylation is the addition of a phosphate (PO43−) group to a protein or other organic molecule. Phosphorylation and its counterpart, dephosphorylation, turn many protein enzymes on and off, thereby altering their function and activity. Protein phosphorylation is one type of post-translational modification.Protein phosphorylation in particular plays a significant role in a wide range of cellular processes. Its prominent role in biochemistry is the subject of a very large body of research (as of March 2015, the Medline database returns over 240,000 articles on the subject, largely on protein phosphorylation).