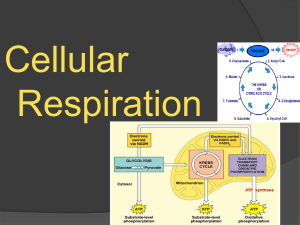
- WordPress.com
... Fructose is metabolized by A. fructose 1-phosphate pathway B. fructose 6-phosphate pathway C. glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate pathway D.both (a) and (b) Answer: Option D ...
... Fructose is metabolized by A. fructose 1-phosphate pathway B. fructose 6-phosphate pathway C. glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate pathway D.both (a) and (b) Answer: Option D ...
ADP
... 1. Basic Process of Glycolysis * Definition of Glycolysis The process in which a molecule of glucose is degraded in a series of enzymatic reactions to yield two molecules of pyruvate or lactate under anaerobic condition is term glycolysis. * The site of glycolysis is cytoplasm. ...
... 1. Basic Process of Glycolysis * Definition of Glycolysis The process in which a molecule of glucose is degraded in a series of enzymatic reactions to yield two molecules of pyruvate or lactate under anaerobic condition is term glycolysis. * The site of glycolysis is cytoplasm. ...
AP Bio Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration 1. What is the term for
... b. accepting electrons at the end of the electron transport chain c. the citric acid cycle d. the oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA e. the phosphorylation of ADP to form ATP 8. Which process in eukaryotic cells will proceed normally whether oxygen (O2) is present or absent? a. electron transport b ...
... b. accepting electrons at the end of the electron transport chain c. the citric acid cycle d. the oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA e. the phosphorylation of ADP to form ATP 8. Which process in eukaryotic cells will proceed normally whether oxygen (O2) is present or absent? a. electron transport b ...
Chemistry of Carbohydrates
... Reaction 3-produce oneNADH2+ molecule which enter the respiratory chain producing 2.5 ATP molecules . Reaction 4- produce oneNADH2+ molecule which enter the respiratory chain producing 2.5 ATP molecules . Reaction 5-produce 1 ATP molecule. Reaction 6-produce one FADH2+ molecule which enter the respi ...
... Reaction 3-produce oneNADH2+ molecule which enter the respiratory chain producing 2.5 ATP molecules . Reaction 4- produce oneNADH2+ molecule which enter the respiratory chain producing 2.5 ATP molecules . Reaction 5-produce 1 ATP molecule. Reaction 6-produce one FADH2+ molecule which enter the respi ...
7 | cellular respiration
... Step 1. The first step in glycolysis (Figure 7.6) is catalyzed by hexokinase, an enzyme with broad specificity that catalyzes the phosphorylation of six-carbon sugars. Hexokinase phosphorylates glucose using ATP as the source of the phosphate, producing glucose-6-phosphate, a more reactive form of g ...
... Step 1. The first step in glycolysis (Figure 7.6) is catalyzed by hexokinase, an enzyme with broad specificity that catalyzes the phosphorylation of six-carbon sugars. Hexokinase phosphorylates glucose using ATP as the source of the phosphate, producing glucose-6-phosphate, a more reactive form of g ...
Module 3- Bioenergetics - Bangen Athletic Development
... Endurance training at intensities near or above the lactate threshold or onset of blood lactate threshold pushes these markers to occur at higher exercise intensities. This shift probably occurs as a result of changes in hormone release and increased mitochondrial content. This shift allows athletes ...
... Endurance training at intensities near or above the lactate threshold or onset of blood lactate threshold pushes these markers to occur at higher exercise intensities. This shift probably occurs as a result of changes in hormone release and increased mitochondrial content. This shift allows athletes ...
Glucose homeostasis in the blood (2) – un-storing energy
... glucose levels are low Figure 2: Low levels of glucose stimulate the pancreas to make glucagon that signals the liver to un-store glucose. and send the message to storage organs that more glucose is needed in the blood. The pancreas sends this signal in the form of glucagon, a hormone made out of am ...
... glucose levels are low Figure 2: Low levels of glucose stimulate the pancreas to make glucagon that signals the liver to un-store glucose. and send the message to storage organs that more glucose is needed in the blood. The pancreas sends this signal in the form of glucagon, a hormone made out of am ...
Lipid modifications of proteins – slipping in and out of membranes
... can occur enzymatically and non-enzymatically, and the mechanisms that regulate each of these reactions are unknown. The most extensively studied examples of palmitoylated proteins are the a-subunits of trimeric GTP-binding proteins (Ga) in animal cells. Following association with an effector, Ga is ...
... can occur enzymatically and non-enzymatically, and the mechanisms that regulate each of these reactions are unknown. The most extensively studied examples of palmitoylated proteins are the a-subunits of trimeric GTP-binding proteins (Ga) in animal cells. Following association with an effector, Ga is ...
Cell-Specific Localization of Glucose Transporter Proteins in
... was localized to cells of neuroendocrine origin. Neither the perineural sheaths nor the nerve terminal fibers demonstrated any Glut-3 immunoreactivity. In addition, as described previously, Glut-3 was present in white blood cells (20,39). Of interest was the developmental pattern of Glut-3 expressio ...
... was localized to cells of neuroendocrine origin. Neither the perineural sheaths nor the nerve terminal fibers demonstrated any Glut-3 immunoreactivity. In addition, as described previously, Glut-3 was present in white blood cells (20,39). Of interest was the developmental pattern of Glut-3 expressio ...
Metabolic changes in Diabetes mellitus (DM)
... • Lipase converts triglycerides to free fatty acids (FFA) and glycerol. Insulin inhibits the hormone sensitive lipase in adipose tissue and in the absence of insulin, the plasma level of FFA doubles. In liver and other tissues, the FFA are catabolised to acetyl Co A, and the excess acetyl Co A is co ...
... • Lipase converts triglycerides to free fatty acids (FFA) and glycerol. Insulin inhibits the hormone sensitive lipase in adipose tissue and in the absence of insulin, the plasma level of FFA doubles. In liver and other tissues, the FFA are catabolised to acetyl Co A, and the excess acetyl Co A is co ...
Systemic Delivery of siRNA by a Plant PHLOEM SMALL RNA
... plants in which c-Myc4-His8 tagged rbcS, GFP, CmPSRP1 WT, Qm and ∆C were expressed using a ZYMV vector. Total proteins extracted from infected tissues (10 µg) and phloem exudate (40 µg) were separated on 13% SDS-PAGE gels and analyzed by protein gel blot analysis using anti-c-Myc mAb. (b) CmPSRP1, Q ...
... plants in which c-Myc4-His8 tagged rbcS, GFP, CmPSRP1 WT, Qm and ∆C were expressed using a ZYMV vector. Total proteins extracted from infected tissues (10 µg) and phloem exudate (40 µg) were separated on 13% SDS-PAGE gels and analyzed by protein gel blot analysis using anti-c-Myc mAb. (b) CmPSRP1, Q ...
The role of Cdc14 phosphatases in the control of cell division
... Net1 tethers Cdc14 at the nucleolus and acts as a competitive inhibitor to keep it inactive during interphase [1]. Cdc14 release from Net1 occurs in two stages. First, early anaphase release depends upon a set of genes termed the FEAR (fourteen early anaphase release) network [1]. Then, the MEN (mit ...
... Net1 tethers Cdc14 at the nucleolus and acts as a competitive inhibitor to keep it inactive during interphase [1]. Cdc14 release from Net1 occurs in two stages. First, early anaphase release depends upon a set of genes termed the FEAR (fourteen early anaphase release) network [1]. Then, the MEN (mit ...
Biology 5.3 Cellular Respiration - Chemistry
... In the first stage of cellular respiration, glucose is broken down to pyruvate during glycolysis. Glycolysis is an anaerobic process (no oxygen required), and it results in a gain of two ATP molecules. ...
... In the first stage of cellular respiration, glucose is broken down to pyruvate during glycolysis. Glycolysis is an anaerobic process (no oxygen required), and it results in a gain of two ATP molecules. ...
Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
... phosphorylation—via the F1F0-ATP synthase in the inner mitochondrial membrane d) reduction of NAD+—in both the cytosol of the cell and the matrix of the mitochondria e) reduction of oxygen gas to water—in the matrix of the mitochondria © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... phosphorylation—via the F1F0-ATP synthase in the inner mitochondrial membrane d) reduction of NAD+—in both the cytosol of the cell and the matrix of the mitochondria e) reduction of oxygen gas to water—in the matrix of the mitochondria © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Chapter 9
... • Following glycolysis and the citric acid cycle, NADH and FADH2 account for most of the energy extracted from food • These two electron carriers donate electrons to the electron transport chain, which powers ATP synthesis via oxidative phosphorylation ...
... • Following glycolysis and the citric acid cycle, NADH and FADH2 account for most of the energy extracted from food • These two electron carriers donate electrons to the electron transport chain, which powers ATP synthesis via oxidative phosphorylation ...
Fe-S
... finally electrons combine with O2 and protons to form H2O. • Associated with cell breath, also called respiratory chain. • Electron carriers located in mitochondria according to a order. ...
... finally electrons combine with O2 and protons to form H2O. • Associated with cell breath, also called respiratory chain. • Electron carriers located in mitochondria according to a order. ...
Chapter 8 – an introduction to metabolism
... 7. Name the three stages of cellular respiration and state the region of the eukaryotic cell where each stage occurs. 8. Describe how the carbon skeleton of glucose changes as it proceeds through glycolysis. 9. Explain why ATP is required for the preparatory steps of glycolysis. 10. Identify where s ...
... 7. Name the three stages of cellular respiration and state the region of the eukaryotic cell where each stage occurs. 8. Describe how the carbon skeleton of glucose changes as it proceeds through glycolysis. 9. Explain why ATP is required for the preparatory steps of glycolysis. 10. Identify where s ...
supplementary information
... Growth rate during exponential phase was measured in minimal media containing 2% glucose and supplemented with the indicated concentration of histidine (error bars indicate s.e.m. of two or more measurements). The growth rate of the cheater strain is not sensitive to the histidine concentration beca ...
... Growth rate during exponential phase was measured in minimal media containing 2% glucose and supplemented with the indicated concentration of histidine (error bars indicate s.e.m. of two or more measurements). The growth rate of the cheater strain is not sensitive to the histidine concentration beca ...
File
... The role of ATP in the transfer of energy and the phosphorylation of molecules by ATP. Metabolic pathways of cellular respiration. The breakdown of glucose to pyruvate in the cytoplasm in glycolysis, and the progression pathways in the presence or absence of oxygen (fermentation). The role of the en ...
... The role of ATP in the transfer of energy and the phosphorylation of molecules by ATP. Metabolic pathways of cellular respiration. The breakdown of glucose to pyruvate in the cytoplasm in glycolysis, and the progression pathways in the presence or absence of oxygen (fermentation). The role of the en ...
Citric acid cycle
... • Following glycolysis and the citric acid cycle, NADH and FADH2 account for most of the energy extracted from food • These two electron carriers donate electrons to the electron transport chain, which powers ATP synthesis via oxidative phosphorylation ...
... • Following glycolysis and the citric acid cycle, NADH and FADH2 account for most of the energy extracted from food • These two electron carriers donate electrons to the electron transport chain, which powers ATP synthesis via oxidative phosphorylation ...
OGT Reivew3 - HensonsBiologyPage
... molecules to one pyruvic acid and 2 ATP 2. Glycolysis converts two glucose molecules to two pyruvic acids and 2 ATP 3. Glycolysis converts one glucose molecule to two pyruvic acid and 1 ATP 4. Glycolysis converts one glucose to two pyruvic acid and two ATP ...
... molecules to one pyruvic acid and 2 ATP 2. Glycolysis converts two glucose molecules to two pyruvic acids and 2 ATP 3. Glycolysis converts one glucose molecule to two pyruvic acid and 1 ATP 4. Glycolysis converts one glucose to two pyruvic acid and two ATP ...
DOC - National Center for Macromolecular Imaging
... different organisms. The daunting task of understanding the functions and regulation of these genes can be simplified by associating each of these genes with one of 200-300 core biological processes. Since most proteins function in association with other proteins in cells, one way to simplify the pr ...
... different organisms. The daunting task of understanding the functions and regulation of these genes can be simplified by associating each of these genes with one of 200-300 core biological processes. Since most proteins function in association with other proteins in cells, one way to simplify the pr ...
Slide 1
... oxidizing glucose to pyruvate In glycolysis, a single molecule of glucose is enzymatically cut in half through a series of steps to produce two molecules of pyruvate – In the process, two molecules of NAD+ are reduced to two molecules of NADH – At the same time, two molecules of ATP are produced b ...
... oxidizing glucose to pyruvate In glycolysis, a single molecule of glucose is enzymatically cut in half through a series of steps to produce two molecules of pyruvate – In the process, two molecules of NAD+ are reduced to two molecules of NADH – At the same time, two molecules of ATP are produced b ...
Carbohydrates - Explore Biology
... Building block molecules = sugars sugar - sugar - sugar - sugar - sugar sugar sugar sugar sugar sugar sugar sugar sugar ...
... Building block molecules = sugars sugar - sugar - sugar - sugar - sugar sugar sugar sugar sugar sugar sugar sugar sugar ...
Phosphorylation

Phosphorylation is the addition of a phosphate (PO43−) group to a protein or other organic molecule. Phosphorylation and its counterpart, dephosphorylation, turn many protein enzymes on and off, thereby altering their function and activity. Protein phosphorylation is one type of post-translational modification.Protein phosphorylation in particular plays a significant role in a wide range of cellular processes. Its prominent role in biochemistry is the subject of a very large body of research (as of March 2015, the Medline database returns over 240,000 articles on the subject, largely on protein phosphorylation).