cell respiration wilk hl ibdp
... • As a result the more and more H+ ions ( protons) are transferred to the inter membrane space. Cytochrome c oxidase ultimately transfers electrons to Oxygen (terminal e acceptor) and water is formed as an end product. ...
... • As a result the more and more H+ ions ( protons) are transferred to the inter membrane space. Cytochrome c oxidase ultimately transfers electrons to Oxygen (terminal e acceptor) and water is formed as an end product. ...
Exam 2 for Review - philipdarrenjones.com
... 38) A patient has had a serious accident and lost a lot of blood. In an attempt to replenish body fluids, distilled water, equal to the volume of blood lost, is transferred directly into one of his veins. What will be the most probable result of this transfusion? A) It will have no unfavorable effec ...
... 38) A patient has had a serious accident and lost a lot of blood. In an attempt to replenish body fluids, distilled water, equal to the volume of blood lost, is transferred directly into one of his veins. What will be the most probable result of this transfusion? A) It will have no unfavorable effec ...
25-1
... • Converted to one of several amino acids in many different cells throughout the body • Glycogenesis – hundreds of glucose molecules combined to form glycogen for storage in liver & skeletal muscles • Lipogenesis (triglyceride synthesis) – converted to glycerol & fatty acids within liver & sent to f ...
... • Converted to one of several amino acids in many different cells throughout the body • Glycogenesis – hundreds of glucose molecules combined to form glycogen for storage in liver & skeletal muscles • Lipogenesis (triglyceride synthesis) – converted to glycerol & fatty acids within liver & sent to f ...
Gene expression of eukaryotic cells
... • posttranscription modification of RNA (removing introns and connecting exons) • complicated regulation system, performed at the several levels (transcription, translation, protein activation + secretion) ...
... • posttranscription modification of RNA (removing introns and connecting exons) • complicated regulation system, performed at the several levels (transcription, translation, protein activation + secretion) ...
Chapter 8 Lecture Notes - Science Learning Center
... Cell Respiration The overall reaction for cell respiration is: C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP (this reaction is the reverse of photosynthesis) There are three stages to cell respiration: glycolysis, Krebs cycle, and electron transport chain/oxidative phosphorylation. ...
... Cell Respiration The overall reaction for cell respiration is: C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP (this reaction is the reverse of photosynthesis) There are three stages to cell respiration: glycolysis, Krebs cycle, and electron transport chain/oxidative phosphorylation. ...
No Slide Title
... • Converted to one of several amino acids in many different cells throughout the body • Glycogenesis – hundreds of glucose molecules combined to form glycogen for storage in liver & skeletal muscles • Lipogenesis (triglyceride synthesis) – converted to glycerol & fatty acids within liver & sent to f ...
... • Converted to one of several amino acids in many different cells throughout the body • Glycogenesis – hundreds of glucose molecules combined to form glycogen for storage in liver & skeletal muscles • Lipogenesis (triglyceride synthesis) – converted to glycerol & fatty acids within liver & sent to f ...
14) Which of the following is a major cause of the size limits for
... 38) A patient has had a serious accident and lost a lot of blood. In an attempt to replenish body fluids, distilled water, equal to the volume of blood lost, is transferred directly into one of his veins. What will be the most probable result of this transfusion? A) It will have no unfavorable effec ...
... 38) A patient has had a serious accident and lost a lot of blood. In an attempt to replenish body fluids, distilled water, equal to the volume of blood lost, is transferred directly into one of his veins. What will be the most probable result of this transfusion? A) It will have no unfavorable effec ...
fat-soluble
... leading to premature breakdown of lipases. 2. The first step in amino acid catabolism requires a coenzyme derivative of B6. 3. B6 deficiency is critical to later steps of amino ...
... leading to premature breakdown of lipases. 2. The first step in amino acid catabolism requires a coenzyme derivative of B6. 3. B6 deficiency is critical to later steps of amino ...
Chapter 25 - FacultyWeb
... leading to premature breakdown of lipases. 2. The first step in amino acid catabolism requires a coenzyme derivative of B6. 3. B6 deficiency is critical to later steps of amino ...
... leading to premature breakdown of lipases. 2. The first step in amino acid catabolism requires a coenzyme derivative of B6. 3. B6 deficiency is critical to later steps of amino ...
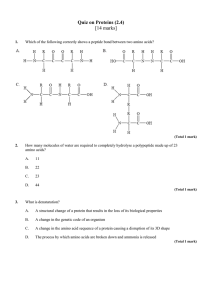
Quiz on Proteins (2.4) - Peoria Public Schools
... A structural change of a protein that results in the loss of its biological properties ...
... A structural change of a protein that results in the loss of its biological properties ...
Ultrafast Solvation: Investigating Molecular Forces in Protein Folding November 12, 2010
... the cooperative behavior of these interactions drives the spontaneous folding and unfolding of large macromolecules. The ability to manipulate these large-scale conformational changes will require a complete understanding of solvent-protein interactions. We investigate solvent-protein interactions b ...
... the cooperative behavior of these interactions drives the spontaneous folding and unfolding of large macromolecules. The ability to manipulate these large-scale conformational changes will require a complete understanding of solvent-protein interactions. We investigate solvent-protein interactions b ...
Second test - rci.rutgers.edu
... In the laboratory, Ribose-5-P and Fructose-6-P can be reacted with the enzyme Transketolase. What would the products of this reaction be? A. glyoxylate-2-P and a 9 carbon ketose B. Glyceraldehyde-3-P and an 8 carbon ketose C. Erythrose-4-P and Sedoheptulose-7-P D. Ribose-5-P and Fructose-6-P E. Allo ...
... In the laboratory, Ribose-5-P and Fructose-6-P can be reacted with the enzyme Transketolase. What would the products of this reaction be? A. glyoxylate-2-P and a 9 carbon ketose B. Glyceraldehyde-3-P and an 8 carbon ketose C. Erythrose-4-P and Sedoheptulose-7-P D. Ribose-5-P and Fructose-6-P E. Allo ...
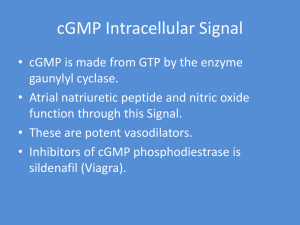
cGMP Intracellular Signal
... • Glucocorticoid hormones are therapeutically useful agents for the treatment of a variety of inflammatory and immune diseases.. • These actions in part are explained by the inhibition of NF-кB pathway. • Increase the level of inhibitoe • Compete with the Co activators for the receptor. • Directly b ...
... • Glucocorticoid hormones are therapeutically useful agents for the treatment of a variety of inflammatory and immune diseases.. • These actions in part are explained by the inhibition of NF-кB pathway. • Increase the level of inhibitoe • Compete with the Co activators for the receptor. • Directly b ...
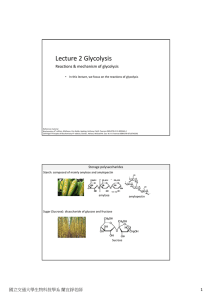
Lecture 2 Glycolysis
... Phosphotransferase system (PTS) used by many bacteria In many bacteria, glucose is simultaneously transported and activated by the PTS. PTS uses PEP as the phosphate donor, which in a series of reactions, phosphorylates glucose ...
... Phosphotransferase system (PTS) used by many bacteria In many bacteria, glucose is simultaneously transported and activated by the PTS. PTS uses PEP as the phosphate donor, which in a series of reactions, phosphorylates glucose ...
(1-4) D-glucose, a
... Mannose-6-Phosphate Receptor: Targets proteins for destruction in the lysosomes ZP3 Receptor on surface of sperm: ZP3 glycoprotein in extracellular coat of ovulated eggs a-linked galactose at the non-reducing end Binding triggers release of sperm enzymes, dissolves zona pellucida to allow sperm to e ...
... Mannose-6-Phosphate Receptor: Targets proteins for destruction in the lysosomes ZP3 Receptor on surface of sperm: ZP3 glycoprotein in extracellular coat of ovulated eggs a-linked galactose at the non-reducing end Binding triggers release of sperm enzymes, dissolves zona pellucida to allow sperm to e ...
Bio102 Problems
... 12. In our discussions of oxidative phosphorylation, we mainly discussed the mitochondrial inner membrane. Prokaryotes can also carry out electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation, but prokaryotes have no mitochondria. How does oxidative phosphorylation in prokaryotes happen without a mitocho ...
... 12. In our discussions of oxidative phosphorylation, we mainly discussed the mitochondrial inner membrane. Prokaryotes can also carry out electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation, but prokaryotes have no mitochondria. How does oxidative phosphorylation in prokaryotes happen without a mitocho ...
foga i - is there such a thing as a gene? = formatting the
... * Systemic (modular-interactive) nature of each protein molecule and DNA element * Weak interactions, specific binding & cooperativity essential aspects of molecular computations in cells * Layering of weak and “fuzzy” interactions provides overall precision to integrated cellular responses * Allost ...
... * Systemic (modular-interactive) nature of each protein molecule and DNA element * Weak interactions, specific binding & cooperativity essential aspects of molecular computations in cells * Layering of weak and “fuzzy” interactions provides overall precision to integrated cellular responses * Allost ...
Chapter 5 – Proteins and Amino Acids
... 1. Digestibility 2. Amino Acid Composition 3. High-Quality Proteins 4. Complementary Proteins B. Protein Sparing Nutrition in Practice – Vegetarian Diets A. Are vegetarian diets nutritionally sound? B. What should be my main concerns when planning a nutritionally sound vegetarian diet? C. Isn’t prot ...
... 1. Digestibility 2. Amino Acid Composition 3. High-Quality Proteins 4. Complementary Proteins B. Protein Sparing Nutrition in Practice – Vegetarian Diets A. Are vegetarian diets nutritionally sound? B. What should be my main concerns when planning a nutritionally sound vegetarian diet? C. Isn’t prot ...
Test questions used for assessment
... 1. ATP formation... a. is important because ATP is the usable form of energy for all the cell's energy needs b. occurs mainly in the mitochondria c. includes glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain d. all of the above e. a and b 2. Which of the following are true? a. in g ...
... 1. ATP formation... a. is important because ATP is the usable form of energy for all the cell's energy needs b. occurs mainly in the mitochondria c. includes glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain d. all of the above e. a and b 2. Which of the following are true? a. in g ...
Metabolic Processes Unit
... Part B - Factual Questions (Answer all of the following questions. Point form may be used.) ...
... Part B - Factual Questions (Answer all of the following questions. Point form may be used.) ...
Chapter 5 - Missouri State University
... Glycolysis = ____________________________________ Metabolic pathway by which glucose is converted to _______ molecules of ...
... Glycolysis = ____________________________________ Metabolic pathway by which glucose is converted to _______ molecules of ...
Question 2. Which of the following statements about G proteins are
... d) They constitute a protein family of five isoforms. ...
... d) They constitute a protein family of five isoforms. ...
Phosphorylation

Phosphorylation is the addition of a phosphate (PO43−) group to a protein or other organic molecule. Phosphorylation and its counterpart, dephosphorylation, turn many protein enzymes on and off, thereby altering their function and activity. Protein phosphorylation is one type of post-translational modification.Protein phosphorylation in particular plays a significant role in a wide range of cellular processes. Its prominent role in biochemistry is the subject of a very large body of research (as of March 2015, the Medline database returns over 240,000 articles on the subject, largely on protein phosphorylation).