Chapter 5 – Rome and the Rise of Christianity
... 25. Procurator26. New Testament27. Clergy28. Laity29. Jesus30. Simon Peter31. Paul of Tarsus32. Constantine33. Theodosius the Great34. Plague35. Inflation36. Diocletian37. Constantine38. Huns39. Visigoths40. Vandals41. Romulus AugustulusSection 1 1. What role did geography play in the prosperity an ...
... 25. Procurator26. New Testament27. Clergy28. Laity29. Jesus30. Simon Peter31. Paul of Tarsus32. Constantine33. Theodosius the Great34. Plague35. Inflation36. Diocletian37. Constantine38. Huns39. Visigoths40. Vandals41. Romulus AugustulusSection 1 1. What role did geography play in the prosperity an ...
Ch.1 Section 2 The Roman Republic and Empire
... 8. Julius Caesar 9. Augustus Caesar 10. Justinian ...
... 8. Julius Caesar 9. Augustus Caesar 10. Justinian ...
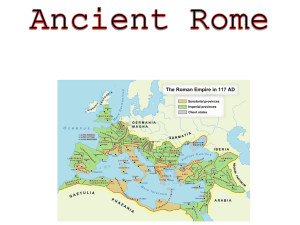
The Roman Empire
... around the Mediterranean Sea • They were proud and called the Mediterranean Sea “Our Sea” • Augustus was an intelligent ruler, he first ignored the senate, but then embraced them in order to gain their trust and loyalty • The senate and the people were so grateful that they gave Augustus as much pow ...
... around the Mediterranean Sea • They were proud and called the Mediterranean Sea “Our Sea” • Augustus was an intelligent ruler, he first ignored the senate, but then embraced them in order to gain their trust and loyalty • The senate and the people were so grateful that they gave Augustus as much pow ...
Roman Empire - Gilbert Public Schools
... • Geography of Italy much easier for unification • Probably settled by Etruscans – Romans borrowed their alphabet • Etruscans borrowed from Greeks ...
... • Geography of Italy much easier for unification • Probably settled by Etruscans – Romans borrowed their alphabet • Etruscans borrowed from Greeks ...
Humanities 2020 Chapter 4
... Diocletian: Empire had grown unwieldy. Divided into East and West. In the third century, Constantine moved the capital to the East, in Constantinople ...
... Diocletian: Empire had grown unwieldy. Divided into East and West. In the third century, Constantine moved the capital to the East, in Constantinople ...
Rome after Augustus
... building roads. However, one problem was not solved: who would rule after the emperor dies? ...
... building roads. However, one problem was not solved: who would rule after the emperor dies? ...
Ancient Rome Anticipation Guide Downey Ch. 7
... Ancient Rome Anticipation Guide Downey Ch. 7 Name____________________ Before reading: In the space to the left of each statement, place a check mark if you agree or think the statement is true. After reading: Add new check marks or cross through those about which you have changed your mind. Keep in ...
... Ancient Rome Anticipation Guide Downey Ch. 7 Name____________________ Before reading: In the space to the left of each statement, place a check mark if you agree or think the statement is true. After reading: Add new check marks or cross through those about which you have changed your mind. Keep in ...
Rome and the Roots of Western Civilization
... Educated Romans learned the Greek language The mixing of Roman, Hellenistic, and Greek culture produced a new culture, called Greco-Roman culture. ...
... Educated Romans learned the Greek language The mixing of Roman, Hellenistic, and Greek culture produced a new culture, called Greco-Roman culture. ...
Chapter 24: World War I Outline
... B. The Roman Republic 1. The Romans ultimately established a _____________. 2. In 46 B.C., _______ ___________ seized control of the government; he ruled for about two years before he was assassinated. C. Growth of the Roman Empire – 1. The first emperor of Rome renamed himself ___________, which me ...
... B. The Roman Republic 1. The Romans ultimately established a _____________. 2. In 46 B.C., _______ ___________ seized control of the government; he ruled for about two years before he was assassinated. C. Growth of the Roman Empire – 1. The first emperor of Rome renamed himself ___________, which me ...
Ancient Rome Review 1. Who are the Etruscans? What did the
... 11. What did it mean to be a Roman soldier? What is a legion? What happened if you left your legion? 12. What is the significance of the statement “Crossing of the Rubicon” 13. What is a triumvirate? 14. Why was Julius Caesar killed? On what day? 15. Who is Cleopatra and Mark Antony? 16. What is Pax ...
... 11. What did it mean to be a Roman soldier? What is a legion? What happened if you left your legion? 12. What is the significance of the statement “Crossing of the Rubicon” 13. What is a triumvirate? 14. Why was Julius Caesar killed? On what day? 15. Who is Cleopatra and Mark Antony? 16. What is Pax ...
Alpine regiments of the Roman army

The Alpine regiments of the Roman army were those auxiliary units of the army that were originally raised in the Alpine provinces of the Roman Empire: Tres Alpes, Raetia and Noricum. All these regions were inhabited by predominantly Celtic-speaking tribes. They were annexed, or at least occupied, by the emperor Augustus' forces during the period 25-14 BC. The term ""Alpine"" is used geographically in this context and does not necessarily imply that the regiments in question were specialised in mountain warfare. However, in the Julio-Claudian period (ante AD 68), when the regiments were still largely composed of Alpine recruits, it is likely that they were especially adept at mountain operations.As would be expected from mountain people, the Alpine provinces predominantly supplied infantry; only one Alpine cavalry ala is recorded. About 26 Alpine regiments were raised in the Julio-Claudian period, the great majority under Augustus or his successor Tiberius (i.e. before AD 37). Of these, 6 regiments disappeared, either destroyed in action or disbanded, by AD 68. A further 2 regiments were raised by Vespasian (ruled 69-96). These and the 20 surviving Julio-Claudian units are recorded at least until the mid 2nd century, but by that time only around a quarter were still based in the Alpine provinces or in neighbouring Germania Superior (Upper Rhine area). The rest were scattered all over the empire and would probably have long since lost their ethnic Alpine identity through local recruitment.