Transfusions in Surgery
... • Hypothermia – slows activity of coagulation cascade, increases fibrinolysis and alters platelet function • Dilutional coagulopathy – exacerbated by initial volume contraction, fluid resuscitation and transfusion of factor and platelet-deficient PRBCs • Fibrinogen < 1.0 g/L when blood loss 142% • D ...
... • Hypothermia – slows activity of coagulation cascade, increases fibrinolysis and alters platelet function • Dilutional coagulopathy – exacerbated by initial volume contraction, fluid resuscitation and transfusion of factor and platelet-deficient PRBCs • Fibrinogen < 1.0 g/L when blood loss 142% • D ...
Training - Powerpoint
... proteins are called antigens. The pipe cleaners are the antigens (pink is the “A” antigen, blue is the “B” antigen). Jab a ball with a pink pipe cleaner. This red blood cell now has the “A” antigen and is an A blood cell. Jab a blue pipe cleaner into another red ball. This RBC has a “B” antigen and ...
... proteins are called antigens. The pipe cleaners are the antigens (pink is the “A” antigen, blue is the “B” antigen). Jab a ball with a pink pipe cleaner. This red blood cell now has the “A” antigen and is an A blood cell. Jab a blue pipe cleaner into another red ball. This RBC has a “B” antigen and ...
blood type - studentorg
... proteins are called antigens. The pipe cleaners are the antigens (pink is the “A” antigen, blue is the “B” antigen). Jab a ball with a pink pipe cleaner. This red blood cell now has the “A” antigen and is an A blood cell. Jab a blue pipe cleaner into another red ball. This RBC has a “B” antigen and ...
... proteins are called antigens. The pipe cleaners are the antigens (pink is the “A” antigen, blue is the “B” antigen). Jab a ball with a pink pipe cleaner. This red blood cell now has the “A” antigen and is an A blood cell. Jab a blue pipe cleaner into another red ball. This RBC has a “B” antigen and ...
Sickle Cell Anemia - International Journal of Scientific and Research
... with sickle cell disease are at high risk for septicemia and meningitis with pneumococci and other encapsulated bacteria including Streptococcus pneumonia, Neisseria meningiditis, and Haemophilus influenza. Historically, the single most common cause of death in children with sickle cell disease was ...
... with sickle cell disease are at high risk for septicemia and meningitis with pneumococci and other encapsulated bacteria including Streptococcus pneumonia, Neisseria meningiditis, and Haemophilus influenza. Historically, the single most common cause of death in children with sickle cell disease was ...
Blood - Dr Magrann
... An embryo has lots of stem cells which have not decided to become a nerve cell, muscle cell, liver cell, etc. Stem cells become the type of cell the body needs. The placenta of a newborn infant has many of these stem cells, too, but not as many as an embryo. That’s why people want to research stem ...
... An embryo has lots of stem cells which have not decided to become a nerve cell, muscle cell, liver cell, etc. Stem cells become the type of cell the body needs. The placenta of a newborn infant has many of these stem cells, too, but not as many as an embryo. That’s why people want to research stem ...
AACC JALMTalk Transcript Document
... hemoglobinopathy variant that could cause transfusionrelated harm and two, like any test, there’s always a risk for false negatives and false positives. On the other hand, centers could advocate for the use of high-performance liquid chromatography, but the cost and times run specimens will not be f ...
... hemoglobinopathy variant that could cause transfusionrelated harm and two, like any test, there’s always a risk for false negatives and false positives. On the other hand, centers could advocate for the use of high-performance liquid chromatography, but the cost and times run specimens will not be f ...
56 Facts - Update - Blood Centers of the Pacific
... . Healthy bone marrow makes a constant supply of red cells, plasma and platelets. . Victims of car accidents who have suffered massive blood loss can need transfusions of 50 pints or more of red blood cells. . The average bone marrow transplant requires 120 units of platelets and about 20 units of r ...
... . Healthy bone marrow makes a constant supply of red cells, plasma and platelets. . Victims of car accidents who have suffered massive blood loss can need transfusions of 50 pints or more of red blood cells. . The average bone marrow transplant requires 120 units of platelets and about 20 units of r ...
Some - Uplift Education
... Transplanted tissue / organs Antibodies are proteins produced by white blood cells that bind to and destroy antigens. Antibodies are specific to certain antigens ...
... Transplanted tissue / organs Antibodies are proteins produced by white blood cells that bind to and destroy antigens. Antibodies are specific to certain antigens ...
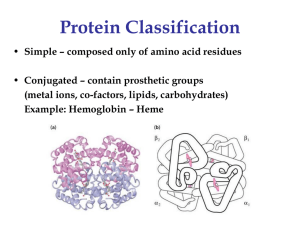
Heme group
... The substitution of a hydrophobic amino acid for a hydrophilic one makes the resulting molecule “sticky.” This is because a hydrophobic patch has been created, which causes molecules to stick together at this point. This causes aggregation to occur in deoxyhemoglobin. Subsequent to strand formation, ...
... The substitution of a hydrophobic amino acid for a hydrophilic one makes the resulting molecule “sticky.” This is because a hydrophobic patch has been created, which causes molecules to stick together at this point. This causes aggregation to occur in deoxyhemoglobin. Subsequent to strand formation, ...
consumer information
... HAPPEN AND WHAT TO DO ABOUT THEM Additional side effects which have been reported more often in chronic renal failure patients than other patients include increases in blood pressure, clotted access, seizures and pure red cell aplasia (PRCA). PRCA is a condition in which severe and sudden anemia (ch ...
... HAPPEN AND WHAT TO DO ABOUT THEM Additional side effects which have been reported more often in chronic renal failure patients than other patients include increases in blood pressure, clotted access, seizures and pure red cell aplasia (PRCA). PRCA is a condition in which severe and sudden anemia (ch ...
Gastrointestinal Hemorrhage
... approach to the pediatric patient with GI bleeding Review the most common etiologies for GI bleeding in pediatric patients in various age groups ...
... approach to the pediatric patient with GI bleeding Review the most common etiologies for GI bleeding in pediatric patients in various age groups ...
Lab 4
... antibodies can cross the placenta and destroy the fetal RBCs leading to fetal death. To prevent this, all Rh- mothers are given RhoGAM, a serum derived product, which can block the mother’s immune system from generating anti-D antibodies by agglutinating the Rh factor that enters her blood stream. I ...
... antibodies can cross the placenta and destroy the fetal RBCs leading to fetal death. To prevent this, all Rh- mothers are given RhoGAM, a serum derived product, which can block the mother’s immune system from generating anti-D antibodies by agglutinating the Rh factor that enters her blood stream. I ...
What are blood types?
... Blood is living tissue that carries oxygen and nutrients to all parts of the body, and carries carbon dioxide and other waste products back to the lungs, kidneys and liver for disposal. It also fights against infection and helps heal wounds, so we can stay healthy. There are about one billion red bl ...
... Blood is living tissue that carries oxygen and nutrients to all parts of the body, and carries carbon dioxide and other waste products back to the lungs, kidneys and liver for disposal. It also fights against infection and helps heal wounds, so we can stay healthy. There are about one billion red bl ...
ppt
... • found in muscles: binds O2 „for storrage“ • higher affinity to oxygen than hemoglobin The figures are found at http://www.virtuallaboratory.net/Biofundamentals/lectureNotes/AllGraphics/myoglobinSurface.jpg and http://courses.washington.edu/conj/protein/hemo.gif (March 2007) ...
... • found in muscles: binds O2 „for storrage“ • higher affinity to oxygen than hemoglobin The figures are found at http://www.virtuallaboratory.net/Biofundamentals/lectureNotes/AllGraphics/myoglobinSurface.jpg and http://courses.washington.edu/conj/protein/hemo.gif (March 2007) ...
Agglutination of an EDTA Blood Sample Caused by an EDTA
... cells from the EDTA specimen could not be interpreted because of spontaneous agglutination. In fact, the EDTA tube appeared like a clotted specimen. This finding was reproducible both on repeat testing and on a repeat sample. The spontaneous agglutination was not dispersed by either cooling the tube ...
... cells from the EDTA specimen could not be interpreted because of spontaneous agglutination. In fact, the EDTA tube appeared like a clotted specimen. This finding was reproducible both on repeat testing and on a repeat sample. The spontaneous agglutination was not dispersed by either cooling the tube ...
Nutrition education material to address iron deficiency anemia in
... that, anemia may worsen with increase inflammatory cytokines (interleukin-1, interkeukin-6, tumor necrosis factor and interferon), which have been shown to alter red blood cell formation in varying ways (in vitro). For instance, tumor necrosis factor-a has been shown to inhibit erthropoiesis in vitr ...
... that, anemia may worsen with increase inflammatory cytokines (interleukin-1, interkeukin-6, tumor necrosis factor and interferon), which have been shown to alter red blood cell formation in varying ways (in vitro). For instance, tumor necrosis factor-a has been shown to inhibit erthropoiesis in vitr ...
Peripheral Nucleated Red Blood Cells in Cats and their Association
... The distribution pattern of continuous parameters was examined using the Shapiro-Wilk test. Continuous parameters were compared between the two groups using Student’s t-test and Mann-Whitney U-test, for normally and nonnormally distributed parameters respectively. Comparison of more than two groups ...
... The distribution pattern of continuous parameters was examined using the Shapiro-Wilk test. Continuous parameters were compared between the two groups using Student’s t-test and Mann-Whitney U-test, for normally and nonnormally distributed parameters respectively. Comparison of more than two groups ...
Blood Type Genetics
... What is blood made up of? Red blood cells (RBCs) contain hemoglobin, a protein that binds oxygen. RBCs transport oxygen to, and remove carbon dioxide from the tissues. The white blood cells include T-Cells, B-Cells and other immune system cells that help fight infections and maintain homeostasis. T ...
... What is blood made up of? Red blood cells (RBCs) contain hemoglobin, a protein that binds oxygen. RBCs transport oxygen to, and remove carbon dioxide from the tissues. The white blood cells include T-Cells, B-Cells and other immune system cells that help fight infections and maintain homeostasis. T ...
What is Blood Type?
... A person with A type blood receives from AB or B donors? A person of O type blood receives from type A, B or AB donors? A person of type AB receives from type A or ...
... A person with A type blood receives from AB or B donors? A person of O type blood receives from type A, B or AB donors? A person of type AB receives from type A or ...
guidelines for transfusion of red blood cells – adults
... progressively conservative approach has been applied to blood transfusion since the publication of the 2004 edition of this guideline. This restraint is due in part to concerns about transmission of new infectious agents/diseases either not previously present in this country, or not considered signi ...
... progressively conservative approach has been applied to blood transfusion since the publication of the 2004 edition of this guideline. This restraint is due in part to concerns about transmission of new infectious agents/diseases either not previously present in this country, or not considered signi ...
Full-Text PDF
... 2. Genome-Wide Association Studies (GWAS) for Blood Cell Phenotypes Before GWAS, little was known about the role of SNPs and other common DNA sequence variants on normal variation in blood cell phenotypes. Candidate gene DNA sequencing experiments have identified mutations in the globin loci, but al ...
... 2. Genome-Wide Association Studies (GWAS) for Blood Cell Phenotypes Before GWAS, little was known about the role of SNPs and other common DNA sequence variants on normal variation in blood cell phenotypes. Candidate gene DNA sequencing experiments have identified mutations in the globin loci, but al ...
Anemia

Anemia or anaemia (/əˈniːmiə/; also spelled anæmia) is usually defined as a decrease in the amount of red blood cells (RBCs) or hemoglobin in the blood. It can also be defined as a lowered ability of the blood to carry oxygen. When anemia comes on slowly the symptoms are often vague and may include: feeling tired, weakness, shortness of breath or a poor ability to exercise. Anemia that comes on quickly often has greater symptoms which may include: confusion, feeling like one is going to pass out, and increased thirst. Anemia must be significant before a person becomes noticeably pale. Additional symptoms may occur depending on the underlying cause.There are three main types of anemia: that due to blood loss, that due to decreased red blood cell production, and that due to increased red blood cell breakdown. Causes of blood loss include trauma and gastrointestinal bleeding, among others. Causes of decreased production include iron deficiency, a lack of vitamin B12, thalassemia and a number of neoplasms of the bone marrow among others. Causes of increased breakdown include a number of genetic conditions such as sickle cell anemia, infections like malaria and some autoimmune diseases among others. It can also be classified based on the size of red blood cells and amount of hemoglobin in each cell. If the cells are small it is microcytic anemia, if they are large it is macrocytic anemia and if they are normal sized it is normocytic anemia. Diagnosis in men is based on a hemoglobin of less than 130 to 140 g/L (13 to 14 g/dL), while in women it must be less than 120 to 130 g/L (12 to 13 g/dL). Further testing is then required to determine the cause.Certain groups of individuals, such as pregnant women, benefit from the use of iron pills for prevention. Dietary supplementation, without determining the specific cause, is not recommended. The use of blood transfusions is typically based on a person's signs and symptoms. In those without symptoms they are not recommended unless hemoglobin levels are less than 60 to 80 g/L (6 to 8 g/dL). These recommendations may also apply to some people with acute bleeding. Erythropoiesis-stimulating medications are only recommended in those with severe anemia.Anemia is the most common disorder of the blood with it affecting about a quarter of people globally. Iron-deficiency anemia affects nearly 1 billion. In 2013 anemia due to iron deficiency resulted in about 183,000 deaths – down from 213,000 deaths in 1990. It is more common in females than males, among children, during pregnancy, and in the elderly. Anemia increases costs of medical care and lowers a person's productivity through a decreased ability to work. The name is derived from Ancient Greek: ἀναιμία anaimia, meaning ""lack of blood"", from ἀν- an-, ""not"" + αἷμα haima, ""blood"".