* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is Blood Type?
Hemolytic-uremic syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Blood sugar level wikipedia , lookup
Autotransfusion wikipedia , lookup
Schmerber v. California wikipedia , lookup
Blood transfusion wikipedia , lookup
Jehovah's Witnesses and blood transfusions wikipedia , lookup
Plateletpheresis wikipedia , lookup
Hemorheology wikipedia , lookup
Blood donation wikipedia , lookup
Men who have sex with men blood donor controversy wikipedia , lookup
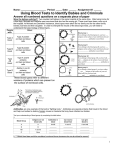
Chapter 11- Blood & Immunity Chapter 11 of your text includes: Blood types Blood parts Blood Clotting Immune System Today’s topic Blood Types A) History of Blood Type! What is Blood Type? In 1901 Karl Landsteiner discovered there were 4 blood types. He called these "A, B, AB, O". Knowledge of blood types helps with transfusions. If they don't match - illness or death could result. Karl Landsteiner An American of Austrian descent He was awarded the Nobel Prize for medicine in 1930 for his work to identify blood types. B) What He observed! Noticed that when some blood was mixed with another it freely intermingled Other times when blood was mixed it would stick in clumps. These clumps are called AGGLUTINATION B) What He observed…. Landsteiner's work saved many lives on the battlefields of WW I Transfusions of compatible blood were first performed on a large scale at this time. C) Why Blood Agglutinates! All cells have protein markers on their membranes called ANTIGENS Each of our cells have unique antigens that identify you as you. That is why when we receive donor organs we sometimes reject them as foreign material. This is called an immune response! C) Why Blood Agglutinates… Red Blood Cells are no different Type A have Antigen A Type B have Antigen B Type AB have both Type O have none SO WHAT? C) Why Blood Agglutinates… Our bodies make Y-shaped ANTIBODIES to attack foreign ANTIGENS. On a first transfusion the blood freely mixes. In the meantime you develop ANTIBODIES The next transfusion with the wrong blood type may be FATAL. D) Blood Donors – Antigens & Antibodies! Universal Donor = type O Blood Possess no antigens to set off an immune response freely mixes with all types of blood (given in the ER) Universal Recipient = type AB Blood Possess both antigens, therefore no immune response will be made can receive blood from anyone. (Who can Type AB donate to?) What blood type can A receive from? B? or O? D) Blood Donors – Antigens & Antibodies! Fill in the following table: E) Inheritance of Blood Type! Both A & B blood are dominant to type O Also type A & B share equal dominance that is why we have people type AB Let’s do a cross: Mom is AA, Dad is BB, what are the kids? Mom is BO, Dad is AO, what are the kids? Dad is AO, Mom is AB, what are the kids? Dad is OO, Mom is OO, what are the kids? F) Sample Problems! 1) 2) 3) 4) State whether the blood mixes or clumps: A person with A type blood receives from AB or B donors? A person of O type blood receives from type A, B or AB donors? A person of type AB receives from type A or O donor? What blood type in the universal donor & recipient? State Why? ALL DONE? F) Sample Problems! 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) Determine the inheritance of blood type! What is the blood type of a child who gets an A from Mom & O from Dad? What is the blood type of a child who gets an A from Dad & B from Mom? What is the blood type of a child who gets an O from both parents? Mom is AA, Dad is AO results? Mom is BB, Dad is BO results? Mom is AB, Dad is OO results? Mom & Dad are AB results? ALL DONE? RH incompatibility test and treatment. a. RH negative women carrying RH positive baby is a problem. b. First pregnancy leads to mother producing antibodies against RH antigens during birth (Blood mixes...). c. Second pregnancy will see antibodies from mom cross the placenta and harm fetal blood cells causing anemia and even death. RH -ve women now given anti RH serum (RHoGAM) after birth to destroy antigens and prevent formation of antibodies. The immune system will attack blood with “foreign” antigens but will ignore the absence of antigens. a. AB+ is a universal recipient b. O- is a universal donor. What Now? Video Immune System: To Defend and Repair Text reading: Chapter 11 p. 270-291 – Brush up on Rh factor for tomorrow Chapter 11 review booklet tomorrow