Reference Tables - Regents to 2011
... A student, wearing chemical safety goggles and a lab apron, is to perform a laboratory test to determine the pH value of two different solutions. The student is given one bottle containing a solution with a pH of 2.0 and another bottle containing a solution with a pH of 5.0. The student is also give ...
... A student, wearing chemical safety goggles and a lab apron, is to perform a laboratory test to determine the pH value of two different solutions. The student is given one bottle containing a solution with a pH of 2.0 and another bottle containing a solution with a pH of 5.0. The student is also give ...
What is it that you can put into a barrel to make the barrel lighter?
... explain the relationship between the atomic number and the mass number of an element, and the difference between isotopes and radioisotopes of an element explain the relationship between isotopic abundance of an element’s isotopes and the relative atomic mass of the element state the periodic law, a ...
... explain the relationship between the atomic number and the mass number of an element, and the difference between isotopes and radioisotopes of an element explain the relationship between isotopic abundance of an element’s isotopes and the relative atomic mass of the element state the periodic law, a ...
Lecture 4
... – The nucleus contains the protons and the neutrons – The electrons are constantly moving around in the electron cloud – In a neutral atom, the number of electrons is equal to the number of protons ...
... – The nucleus contains the protons and the neutrons – The electrons are constantly moving around in the electron cloud – In a neutral atom, the number of electrons is equal to the number of protons ...
Standard Atomic Notation Standard Atomic Notation
... Draw the electrons in their orbits. Only a certain number of electrons can be held in each orbit. • The first orbit can only hold __________ electrons • The second and third orbit can only hold ________ electrons • Although they exist, we will not draw elements with more than three orbits. Extra Rul ...
... Draw the electrons in their orbits. Only a certain number of electrons can be held in each orbit. • The first orbit can only hold __________ electrons • The second and third orbit can only hold ________ electrons • Although they exist, we will not draw elements with more than three orbits. Extra Rul ...
Ionic Bonding
... • Atoms prefer to have a complete outer shell. – One way to accomplish this goal is to form an ionic bond. • Bond that forms when one atom gives up valence electrons and another takes them. ...
... • Atoms prefer to have a complete outer shell. – One way to accomplish this goal is to form an ionic bond. • Bond that forms when one atom gives up valence electrons and another takes them. ...
What are Valence Electrons
... • Valence electrons are electrons that have the highest en______ ergy level and are held most loosely ber of • The num______ valence electrons in an atom of an element determines its perties and the pro________ ways it can bond with other atoms ...
... • Valence electrons are electrons that have the highest en______ ergy level and are held most loosely ber of • The num______ valence electrons in an atom of an element determines its perties and the pro________ ways it can bond with other atoms ...
Chapter 4: Concept 4.2
... the cloud model is helpful. An electron may visit every point around a nucleus over time. Thus you can think of the electron's negative charge as spread out, like a cloud, in all the places the electron might be. In a real atom, the electron cloud is much larger than the nucleus. To give you an idea ...
... the cloud model is helpful. An electron may visit every point around a nucleus over time. Thus you can think of the electron's negative charge as spread out, like a cloud, in all the places the electron might be. In a real atom, the electron cloud is much larger than the nucleus. To give you an idea ...
Chapter 5 Notes
... indivisible particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
... indivisible particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
Unit B: Matter and Chemical Change
... Note: The hydrogen atom has the atomic number of 1 therefore contains 1 electron. This electron is found in the first orbital and has room to gain 1 more electron if it comes in contact with another atom. This would then completely fill the first orbital. Nitrogen’s atom has the atomic number of 7 ...
... Note: The hydrogen atom has the atomic number of 1 therefore contains 1 electron. This electron is found in the first orbital and has room to gain 1 more electron if it comes in contact with another atom. This would then completely fill the first orbital. Nitrogen’s atom has the atomic number of 7 ...
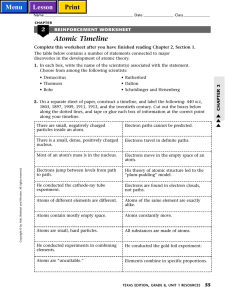
Atomic Timeline
... along the dotted lines, and tape or glue each box of information at the correct point along your timeline. There are small, negatively charged particles inside an atom. 1897 (Thomson) There is a small, dense, positively charged nucleus. 1911 (Rutherford) ...
... along the dotted lines, and tape or glue each box of information at the correct point along your timeline. There are small, negatively charged particles inside an atom. 1897 (Thomson) There is a small, dense, positively charged nucleus. 1911 (Rutherford) ...
AS II Rutherford Model
... NB. mass number ≠ atomic mass (average mass number is not normally used ) General Formula: x1 I1 + x2 I2 + ... = E where, x ...fraction, abundance; x1 +x2 + ... = 1 I atomic mass of isotope E ... atomic mass of “element” ...
... NB. mass number ≠ atomic mass (average mass number is not normally used ) General Formula: x1 I1 + x2 I2 + ... = E where, x ...fraction, abundance; x1 +x2 + ... = 1 I atomic mass of isotope E ... atomic mass of “element” ...
Atomic Masses
... Dalton’s atomic theory. Identify the parts of an atom, their location, charge, and relative mass. Determine the numbers of subatomic particles in an atom. ...
... Dalton’s atomic theory. Identify the parts of an atom, their location, charge, and relative mass. Determine the numbers of subatomic particles in an atom. ...
Atoms and Elements: Are they Related?
... Electron Cloud Model Electrons travel in regions of various thicknesses ...
... Electron Cloud Model Electrons travel in regions of various thicknesses ...
Atomic number
... Modern Reassessment of the Atomic Theory 1. All matter is composed of atoms. Although atoms are composed of smaller particles (electrons, protons, and neutrons), the atom is the smallest body that retains the unique identity of the element. 2. Atoms of one element cannot be converted into atoms of ...
... Modern Reassessment of the Atomic Theory 1. All matter is composed of atoms. Although atoms are composed of smaller particles (electrons, protons, and neutrons), the atom is the smallest body that retains the unique identity of the element. 2. Atoms of one element cannot be converted into atoms of ...
specimen
... The number of marks is given in brackets [ ] at the end of each question or part question. ...
... The number of marks is given in brackets [ ] at the end of each question or part question. ...
Carbon Isotopes
... A new element The original radioisotope is always referred to as the parent nuclide (the unstable nucleus), and the resulting isotope as the daughter nuclide. Many radioactive elements decay as part of a decay chain, in which the original parent nuclide forms an unstable daughter nuclide, which al ...
... A new element The original radioisotope is always referred to as the parent nuclide (the unstable nucleus), and the resulting isotope as the daughter nuclide. Many radioactive elements decay as part of a decay chain, in which the original parent nuclide forms an unstable daughter nuclide, which al ...
The Atom - Effingham County Schools
... Law of definite proportions: a chemical compound contains the same elements in exactly the same proportions by mass regardless of the size of the sample or source of the compound ...
... Law of definite proportions: a chemical compound contains the same elements in exactly the same proportions by mass regardless of the size of the sample or source of the compound ...
Chapter 1
... *Notes- The ______mass number_____________ of an atom is the sum of the protons and the neutrons. *Notes-An atom of boron has 5 protons, 6 neutrons, and 5 electrons. It mass number will be _____11_________. (5 protons + 6 neutrons) C. Naming Isotopes *Notes-The element copper has two isotopes, coppe ...
... *Notes- The ______mass number_____________ of an atom is the sum of the protons and the neutrons. *Notes-An atom of boron has 5 protons, 6 neutrons, and 5 electrons. It mass number will be _____11_________. (5 protons + 6 neutrons) C. Naming Isotopes *Notes-The element copper has two isotopes, coppe ...
The study of chemistry involves the linking up of the phenomena in
... This time he saw a red fluorescence in the tube as well as a green fluorescence. The green fluorescence was caused by electrons. The red glow was caused by rays which were deflected by magnetic and electric fields in the direction opposite to electrons. Thomson called these rays positive rays. The m ...
... This time he saw a red fluorescence in the tube as well as a green fluorescence. The green fluorescence was caused by electrons. The red glow was caused by rays which were deflected by magnetic and electric fields in the direction opposite to electrons. Thomson called these rays positive rays. The m ...
Unit 3 Review Packet
... ________________________. The ability to be shaped into thin wires is known as ___________________________________. These elements have both properties of metals and non-metals; ______________________________________. The amount of matter in a substance. ...
... ________________________. The ability to be shaped into thin wires is known as ___________________________________. These elements have both properties of metals and non-metals; ______________________________________. The amount of matter in a substance. ...
Subatomic Particles - Parkway C-2
... and he said that this gave an element its identity! He rearranged the periodic table according to atomic number, and not according to atomic mass! This cleared up any irregular patterns that were found in the periodic table from before! ...
... and he said that this gave an element its identity! He rearranged the periodic table according to atomic number, and not according to atomic mass! This cleared up any irregular patterns that were found in the periodic table from before! ...
Atoms = basic unit of matter
... Isotope atoms of the same element with different # of neutrons Often identify an element by mass number Example: carbon-12, carbon-14 Atomic Mass Atomic masses shown on the PT (periodic table) represent a weighted average based on the relative abundance of each isotope of a particular ato ...
... Isotope atoms of the same element with different # of neutrons Often identify an element by mass number Example: carbon-12, carbon-14 Atomic Mass Atomic masses shown on the PT (periodic table) represent a weighted average based on the relative abundance of each isotope of a particular ato ...