
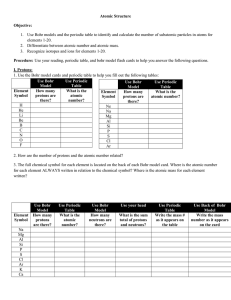
Periodic Properties of the Elements
... Melting and boiling points increase with increasing atomic number ...
... Melting and boiling points increase with increasing atomic number ...
Name: Date: ______ Period: _____ Chemistry 1st semester final
... 40. What type of elements is found in the lower left hand part of the periodic table?metals 41. Where are metalloids found on the periodic table?Along the dark (or red) stair case line 42. From which orbital in a lithium atom is an electron transferred to form Li ion? Looses electrons from 2s 43. Wh ...
... 40. What type of elements is found in the lower left hand part of the periodic table?metals 41. Where are metalloids found on the periodic table?Along the dark (or red) stair case line 42. From which orbital in a lithium atom is an electron transferred to form Li ion? Looses electrons from 2s 43. Wh ...
Atomic Structure_Bohr Flashcards
... 8. a. Compare the number of protons and neutrons in H-1 to H-2 to H-3. List any similarities and differences. b. Compare the number of protons and neutrons in C-12 to C-13 to C-14. List any similarities and differences. ...
... 8. a. Compare the number of protons and neutrons in H-1 to H-2 to H-3. List any similarities and differences. b. Compare the number of protons and neutrons in C-12 to C-13 to C-14. List any similarities and differences. ...
GED Chemistry Note 1[Atoms, Molecules and their properties]
... GED Chemistry Note 1[Atoms, Molecules and their properties] What is Atom? An atom is the smallest constituent unit of ordinary matter that has the properties of a chemical element. Every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Atoms are very small; typical sizes are a ...
... GED Chemistry Note 1[Atoms, Molecules and their properties] What is Atom? An atom is the smallest constituent unit of ordinary matter that has the properties of a chemical element. Every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Atoms are very small; typical sizes are a ...
atomic number
... • all symbols must either be one capital letter, or one capital and one lowercase. •atomic number = number of p+. Written in bottomleft-hand corner of symbol. Identifies the element. •mass number = number of p+ & n0. Identifies the isotope. Written in top-left-hand corner. •average atomic mass = wei ...
... • all symbols must either be one capital letter, or one capital and one lowercase. •atomic number = number of p+. Written in bottomleft-hand corner of symbol. Identifies the element. •mass number = number of p+ & n0. Identifies the isotope. Written in top-left-hand corner. •average atomic mass = wei ...
Fall 2015 Review-2
... ____ 40. Using the table list the following elements in order of increasing ionization energy a. F, O, Ca c. O, F, Ca b. O, Ca, F d. Ca, O, F ____ 41. Using the table list the following elements in order of decreasing atomic size. a. S, Se, Rb c. Rb, S, Se b. Rb, Se, S d. Se, Rb, S ____ 42. Using th ...
... ____ 40. Using the table list the following elements in order of increasing ionization energy a. F, O, Ca c. O, F, Ca b. O, Ca, F d. Ca, O, F ____ 41. Using the table list the following elements in order of decreasing atomic size. a. S, Se, Rb c. Rb, S, Se b. Rb, Se, S d. Se, Rb, S ____ 42. Using th ...
atoms
... • What makes an atom of one element different from an atom of another element: A characteristic number of protons of the atoms. • Atomic number: The number of protons in the nucleus. It is written as a subscript BEFORE the symbol. • Mass number: The total number of protons and neutrons in the atom. ...
... • What makes an atom of one element different from an atom of another element: A characteristic number of protons of the atoms. • Atomic number: The number of protons in the nucleus. It is written as a subscript BEFORE the symbol. • Mass number: The total number of protons and neutrons in the atom. ...
3. Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
... clearly for the first time the existence of atoms. This was necessary to explain the fixed properties of an element. Third postulate was necessary to explain the existence of compounds and the breaking of compounds into elements. Fourth postulate was necessary to define and describe the chemical rea ...
... clearly for the first time the existence of atoms. This was necessary to explain the fixed properties of an element. Third postulate was necessary to explain the existence of compounds and the breaking of compounds into elements. Fourth postulate was necessary to define and describe the chemical rea ...
Unit 6 Naming Binary Compounds
... An oxidation number is a positive or negative number assigned to an atom to indicate its degree of oxidation or reduction. ...
... An oxidation number is a positive or negative number assigned to an atom to indicate its degree of oxidation or reduction. ...
File
... The normal atom (also called a stable atom) has three main parts (or particles) that we are concerned with; protons, neutrons, and electrons. A fourth part, the nucleus, is often referred to but we are not focusing on it as much as we are on protons, neutrons, and electrons. The nucleus is the centr ...
... The normal atom (also called a stable atom) has three main parts (or particles) that we are concerned with; protons, neutrons, and electrons. A fourth part, the nucleus, is often referred to but we are not focusing on it as much as we are on protons, neutrons, and electrons. The nucleus is the centr ...
Powerpoint Review
... *Rutherford proved the atom had a very dense core by his gold foil experiment. Investigating further, scientists discovered that an atom consisted of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, and electrons that orbit around that nucleus ...
... *Rutherford proved the atom had a very dense core by his gold foil experiment. Investigating further, scientists discovered that an atom consisted of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, and electrons that orbit around that nucleus ...
Unit 1 Problem Set
... observable quantity of the element has never been achieved, and may well never be. This is because meitnerium decays very rapidly. (a) Suggest the electron configuration of the ground-state atom of the element. ...
... observable quantity of the element has never been achieved, and may well never be. This is because meitnerium decays very rapidly. (a) Suggest the electron configuration of the ground-state atom of the element. ...
Ch 4 Powerpoint
... Electrons are the parts of atoms that “intermingle” when atoms combine to form molecules. It is the number of electrons that really determines ...
... Electrons are the parts of atoms that “intermingle” when atoms combine to form molecules. It is the number of electrons that really determines ...
Atom? - Its All about the Science
... Atomic Theory: Like charges repel so the nucleus must have a positive charge. If electrons have a negative charge they could not be in a positively charged nucleus. Electrons must surround the nucleus at a distance. Result: The diameter of the nucleus is 100,000 times smaller than the diameter of th ...
... Atomic Theory: Like charges repel so the nucleus must have a positive charge. If electrons have a negative charge they could not be in a positively charged nucleus. Electrons must surround the nucleus at a distance. Result: The diameter of the nucleus is 100,000 times smaller than the diameter of th ...
Atomic Structure
... 4. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated from each other, joined, or rearranged in different combinations. Atoms of one element are never changed into atoms of another element as a result of a chemical reaction. ...
... 4. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated from each other, joined, or rearranged in different combinations. Atoms of one element are never changed into atoms of another element as a result of a chemical reaction. ...
Week 6 Review 2014-15
... • Pure substance: matter that has a fixed (constant) composition and unique properties. Contains only 1 type element or compound; homogeneous ...
... • Pure substance: matter that has a fixed (constant) composition and unique properties. Contains only 1 type element or compound; homogeneous ...
Study Guide 1-3
... Rubidium has two common isotopes, 85Rb and 87Rb. If the abundance of Rubidium-85 is 72.20% with an atomic mass of 84.91g, and the abundance of Rubidium-87 is 27.80% with an atomic mass of 86.91 g, what is the average atomic mass of Rubidium? ...
... Rubidium has two common isotopes, 85Rb and 87Rb. If the abundance of Rubidium-85 is 72.20% with an atomic mass of 84.91g, and the abundance of Rubidium-87 is 27.80% with an atomic mass of 86.91 g, what is the average atomic mass of Rubidium? ...
Chapter 2
... Valence electrons: in the outermost shell, or valence shell Elements with full valence shell are chemically inert Chemical behavior of atom determined by distribution of electrons in electron shells, MOSTLY by valence electrons ...
... Valence electrons: in the outermost shell, or valence shell Elements with full valence shell are chemically inert Chemical behavior of atom determined by distribution of electrons in electron shells, MOSTLY by valence electrons ...
General Chemistry/Atomic Structure/History of Atomic Structure
... theory was the ancient Greek thinker Democritus. He proposed the existence of indivisible atoms as a response to the arguments of Parmenides, and the paradoxes of Zeno. Parmenides argued against the possibility of movement, change, and plurality on the premise that something cannot come from nothing ...
... theory was the ancient Greek thinker Democritus. He proposed the existence of indivisible atoms as a response to the arguments of Parmenides, and the paradoxes of Zeno. Parmenides argued against the possibility of movement, change, and plurality on the premise that something cannot come from nothing ...
Chemistry Mid-Term Review Sheet
... 15. List the SI units for the following quantities: length, mass, temperature, time, amount of substance, luminous intensity, and electric current. 16. How many significant figures are in the following numbers: a. 702000m b. 40 crayons c. 0.00630100g d. 170.4380s 17. Convert 14.8g to micrograms. 18. ...
... 15. List the SI units for the following quantities: length, mass, temperature, time, amount of substance, luminous intensity, and electric current. 16. How many significant figures are in the following numbers: a. 702000m b. 40 crayons c. 0.00630100g d. 170.4380s 17. Convert 14.8g to micrograms. 18. ...
Trends of period 3
... Members of group 7 lower down the group are solids, while those such as Bromine near the middle are liquid and Fluorine & Chlorine near the top are gases at room temperature. Explain this graded change of state from solid to gas? ...
... Members of group 7 lower down the group are solids, while those such as Bromine near the middle are liquid and Fluorine & Chlorine near the top are gases at room temperature. Explain this graded change of state from solid to gas? ...

![GED Chemistry Note 1[Atoms, Molecules and their properties]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015791288_1-b34903533007e866662649e94180f015-300x300.png)




















