Atomic
... To find the AVERAGE # of Neutrons in the atom • Round the atomic mass to a whole # • Subtract the # of protons (also the atomic #) • The difference is the average # of neutrons in the nucleus. ...
... To find the AVERAGE # of Neutrons in the atom • Round the atomic mass to a whole # • Subtract the # of protons (also the atomic #) • The difference is the average # of neutrons in the nucleus. ...
Atomic Theory, Mole Relationships, Percent Compositions, and
... (different elements have a different number of protons). This number defines the atom. Mass Number: Protons + Neutrons Isotopes: atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. Ion: atom that has gained or lost 1 or more electrons. Ex: Na+ has a charge of +1 because it has lost 1 ...
... (different elements have a different number of protons). This number defines the atom. Mass Number: Protons + Neutrons Isotopes: atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. Ion: atom that has gained or lost 1 or more electrons. Ex: Na+ has a charge of +1 because it has lost 1 ...
Chapter #4 Section Assessment #1 - 33
... Is everything he said here still believed to be true? ii) Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of another element. Is everything he said here still believed to be true? iii) Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemi ...
... Is everything he said here still believed to be true? ii) Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of another element. Is everything he said here still believed to be true? iii) Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemi ...
Chapter 2 Expanded Notes
... The Atomic Number: This is more important for chemistry. Note as mentioned earlier that atoms are classified into elements based on certain characteristics, which we call identity, and they retain this identity through chemical reactions. Atoms of one element are different from atoms of another ele ...
... The Atomic Number: This is more important for chemistry. Note as mentioned earlier that atoms are classified into elements based on certain characteristics, which we call identity, and they retain this identity through chemical reactions. Atoms of one element are different from atoms of another ele ...
Answers - Dr Terry Dwyer National Curriculum mathematics and
... silicon is 28.085, which isotope is the most abundant? {Abundant means large quantity} ...
... silicon is 28.085, which isotope is the most abundant? {Abundant means large quantity} ...
Review
... 5. What is the average atomic mass of silicon if 92.21 % of its atoms have a mass of 27.977 amu, 4.07 % have a mass of 28.976 amu, and 3.09 % have a mass of 29.974 amu? ...
... 5. What is the average atomic mass of silicon if 92.21 % of its atoms have a mass of 27.977 amu, 4.07 % have a mass of 28.976 amu, and 3.09 % have a mass of 29.974 amu? ...
Section 2: “The Structure of Atoms
... hold a maximum of 2 electrons. Each “p” orbital is shaped like a bar bell. There are 3 different types that can each hold 2 electrons. The “p” orbital, therefore, can hold up to 6 electrons. “d” and “f” orbitals are more complex. There are 5 types of “d” orbitals and 7 types of “f” orbitals each tha ...
... hold a maximum of 2 electrons. Each “p” orbital is shaped like a bar bell. There are 3 different types that can each hold 2 electrons. The “p” orbital, therefore, can hold up to 6 electrons. “d” and “f” orbitals are more complex. There are 5 types of “d” orbitals and 7 types of “f” orbitals each tha ...
04_Lecture Atoms and Elements
... • When an atom gains or loses electrons, it becomes an ion. • Positively charged ions are called cations. • Negatively charged ions are called anions. • Cations and anions occur together so that matter is chargeneutral. Isotopes: • Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons are cal ...
... • When an atom gains or loses electrons, it becomes an ion. • Positively charged ions are called cations. • Negatively charged ions are called anions. • Cations and anions occur together so that matter is chargeneutral. Isotopes: • Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons are cal ...
04_Lecture Atoms and Elements
... • When an atom gains or loses electrons, it becomes an ion. • Positively charged ions are called cations. • Negatively charged ions are called anions. • Cations and anions occur together so that matter is chargeneutral. Isotopes: • Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons are cal ...
... • When an atom gains or loses electrons, it becomes an ion. • Positively charged ions are called cations. • Negatively charged ions are called anions. • Cations and anions occur together so that matter is chargeneutral. Isotopes: • Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons are cal ...
Symbols of Elements - Chemistry with Mr. Patmos
... He then arranged columns so that elements with most similar properties were next to each other – First Periodic table Blank spaces left bc/ no known elements with mass and properties that fit ...
... He then arranged columns so that elements with most similar properties were next to each other – First Periodic table Blank spaces left bc/ no known elements with mass and properties that fit ...
4.1 PPT- Atomic Theory and Bonding
... The noble gases are stable because they have FULL outer shells of electrons. They don’t need to lose or gain any e-s. Atoms in each period want to have the same number of electrons in their outer shell (VALENCE ELECTRONS) as the noble gases on the end of their period. ...
... The noble gases are stable because they have FULL outer shells of electrons. They don’t need to lose or gain any e-s. Atoms in each period want to have the same number of electrons in their outer shell (VALENCE ELECTRONS) as the noble gases on the end of their period. ...
with answers
... Foreign students may use a dictionary (mother tongue – English) but this may not contain any handwritten notes. The use of a calculator is not permitted. Numerical answers that are given without showing any working or explanation will receive no marks. In general, short answers with keywords will be ...
... Foreign students may use a dictionary (mother tongue – English) but this may not contain any handwritten notes. The use of a calculator is not permitted. Numerical answers that are given without showing any working or explanation will receive no marks. In general, short answers with keywords will be ...
FE Exam review for Chemistry
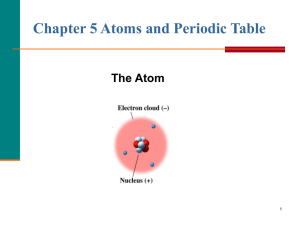
... The modern atomic model? Prior to the modern atomic model (proved by Rutherford in the goldfoil experiment no one knew how subatomic particles were arranged. Rutherford proved that protons & neutrons form a central nucleus, and that electrons surrounded the nucleus in a diffuse cloud. The Bohr or pl ...
... The modern atomic model? Prior to the modern atomic model (proved by Rutherford in the goldfoil experiment no one knew how subatomic particles were arranged. Rutherford proved that protons & neutrons form a central nucleus, and that electrons surrounded the nucleus in a diffuse cloud. The Bohr or pl ...
4.1 Experiencing Atoms at Tiburon 4.1 Experiencing Atoms
... • The nuclei of some isotopes of a given element are not stable. • These atoms emit a few energetic subatomic particles from their nuclei and change into different isotopes of different elements. • The emitted subatomic particles are called nuclear radiation. • The isotopes that emit them are te ...
... • The nuclei of some isotopes of a given element are not stable. • These atoms emit a few energetic subatomic particles from their nuclei and change into different isotopes of different elements. • The emitted subatomic particles are called nuclear radiation. • The isotopes that emit them are te ...
Chapter 4 Atoms and Elements
... • When an atom gains or loses electrons, it becomes an ion. • Positively charged ions are called cations. • Negatively charged ions are called anions. • Cations and anions occur together so that matter is chargeneutral. Isotopes: • Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons are cal ...
... • When an atom gains or loses electrons, it becomes an ion. • Positively charged ions are called cations. • Negatively charged ions are called anions. • Cations and anions occur together so that matter is chargeneutral. Isotopes: • Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons are cal ...
Document
... steer the particles into each other or into a fixed target. Observing these particles is a difficult task because they are too small to be seen by the human eye. To do this, researchers have designed and built special detectors to monitor and record particle interactions. With these detectors, scien ...
... steer the particles into each other or into a fixed target. Observing these particles is a difficult task because they are too small to be seen by the human eye. To do this, researchers have designed and built special detectors to monitor and record particle interactions. With these detectors, scien ...
Matter - GEOCITIES.ws
... Therefor, a dead plant after 5800 years will have only half as much C-14 as a living plant. Thus by knowing the ratio of C-14 and C-12 in the living as well as the dead plant, we can determine how long back the plant died. This technique is known as radio isotope dating or radio carbon dating. Isoto ...
... Therefor, a dead plant after 5800 years will have only half as much C-14 as a living plant. Thus by knowing the ratio of C-14 and C-12 in the living as well as the dead plant, we can determine how long back the plant died. This technique is known as radio isotope dating or radio carbon dating. Isoto ...
atoms
... Charge of 1Mass of 1/1836 of a p+ Equal to the number of protons The outermost shell of electrons is called the VALENCE SHELL which holds the VALENCE ELECTRONS. ...
... Charge of 1Mass of 1/1836 of a p+ Equal to the number of protons The outermost shell of electrons is called the VALENCE SHELL which holds the VALENCE ELECTRONS. ...
Name __KEY____________ Per. ______ Polarity and
... Polarity and Stoichiometry Review When examining trends in the periodic table, as we move towards the top-right the elements have a greater _electronegativity_ (atomic radius/ electronegativity), which is a measure of how much they want to _ hold onto_ (hold onto/ let go of) their electrons. For any ...
... Polarity and Stoichiometry Review When examining trends in the periodic table, as we move towards the top-right the elements have a greater _electronegativity_ (atomic radius/ electronegativity), which is a measure of how much they want to _ hold onto_ (hold onto/ let go of) their electrons. For any ...
Symbols of Elements
... • of an element is electrically neutral; the net charge of an atom is zero. • has an equal number of protons and electrons. number of protons = number of electrons Aluminum has 13 protons and 13 electrons. The net (overall) charge is zero. 13 protons (13+) + 13 electrons (13 -) = 0 ...
... • of an element is electrically neutral; the net charge of an atom is zero. • has an equal number of protons and electrons. number of protons = number of electrons Aluminum has 13 protons and 13 electrons. The net (overall) charge is zero. 13 protons (13+) + 13 electrons (13 -) = 0 ...
Chapter 4 Review Packet Section 4.1
... According to the prevailing theory, the alpha particles should have passed easily through the gold, with only a slight deflection due to the positive charge thought to be spread out in the gold atoms. Rutherford’s results were that most alpha particles went straight through, or were slightly deflect ...
... According to the prevailing theory, the alpha particles should have passed easily through the gold, with only a slight deflection due to the positive charge thought to be spread out in the gold atoms. Rutherford’s results were that most alpha particles went straight through, or were slightly deflect ...