Period:______ Table Number
... 46. The smallest particle of any element that you can have which still possesses all of the physical and chemical properties of that element is a single ATOM of that element. P. 10, VCR: Atoms and Molecules 47. Nearly 2000 years ago the Greek philosopher DEMOCRITUS gave us the word atom when he said ...
... 46. The smallest particle of any element that you can have which still possesses all of the physical and chemical properties of that element is a single ATOM of that element. P. 10, VCR: Atoms and Molecules 47. Nearly 2000 years ago the Greek philosopher DEMOCRITUS gave us the word atom when he said ...
Chapter 3-3—Parts of the Atom - Phoenix Union High School District
... Atoms have a center or core called a nucleus The nucleus contains 2 subatomic particles: Proton that has a positive charge Neutron that has a NEUTRAL charge Protons and neutrons together are called nucleons because they are in the nucleus The nucleus is surrounded by a cloud of very tiny particle ...
... Atoms have a center or core called a nucleus The nucleus contains 2 subatomic particles: Proton that has a positive charge Neutron that has a NEUTRAL charge Protons and neutrons together are called nucleons because they are in the nucleus The nucleus is surrounded by a cloud of very tiny particle ...
Document
... • More than 97% of the mass of most organisms comprises just six elements (O, C, H, N, P and S). These are the most important elements for life • Carbon is the most common element in the solid components of cells. • The next most important ions are Na+, Mg2+, K+, Ca2+, and Cl– . • The other required ...
... • More than 97% of the mass of most organisms comprises just six elements (O, C, H, N, P and S). These are the most important elements for life • Carbon is the most common element in the solid components of cells. • The next most important ions are Na+, Mg2+, K+, Ca2+, and Cl– . • The other required ...
Identify the following properties as either - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
... 4. Describe the difference between a natural law and a theory. Natural law – describes events in nature laws do not change laws of nature will always occur and are not man-made Theory – an explanation of an event theories can change as new evidence is discovered. theories are man-made A theory does ...
... 4. Describe the difference between a natural law and a theory. Natural law – describes events in nature laws do not change laws of nature will always occur and are not man-made Theory – an explanation of an event theories can change as new evidence is discovered. theories are man-made A theory does ...
Chapter 18: The Representative Elements
... ns2np5 (n is the period number). In its elemental state, all halogens atoms combine to form diatomic molecules (ex. F2,I2,…). With the exception of F, the halogens can also lose valence electrons and their oxidation states can range from -1 to +7. Chapter 18: The Representative Elements ...
... ns2np5 (n is the period number). In its elemental state, all halogens atoms combine to form diatomic molecules (ex. F2,I2,…). With the exception of F, the halogens can also lose valence electrons and their oxidation states can range from -1 to +7. Chapter 18: The Representative Elements ...
Chapter 18: The Representative Elements The Representative
... ns2np5 (n is the period number). In its elemental state, all halogens atoms combine to form diatomic molecules (ex. F2,I2,…). With the exception of F, the halogens can also lose valence electrons and their oxidation states can range from -1 to +7. Chapter 18: The Representative Elements ...
... ns2np5 (n is the period number). In its elemental state, all halogens atoms combine to form diatomic molecules (ex. F2,I2,…). With the exception of F, the halogens can also lose valence electrons and their oxidation states can range from -1 to +7. Chapter 18: The Representative Elements ...
Radioactive Decay Mechanisms
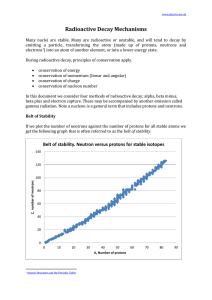
... Note that 1. there are no stable nuclei with an atomic number of 84 or greater. 2. for smaller atoms the ratio neutrons:protons is 1:1 3. for larger atoms the ratio of neutrons:protons approaches about 1.5:1 Since the strong nuclear force weakens significantly with distance, as the atom gets bigger. ...
... Note that 1. there are no stable nuclei with an atomic number of 84 or greater. 2. for smaller atoms the ratio neutrons:protons is 1:1 3. for larger atoms the ratio of neutrons:protons approaches about 1.5:1 Since the strong nuclear force weakens significantly with distance, as the atom gets bigger. ...
File - Rogers` Honors Chemistry
... unknown. Therefore, if one of these two values were to be discovered, the other could easily be calculated. Millikan and his then graduate student Harvey Fletcher used the oil-drop experiment to measure the charge of the electron (as well as the electron mass, and Avogadro’s number, since their rela ...
... unknown. Therefore, if one of these two values were to be discovered, the other could easily be calculated. Millikan and his then graduate student Harvey Fletcher used the oil-drop experiment to measure the charge of the electron (as well as the electron mass, and Avogadro’s number, since their rela ...
Recommended Lesson PlansCOMPREHENSIVE SCIENCE
... 2) Compare particle mass and charge. 3) Define mass number, atomic number, and atomic mass. 4) Present chemical symbols. 5) Explain periodic table shorthand. HSTI Resources: 1) Student Handouts: Neutrons, Protons, Electrons; Atomic Structure; Structure and Size of an Atom 2) Student Activities: a) W ...
... 2) Compare particle mass and charge. 3) Define mass number, atomic number, and atomic mass. 4) Present chemical symbols. 5) Explain periodic table shorthand. HSTI Resources: 1) Student Handouts: Neutrons, Protons, Electrons; Atomic Structure; Structure and Size of an Atom 2) Student Activities: a) W ...
notes-part-1
... describing known substances and discovering new compounds. Applied chemistry is the search for uses for chemical substances. New chemicals are being discovered or produced every day. Isotopes and Atomic Mass . Investigations conducted as long ago as the late 1700's revealed that atoms of different e ...
... describing known substances and discovering new compounds. Applied chemistry is the search for uses for chemical substances. New chemicals are being discovered or produced every day. Isotopes and Atomic Mass . Investigations conducted as long ago as the late 1700's revealed that atoms of different e ...
Powerpoint slides
... • The Greek symbol indicates summing of terms. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... • The Greek symbol indicates summing of terms. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Chapter 3—Time and Geology
... b. Radiometric dating works differently on Earth than it does on other planets. c. The Earth formed from a collision of a meteorite with the Moon. d. The Earth is geologically active and older rocks may have been altered and converted to other rocks by geologic processes such as erosion, metamorphis ...
... b. Radiometric dating works differently on Earth than it does on other planets. c. The Earth formed from a collision of a meteorite with the Moon. d. The Earth is geologically active and older rocks may have been altered and converted to other rocks by geologic processes such as erosion, metamorphis ...
Chapter 2 - My Teacher Site
... can form – This bonding capacity is called an atom’s valence – It usually equals the number of unpaired electrons required to complete the atom’s outermost (valence) shell • Ex) Oxygen, with 6 electrons in its outermost shell, has a valence of 2 ...
... can form – This bonding capacity is called an atom’s valence – It usually equals the number of unpaired electrons required to complete the atom’s outermost (valence) shell • Ex) Oxygen, with 6 electrons in its outermost shell, has a valence of 2 ...
C. - Taylor County Schools
... terms of relative charge and mass. • Describe the structure of the atom, including the locations of the subatomic particles. ...
... terms of relative charge and mass. • Describe the structure of the atom, including the locations of the subatomic particles. ...
Electron
... Atoms either share or give/take electrons. Atoms work together to become stable and fill their energy shells. Example: Covalent bond – HCl Oxidation numbers: H= +1 Cl = -1 Cl ...
... Atoms either share or give/take electrons. Atoms work together to become stable and fill their energy shells. Example: Covalent bond – HCl Oxidation numbers: H= +1 Cl = -1 Cl ...
Quarterly 1 Review Trupia - Trupia
... electrons present in the fifth energy level (shell)? ____60. Which element forms an ion that is larger (1) Sb (3) I than its atom? (2) Bi (4) Br (1) aluminum (3) magnesium (2) chlorine (4) sodium ____54. Lithium and potassium have similar chemical properties because the atoms of both ____61. As the ...
... electrons present in the fifth energy level (shell)? ____60. Which element forms an ion that is larger (1) Sb (3) I than its atom? (2) Bi (4) Br (1) aluminum (3) magnesium (2) chlorine (4) sodium ____54. Lithium and potassium have similar chemical properties because the atoms of both ____61. As the ...
atomic number - cloudfront.net
... • Democritus proposed that all the matter is composed of tiny particles called “Atomos” – These “particles” were thought to be indivisible ...
... • Democritus proposed that all the matter is composed of tiny particles called “Atomos” – These “particles” were thought to be indivisible ...
February Homework Packet
... Rutherford’s gold foil experiment concluded that the atom had a positively charged nucleus and that the atom is mostly empty space The Bohr model suggests that electrons travel in circular orbits The wave-mechanical model of the atom claims that electrons exist in orbitals, regions with high p ...
... Rutherford’s gold foil experiment concluded that the atom had a positively charged nucleus and that the atom is mostly empty space The Bohr model suggests that electrons travel in circular orbits The wave-mechanical model of the atom claims that electrons exist in orbitals, regions with high p ...
Chapter 1.1 –Chemistry is a Physical Science Chemistry is one of
... • Ice melting, water freezing, water evaporating, and steam condensing are all examples of a state change. • These are physical changes, not chemical. • Diluting a solution is a physical change, even if the color becomes fainter. ...
... • Ice melting, water freezing, water evaporating, and steam condensing are all examples of a state change. • These are physical changes, not chemical. • Diluting a solution is a physical change, even if the color becomes fainter. ...
Chapter 3 Notes
... • Democritus proposed that all the matter is composed of tiny particles called “Atomos” – These “particles” were thought to be indivisible ...
... • Democritus proposed that all the matter is composed of tiny particles called “Atomos” – These “particles” were thought to be indivisible ...
atoms of different elements differ in size, mass
... Cathode rays have identical properties regardless of the element used to produce them. All elements must contain identically charged electrons. Atoms are neutral, so there must be positive particles in the atom to balance the negative charge of the electrons Electrons have so little mass that a ...
... Cathode rays have identical properties regardless of the element used to produce them. All elements must contain identically charged electrons. Atoms are neutral, so there must be positive particles in the atom to balance the negative charge of the electrons Electrons have so little mass that a ...
Chapter 4—Student Reading Parts of the atom http://www
... up the element. The mass of the atoms is based on the protons, neutrons, and electrons of the atoms. The mass of the proton and neutron are about the same but the mass of the electron is much smaller (about 1/2000 the mass of the proton or neutron). The vast majority of the atomic mass is contribute ...
... up the element. The mass of the atoms is based on the protons, neutrons, and electrons of the atoms. The mass of the proton and neutron are about the same but the mass of the electron is much smaller (about 1/2000 the mass of the proton or neutron). The vast majority of the atomic mass is contribute ...
Chapter 4 and 25 Study Guide
... 22. How is the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom calculated? Mass number – atomic number =number of neutrons 23. How many neutrons are in 17O? What does the 17 represent? 17 represents mass number; oxygen has atomic number of 8 (17-8 = 9 neutrons) 24. What is mass defect? The mass lost in ...
... 22. How is the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom calculated? Mass number – atomic number =number of neutrons 23. How many neutrons are in 17O? What does the 17 represent? 17 represents mass number; oxygen has atomic number of 8 (17-8 = 9 neutrons) 24. What is mass defect? The mass lost in ...
Flavors of the Atom
... discovered could be decomposed into one of a handful of unique substances that could not themselves be decomposed. The called those hand full of cornerstone substances elements. Between the early 1700’s and mid 1800’s chemists sought out and found over 50 of those those essential substances. At we f ...
... discovered could be decomposed into one of a handful of unique substances that could not themselves be decomposed. The called those hand full of cornerstone substances elements. Between the early 1700’s and mid 1800’s chemists sought out and found over 50 of those those essential substances. At we f ...
Atomic
... To find the AVERAGE # of Neutrons in the atom • Round the atomic mass to a whole # • Subtract the # of protons (also the atomic #) • The difference is the average # of neutrons in the nucleus. ...
... To find the AVERAGE # of Neutrons in the atom • Round the atomic mass to a whole # • Subtract the # of protons (also the atomic #) • The difference is the average # of neutrons in the nucleus. ...