Unit 2
... A. This term refers to atoms of an element that have different masses (AMUs) because they have different numbers of neutrons within the atom; even though it is the same element because they have the same number of protons. (Remember, protons identify the element.) 1. The isotopes behave relatively t ...
... A. This term refers to atoms of an element that have different masses (AMUs) because they have different numbers of neutrons within the atom; even though it is the same element because they have the same number of protons. (Remember, protons identify the element.) 1. The isotopes behave relatively t ...
Essential Question: What type of model did Thompson ,Rutherford
... Corresponds to group number in the periodic table. Group 2 elements have 2 valence electrons: ...
... Corresponds to group number in the periodic table. Group 2 elements have 2 valence electrons: ...
Science 9 - Ms. J Reed
... Draw a circle and put the symbol and number of protons and neutrons inside of it ◦ Number of protons equals the atomic number ◦ Number of neutrons equals the atomic mass – the number of protons number of protons + number of neutrons = atomic mass ...
... Draw a circle and put the symbol and number of protons and neutrons inside of it ◦ Number of protons equals the atomic number ◦ Number of neutrons equals the atomic mass – the number of protons number of protons + number of neutrons = atomic mass ...
CHM100PracticeExam2
... Do not begin the exam until you have been instructed to do so. You have 120 minutes to complete this exam. There are 50 multiple choice questions. You must use a number 2 pencil. You may use a scientific calculator. Make sure that you have written your name legibly on the scantron form. Circle bubbl ...
... Do not begin the exam until you have been instructed to do so. You have 120 minutes to complete this exam. There are 50 multiple choice questions. You must use a number 2 pencil. You may use a scientific calculator. Make sure that you have written your name legibly on the scantron form. Circle bubbl ...
Unit PowerPoint
... However, not all of the elements fit into the periodic table in order of increasing atomic mass. Mendeleev arranged tellurium and iodine and cobalt and nickel out of order by atomic mass so that they could be placed in the groups with which they shared similar chemical properties. (Mendeleev believe ...
... However, not all of the elements fit into the periodic table in order of increasing atomic mass. Mendeleev arranged tellurium and iodine and cobalt and nickel out of order by atomic mass so that they could be placed in the groups with which they shared similar chemical properties. (Mendeleev believe ...
Chapter 7. Atomic Structure - The University of New Mexico
... Matter refers to any ponderable object, i.e. any object having mass (and therefore attracted through gravitational force to other material bodies such as the earth). The fundamental particles of nature are the smallest material objects.2 They are principally (but not exclusively) the objects of stud ...
... Matter refers to any ponderable object, i.e. any object having mass (and therefore attracted through gravitational force to other material bodies such as the earth). The fundamental particles of nature are the smallest material objects.2 They are principally (but not exclusively) the objects of stud ...
Atoms
... the isotopes weighs 35 and other isotope weighs 37. Since they are both chlorine atoms, they each have 17 protons (the atomic number for chlorine). One of the isotopes has 18 neutrons and the other isotope has 20 neutrons. The average weight of ...
... the isotopes weighs 35 and other isotope weighs 37. Since they are both chlorine atoms, they each have 17 protons (the atomic number for chlorine). One of the isotopes has 18 neutrons and the other isotope has 20 neutrons. The average weight of ...
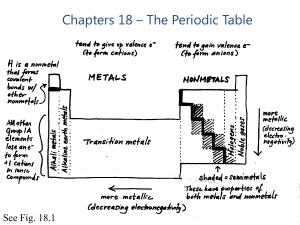
Chapters 18 – The Periodic Table
... agent such as potassium chlorate together with tetraphosphorus trisulfide (P4S3), glass and binder. The phosphorus sulfide is easily ignited, the potassium chlorate decomposes to give oxygen, which in turn causes the phosphorus sulfide to burn more vigorously. The head of safety matches are made of ...
... agent such as potassium chlorate together with tetraphosphorus trisulfide (P4S3), glass and binder. The phosphorus sulfide is easily ignited, the potassium chlorate decomposes to give oxygen, which in turn causes the phosphorus sulfide to burn more vigorously. The head of safety matches are made of ...
Topic IX Counting atoms
... • The isotopes of a particular element all have the same number of protons and electrons but different numbers of neutrons. • Most of the elements consist of mixtures of isotopes. ...
... • The isotopes of a particular element all have the same number of protons and electrons but different numbers of neutrons. • Most of the elements consist of mixtures of isotopes. ...
Matter - tompkinsmath
... a) Homogeneous (i.e. solutions) – the same throughout. They are uniform and consist of only one phase (i.e. solid, liquid or gas) Ex. tap water, air or brass. b) Heterogeneous - not the same consistency throughout. May consist of more than one phase (i.e. solid, liquid or gas). Ex. Salad dressing. ...
... a) Homogeneous (i.e. solutions) – the same throughout. They are uniform and consist of only one phase (i.e. solid, liquid or gas) Ex. tap water, air or brass. b) Heterogeneous - not the same consistency throughout. May consist of more than one phase (i.e. solid, liquid or gas). Ex. Salad dressing. ...
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure
... • Dalton’s atomic theory states that all atoms of a given element are identical. This is mostly true • Atoms of the same element can differ in the number of neutrons • most elements have two or more isotopes • Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons (and therefore d ...
... • Dalton’s atomic theory states that all atoms of a given element are identical. This is mostly true • Atoms of the same element can differ in the number of neutrons • most elements have two or more isotopes • Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons (and therefore d ...
AS specification - word format File
... types of bonding and by exploring the nature and effects of intermolecular forces. Study of the periodic table is extended to cover the chemistry of groups 2 and 7. Ideas about redox reactions are applied in particular to the reactions of halogens and their compounds. The unit develops a largely qua ...
... types of bonding and by exploring the nature and effects of intermolecular forces. Study of the periodic table is extended to cover the chemistry of groups 2 and 7. Ideas about redox reactions are applied in particular to the reactions of halogens and their compounds. The unit develops a largely qua ...
Chapter 2 - Old Saybrook Public Schools
... LO 2.17 The student can predict the type of bonding present between two atoms in a binary compound based on position in the periodic table and the electronegativity of the elements. (Sec 2.6, 2.7) LO 3.5 The student is able to design a plan in order to collect data on the synthesis or decomposit ...
... LO 2.17 The student can predict the type of bonding present between two atoms in a binary compound based on position in the periodic table and the electronegativity of the elements. (Sec 2.6, 2.7) LO 3.5 The student is able to design a plan in order to collect data on the synthesis or decomposit ...
AP_PPT_ch_2
... LO 2.17 The student can predict the type of bonding present between two atoms in a binary compound based on position in the periodic table and the electronegativity of the elements. (Sec 2.6, 2.7) LO 3.5 The student is able to design a plan in order to collect data on the synthesis or decomposit ...
... LO 2.17 The student can predict the type of bonding present between two atoms in a binary compound based on position in the periodic table and the electronegativity of the elements. (Sec 2.6, 2.7) LO 3.5 The student is able to design a plan in order to collect data on the synthesis or decomposit ...
Chapter 2 Atoms and Molecules
... to base everything on. At different times we have used different atoms as our key atom that we base the weights on, H one time, Oxygen another. Currently our mass system is based on carbon (more on this later) The term atomic mass ratio has since been shortened to simply atomic mass. While the Atomi ...
... to base everything on. At different times we have used different atoms as our key atom that we base the weights on, H one time, Oxygen another. Currently our mass system is based on carbon (more on this later) The term atomic mass ratio has since been shortened to simply atomic mass. While the Atomi ...
PowerPoint Lecture Chapter 17-20
... A. nucleus– center of atom containing protons and neutrons 1. Almost all mass of atom exists here 2. Nucleus occupies only trillionth of the volume of an atom ...
... A. nucleus– center of atom containing protons and neutrons 1. Almost all mass of atom exists here 2. Nucleus occupies only trillionth of the volume of an atom ...
Atoms
... Which will identify isotopes Example: How many protons, electrons and neutrons are there in an atom of chlorine-37? 37 – 17(atomic # =protons and electrons) =20 neutrons ...
... Which will identify isotopes Example: How many protons, electrons and neutrons are there in an atom of chlorine-37? 37 – 17(atomic # =protons and electrons) =20 neutrons ...
File
... 1) Represented by a symbol; all are found on the Periodic Table 2) Made a mental model of the atom; Greek philosopher 3) Used by Rutherford in his experiment; made of two protons and two neutrons 4) The paths in which electrons circle the nucleus according to the Bohr model 5) The positive particle ...
... 1) Represented by a symbol; all are found on the Periodic Table 2) Made a mental model of the atom; Greek philosopher 3) Used by Rutherford in his experiment; made of two protons and two neutrons 4) The paths in which electrons circle the nucleus according to the Bohr model 5) The positive particle ...
Atomic Structure Notepacket
... By the end of the lesson, the student will: Know the 3 particles of the atom and where they reside Know the difference between atomic number and mass number Know how to write nuclide symbols Know the three isotopes of hydrogen Know how to calculate atomic mass Know how to calculate perce ...
... By the end of the lesson, the student will: Know the 3 particles of the atom and where they reside Know the difference between atomic number and mass number Know how to write nuclide symbols Know the three isotopes of hydrogen Know how to calculate atomic mass Know how to calculate perce ...
CHAPTER 3
... g. Through the performance of his Gold Foil experiment, this scientist was able to suggest that atoms were not solid particles found within all forms of matter, rather they were mostly empty spaces with a centrally located positively charged core which he called the nucleus of the atom. h. Gave 5 sc ...
... g. Through the performance of his Gold Foil experiment, this scientist was able to suggest that atoms were not solid particles found within all forms of matter, rather they were mostly empty spaces with a centrally located positively charged core which he called the nucleus of the atom. h. Gave 5 sc ...
AP Chap 2
... • The chemical behavior of an atom is mostly determined by the valence electrons… • Atoms will bond to fill their valence electron shells. • Elements with a full valence shell are chemically inert (nonreactive) ...
... • The chemical behavior of an atom is mostly determined by the valence electrons… • Atoms will bond to fill their valence electron shells. • Elements with a full valence shell are chemically inert (nonreactive) ...
Matter -White packet 16-17 (PDF - 1.63 MB)
... The Periodic Table In 1869, a Russian scientist named Dmitri Mendeleev created the Periodic Table, which is a way of organizing elements according to their unique characteristics, like atomic number, density, boiling point, and other values (see Figure below). Each element has a one or two letter sy ...
... The Periodic Table In 1869, a Russian scientist named Dmitri Mendeleev created the Periodic Table, which is a way of organizing elements according to their unique characteristics, like atomic number, density, boiling point, and other values (see Figure below). Each element has a one or two letter sy ...
2014 Academic Challenge Sectional Chemistry Exam Solution Set 1
... D. The balanced reaction is: 2CuO(s) + C(s) 2Cu(s) + CO2(g). Using molecular weights to convert the given mass to moles, there are 1.26 moles of CuO. Using the stoichiometry of the reaction: ...
... D. The balanced reaction is: 2CuO(s) + C(s) 2Cu(s) + CO2(g). Using molecular weights to convert the given mass to moles, there are 1.26 moles of CuO. Using the stoichiometry of the reaction: ...