* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CHAPTER 3
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
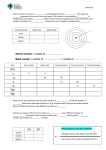
Name ______________________________________ Period ________ Date ___________________ CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 3 MULTIPLE CHOICE PRE – EXAM . Atomic Structure And The Periodic Table Fill in the empty spaces with the finishing information Sample 89 Sr 38 Atomic Number Avg. Atomic Mass Mass Number Protons Neutrons Electrons Atom (A) or Isotope (I) 38 87.68 89 38 51 38 I 20 19 14 39 K 19 14 39.10 54 Fe 26 54 12 47 +1 Ag 12 107.9 47 10 61 Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following statements from Dalton's atomic theory would best describe the following observation: The mass of all of the products is equal to the mass of all the reactants in a given reaction. A) Atoms combine chemically in definite whole number ratios to form compounds. B) Atoms of different elements have different masses. C) Atoms can be neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. D) Each element consists of minute particles called atoms. E) All atoms of a given element are identical. 2) According to Proust, why is only 9 grams of water formed when 10 grams of oxygen reacts with 1 gram of hydrogen? A) because the two additional grams of oxygen are converted into energy B) because oxygen and hydrogen only react in an 8:1 ratio C) because oxygen atoms are 8 times as massive as hydrogen atoms D) Proust wasn't able to provide a reasonable explanation. 3) The nucleus of an electrically neutral iron atom contains 26 protons. How many electrons does this iron atom have? A) 24 B) 26 C) 52 D) none 4) How does Rutherford's model of the atom explain why some of the alpha particles directed at the gold foil were deflected straight back toward the source? A) The atomic nucleus is very small but dense and carries a positive electric charge. B) Alpha particles sling shot around the atomic nucleus much like comets sling shot around the sun. C) The gold nucleus is able to deflect alpha particles much like a mirror is able to reflect photons. D) Each atom has a dense central nucleus that is able to repel larger particles 5) Which of the following statements from Dalton's atomic theory would best describe the following observation: The reaction of 2 liters of hydrogen gas with 1 liter of oxygen gas produce 2 liters of water vapor. A) Each element consists of minute particles called atoms. B) Atoms of different elements have different masses. C) Atoms combine chemically in definite whole number ratios to form compounds. D) Atoms can be neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. E) All atoms of a given element are identical. 6) What is alchemy? A) It is the study of pottery. B) It is the proven process of turning one substance into another and immortality C) It is the philosophy put forth by Aristotle. D) It is the original philosophy dealing with the term atoms. E) It is the science that laid the foundations for modern chemistry. 7) Which of the following statements best describes the Law of Conservation of Mass. A) The mass of a chemical does not change. B) The weight of a compound conserves its mass. C) A compound has more mass than an element because it has more than one element. D) The mass of an element is different from that of a compound. E) The mass of all the products will be the same as the mass of all the reactants. 8) If you heat 50 grams of wood and produce 10 g of ash, what is the total mass of the products? A) 50 g B) 25 g C) 40 g D) 10 g E) none of the above 9) You place a piece of shiny aluminum that weighs exactly 1 gram into a container and seal it. The weight of the container and its contents is exactly 10 g. You allow it to sit for a week and then reweigh the container. After one week the weight of the container and its contents is still 10 g. The mass of the sample inside is now 1.5 g. What is the best explanation for this observation? A) The aluminum reacted with some of the air inside the sealed container because the overall mass did not change. B) Some of the aluminum's mass was replaced by the air in the container. C) The mass of the aluminum atoms has increased. D) The container had a leak because aluminum's mass increased. E) The mass has not really changed because it cannot change due to the Law of Conservation of Volume. 10) Which of the following oxygen : hydrogen mass ratios is the same as the mass ratio found in water (8 g oxygen for every 1 g hydrogen)? A) 1 lb oxygen for every 4 lb hydrogen B) 32 g oxygen for every 4 g hydrogen C) 4 g oxygen for every 4 g hydrogen D) 8 lb oxygen for every 1 g hydrogen E) 16 g oxygen for every 4 g hydrogen 11) Which of the following early chemists initially stated the Law of Conservation of Mass? A) Priestley B) Boyle C) Cavendish D) Proust E) Lavoisier 12) Which statement best describes Aristotle's belief about matter? A) Matter can be converted from one substance to another by altering its components. B) Matter is indestructible. C) Matter is made of small, indivisible particles. D) Matter is composed of four different fundamental qualities and altering the mixture results in new substances. E) Matter is composed of atoms, each with a different set of properties. 13) Which statement best describes Democritus' belief about matter? A) Matter is made of small invisible particles. B) Matter is composed of atoms, each with a different set of properties. C) Matter is composed of four different fundamental qualities and altering the mixture results in new substances. D) Matter can be converted from one substance to another by altering it components. E) Matter is indestructible. 14) Which of the following early chemists discovered was the first to recognize and report the Law of Definite Proportions? A) Proust B) Lavoisier C) Cavendish D) Boyle E) Priestley 15) If a neutral element has the following chemical symbol, how many electrons does it have? 235 U 92 A) 143 B) 92 C) 82 D) 235 E) none of the above 16) The ________ is the sum of an atom's protons and neutrons. A) nucleon number B) atomic mass C) nucleus number D) atomic number E) mass number 17) What is a diatomic molecule? A) a molecule that is composed of two elements B) a molecule with twice the mass of an element C) a molecule that is composed of diatoms D) a molecule that is composed of two atoms that are the same E) none of the above 18) What does the following element description actually mean? 238 92 U A) a uranium atom with 92 protons and 146 neutrons B) a uranium atom with 92 neutrons and 146 protons C) a uranium atom with 238 neutrons and 92 protons D) a uranium atom with 92 neutrons and 238 protons E) none of the above 19) If you remove two protons from a fluorine atom (F), what new element is formed (if any)? A) oxygen B) carbon C) lead D) nitrogen E) hydrogen 20) Which of the following scientists would be considered the father of the modern periodic table? A) Dalton B) Gay-Lussac C) Mendeleev D) Cannizzaro E) Avogadro 21) Arrange the following chemical discoveries in chronological order (starting with earliest). 1. Elements are made of atoms. 2. Chemicals react in definite whole-number ratios. 3. Relative masses of atoms can be measured. 4. The periodic table can be used to predict the properties of the elements. 5. Mass is conserved in a chemical reaction. A) 5, 2, 1, 3, 4 B) 5, 4, 3, 1, 2 C) 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 D) 3, 1, 2, 4, 5 E) 1, 5, 3, 4, 2 22) The following statement describes which subatomic particle/s best? It has a relatively large mass compared to that of the electron. A) an electron B) a proton C) a neutron D) A and B E) B and C 23) The following statement describes which subatomic particle/s best? It is charged. A) an electron B) a proton C) a neutron D) A and B E) B and C 24) Which of the following experiments helped to determine the charge of an electron and (indirectly) its mass? A) R. Millikan's oil drop experiments B) E. Rutherford's gold foil experiments C) Avogadro's number experiments D) J.J. Thompson's cathode ray deflection experiments E) Franklin's kite experiments 25) Which of the following experiments helped to determine that most of an atom is actually empty space except for a very small positive core? A) Franklin's kite experiments B) E. Rutherford's gold foil experiments C) R. Millikan's oil drop experiments D) Avogadro's number experiments E) J.J. Thompson's cathode ray deflection experiments 26) What prompted early scientists to propose that the ray of the cathode ray tube was actually a negatively charged particle? A) The ray was attracted to positively charge electric plates. B) The ray was present regardless of gas, or even without a gas. C) The ray was not seen from the positively charged anode. D) The ray would change colors depending on which gas was used inside the tube. E) The ray could be diverted by a magnetic field. 27) Which of the following does not describe a neutron? A) It is a particle found in the nucleus. B) It is more difficult to detect than a proton or an electron. C) It is much more massive than an electron. D) It has a positive charge equivalent but opposite of an electron's. E) It is often associated with protons. 28) The following statement describes which subatomic particle best? It is located outside of the nucleus. A) an electron B) a proton C) a neutron D) A and B E) B and C 29) The following statement describes which subatomic particle best? It does not have an electrical charge. A) an electron B) a proton C) a neutron D) A and B E) B and C 30) If an element has 9 protons and 10 neutrons and 9 electrons, which expression correctly identifies the element? A) 9 B) 19 C) 9 D) 19 E) 19 F K K K F 19 9 19 19 9 31) Which element has the atomic number 9? A) Na B) Be C) F D) B E) Ne 32) The mass number of an element is ________. A) the sum of the electrons and the neutrons B) the sum of the isotopes C) the number of protons D) the sum of the electrons and the protons E) the sum of the protons and the neutrons 33) If a neutral element has the following chemical symbol, how many electrons does it have? carbon-13 A) 6 B) 7 C) 12 D) 13 34) If a neutral element has the following chemical symbol, how many electrons does it have? A) 18 B) 24 C) 6 D) 12 E) none of the above 60 X 18 35) The ________ is how we classify which element is which. It is also the number of protons in an element. A) mass number B) atomic mass C) nucleus number D) atomic number E) nucleon number 36) Gay-Lussac's experiments showed that two volumes of water vapor are produced from two volumes of hydrogen gas and one volume of oxygen gas. This information lead to the conclusion that A) both hydrogen and oxygen are composed of diatomic molecules. B) oxygen is composed of single atoms and hydrogen is composed of diatomic molecules. C) oxygen atoms are cut in half during the reaction. D) hydrogen is composed of single atoms and oxygen is composed of diatomic molecules. E) a water molecule is composed of two hydrogen atoms and two oxygen atoms. 37) Highlight or circle the correct term/s to add truth to each one of John Dalton’s four postulates Each element is composed of extremely small particles called atoms : molecules All of the atoms within a given element are identical : not identical to one another The atoms of a given element are similar : different from those of any other element Atoms of an element are : are not changed into different types of atoms by chemical reactions; atoms are : are not created or destroyed in chemical reactions Compounds are formed when atoms of one : more than one element combine; a given compound always : never has the same relative number and kinds of atoms : molecules within its composition. 38) Label the major parts of the early atomic model for a particle of Boron + Match each scientist to his or her contribution within chemistry 39. ______ Aristotle 40. ______ Democritus 41. ______ Robert Boyle 42. _______Antoine Lavoisier 43. ______ Joseph Priestly 44. ______ Joseph Proust 45. ______ Amadeus Avogadro 46 ______ Robert Millikian 47. ______ Ernest Rutherford 48. _______John Dalton 49. _______ James Chadwick 50. _______ Gay Lussac 51. _______ JJ Thomsen a. Proposed the law of definite proportions as he took notice that it takes a definite mass of substances to react together to form a specific amount of product consistently. b. An Unitarian minister and political radical known for his ability to isolate oxygen. He devised a technique to carbonate water, found a medicinal use for the isolated gas nitrous oxide and developed a technique with allowed other to isolate various gases using water displacement c. Named the unseen gas oxygen, performed the experiment which allowed him to understand that oxygen composes 20% of atmospheric air, proposed a theory that suggested that matter could not be created or destroyed rather was recycled constantly throughout existence. d. Published many aspects of his work to move the studies of the science of chemistry forward, stressed the importance of challenging the common scientific beliefs of his time, began to question and develop tests to determine whether the substance known as air was in a pure substance. e. Proclaimed that matter might have a composition of tinier parts called "Atomos", which had properties and traits that were responsible for and were similar to the materials of which they were composed. f. As a philosopher, he believed and suggested that matter was composed of 4 basic elementals (Air/Earth/Fire and Water) which in correct proportions were responsible for the traits, characteristics and properties of all materials. g. Through the performance of his Gold Foil experiment, this scientist was able to suggest that atoms were not solid particles found within all forms of matter, rather they were mostly empty spaces with a centrally located positively charged core which he called the nucleus of the atom. h. Gave 5 scientific rules or postulates as fundamental beliefs as to the atomic theories of early chemical compositions, his postulates were based on the relationship of the atom to the inner compositions of all substances. i. Used a self designed 'oil drop' apparatus to determine the mass, speed and negative charge of the elusive particle suggested into existence by JJ Thomsen. His work determined the electron to be a particle of incredible charge while existing as a particle or relatively no real mass. j. As a young scientist he was able to draw similarities and differences between the laws of constant and definite proportions as suggested by his colleagues by examining the context by which these laws were proposed. k. Suggested that materials in the gaseous form combine together according to the law of constant proportions, unchanging in regards to the volumes of gases involved in the reaction. l. Working with Lord Ernest Rutherford, this scientist was able to discover the particle that gave the nucleus of the atom its great density value in comparison to its empty yet large volume, a particle he later termed the neutron m. Noticed that within a beam of light formed within a cathode ray tube there was movement by the energy whenever magnetism was present. This movement he believed was due to he composition of the particles within the light, responding to the magnetic energy. He called these particles electrons based on the fact they were found within electricity. 52. Complete the following chart using the principles discussed in class for determining the amounts of each material involved in the formation of product. Potassium and Oxygen combine to form Potassium Chloride salt in the following proportions: 8 grams of calcium metal reacts with 3 grams of oxygen to form 11 grams of Potassium Chloride Trial A (g) Trial B (g) Mass of Potassium starting with 3 6 Mass of Chlorine starting with 9 4 Mass of Potassium used up Mass of Chlorine used up Which material will remain after the reaction has ended? What is the mass of product formed in this reaction? Determine the volume amounts of each gas in the reaction between: Oxygen gas and Bromine gas to form Oxygen DiBromide product in the following proportions: 3 volume of Oxygen reacts with 5 volumes of Bromine to form 2 volumes of Oxygen Dibromide. Trial A (mL) Trial B (mL) Volume of Oxygen starting with 7 12 Volume of Bromine starting with 9 5 Volume of Oxygen used up 5.4 3 Volume of Bromine used up 9 5 Which material will remain after the reaction has ended? 1.6 9 What is the volume of product formed in this reaction? 22.5 12.5 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. “No answer for the periodic trait table” 1) C 2) B 3) B 4) A 5) C 6) B 7) E 8) A 9) A 10) B 11) E 12) D 13) A 14) A 15) B 16) E 17) D 18) A 19) D 20) C 21) A 22) E 23) D 24) A 25) B 26) E 27) D 28) A 29) C 30) E 31) C 32) E 33) A 34) A 35) D 36) A 37) Each element is composed of extremely small particles called atoms All of the atoms within a given element are identical to one another The atoms of a given element are different froM those of any other element Atoms of an element are not changed into different types of atoms by chemical reactions; atoms are not created or destroyed in chemical reactions Compounds are formed when atoms of more than one element combine; a given compound always has the same relative number and kinds of atoms within its composition 38) Label the major parts of the early atomic model for a particle of Bororn + nucleus electron proton neutron 39. Aristotle (F) 40. Democritus (E) 41. Robert Boyle (D) 42. Antoine Lavoisier (C) 43. Joseph Priestly (B) 44. Joseph Proust (A) 45. Amadeus Avogadro (J) 46. Robert Millikian (i) 47. Ernest Rutherdord (G) 48. John Dalton (H) 49 James Chadwick (l) 50. Gay Lussac (k) 51. JJ Thomson (m) 52. Trial A (g) Trial B (g) Mass of Potassium starting with 3 6 Mass of Chlorine starting with 9 4 Mass of Potassium used up 3 6 Mass of Chlorine used up 1.12 2.25 Which material will remain after the reaction has ended? 7.88 1.75 What is the mass of product formed in this reaction? 4.12 8.25 Trial A (mL) Trial B (mL) Volume of Oxygen starting with 7 12 Volume of Bromine starting with 9 5 Volume of Oxygen used up Volume of Bromine used up Which material will remain after the reaction has ended? What is the volume of product formed in this reaction?