(a) Atoms - Warren County Public Schools
... first period) has one orbital for its electrons. All of the elements in the second row (the second period) have two orbitals for their electrons. It goes down the periodic table like that. At this time, the maximum number of electron orbitals or electron shells for any element is seven. ...
... first period) has one orbital for its electrons. All of the elements in the second row (the second period) have two orbitals for their electrons. It goes down the periodic table like that. At this time, the maximum number of electron orbitals or electron shells for any element is seven. ...
ATOMIC STRUacad test
... A. All matter is made of atoms B. Atoms of the same element are identical C. Atoms are made of protons and electrons D. Atoms unite in definite ratios to form compounds 4. Which of the following ideas is NOT retained in the current theory of atomic structure? A. Electrons can absorb or emit energy B ...
... A. All matter is made of atoms B. Atoms of the same element are identical C. Atoms are made of protons and electrons D. Atoms unite in definite ratios to form compounds 4. Which of the following ideas is NOT retained in the current theory of atomic structure? A. Electrons can absorb or emit energy B ...
Chapter 4: The Structure of the Atom
... 5) An atom of a certain element has a mass number of 112 and is known to contain 64 neutrons. Identify the atom and determine the number of electrons and protons the atom contains. 6) A neutral atom has 78 electrons and a mass number of 198. Identify the atom and determine the number of protons ...
... 5) An atom of a certain element has a mass number of 112 and is known to contain 64 neutrons. Identify the atom and determine the number of electrons and protons the atom contains. 6) A neutral atom has 78 electrons and a mass number of 198. Identify the atom and determine the number of protons ...
Atoms,molecules,nomenclature.
... • Also known as the law of definite proportions. • The elemental composition of a pure substance never varies. • The total mass of substances present at the end of a chemical process is the same as the mass of substances present before the process took place • Protons were discovered by Rutherford i ...
... • Also known as the law of definite proportions. • The elemental composition of a pure substance never varies. • The total mass of substances present at the end of a chemical process is the same as the mass of substances present before the process took place • Protons were discovered by Rutherford i ...
Dalton`s Atomic Theory
... Dalton’s atomic theory has been largely accepted by the scientific community, with the exception of three changes. We know now that (1) an atom can be further sub-divided, (2) all atoms of an element are not identical in mass, and (3) using nuclear fission and fusion techniques, we can create or des ...
... Dalton’s atomic theory has been largely accepted by the scientific community, with the exception of three changes. We know now that (1) an atom can be further sub-divided, (2) all atoms of an element are not identical in mass, and (3) using nuclear fission and fusion techniques, we can create or des ...
Chapter 2
... physicists were using an atomic mass unit defined as equal to one sixteenth of the mass of the oxygen-16 atom (the isotope of oxygen containing 8 protons and 8 neutrons). Thus the two amu scales were inconsistent: for chemists, 1 u was one-sixteenth of the average mass of the oxygen atoms in the che ...
... physicists were using an atomic mass unit defined as equal to one sixteenth of the mass of the oxygen-16 atom (the isotope of oxygen containing 8 protons and 8 neutrons). Thus the two amu scales were inconsistent: for chemists, 1 u was one-sixteenth of the average mass of the oxygen atoms in the che ...
Chapter 3 Atoms and Elements
... Isotopes of Some Elements and Their Atomic Mass Most elements have two or more isotopes that contribute to the atomic mass of that element. ...
... Isotopes of Some Elements and Their Atomic Mass Most elements have two or more isotopes that contribute to the atomic mass of that element. ...
CHAPTER 4 TEST
... _____10. Which statement is false according to Bohr’s model of the atom? a. Electrons cannot be between energy levels b. Electrons orbit the nucleus c. An electron’s path is not known exactly d. Electrons exist in energy levels _____11. Unlike the modern model of the atom, Bohr’s model states that a ...
... _____10. Which statement is false according to Bohr’s model of the atom? a. Electrons cannot be between energy levels b. Electrons orbit the nucleus c. An electron’s path is not known exactly d. Electrons exist in energy levels _____11. Unlike the modern model of the atom, Bohr’s model states that a ...
Chapter 23 (Section 3) Pregnancy, Birth, and
... MASS was the average of the other “2” ELEMENTS *a. (e.g.) calcium [Ca] = 40.08; strontium [Sr] = 87.62; barium [Ba] = 137.33 *2. In 1856, Newlands proposed the Law of Octaves stated that some of the 56 ELEMENTS whose atomic MASS differed by some multiple of EIGHT had similar PROPERTIES *a. this la ...
... MASS was the average of the other “2” ELEMENTS *a. (e.g.) calcium [Ca] = 40.08; strontium [Sr] = 87.62; barium [Ba] = 137.33 *2. In 1856, Newlands proposed the Law of Octaves stated that some of the 56 ELEMENTS whose atomic MASS differed by some multiple of EIGHT had similar PROPERTIES *a. this la ...
Matter unit-structure
... cannot be broken down into any other substances by chemical or physical means. ...
... cannot be broken down into any other substances by chemical or physical means. ...
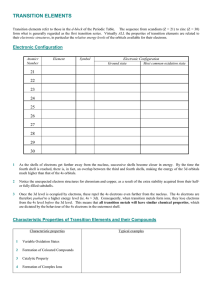
TRANSITION ELEMENTS
... The small, highly charged cations cause greater polarization of associated anions, resulting in the following chemical properties of transition metal compounds compared with those of the s-block metals : their oxides and hydroxides in oxidation states +2 and +3 are less basic and less soluble; their ...
... The small, highly charged cations cause greater polarization of associated anions, resulting in the following chemical properties of transition metal compounds compared with those of the s-block metals : their oxides and hydroxides in oxidation states +2 and +3 are less basic and less soluble; their ...
Science 10 - SharpSchool
... atoms tend to be stable when the outer energy level is full of electrons the octet rule states that atoms bond in a way to have a full valence energy level (there are exceptions) atoms will either share electrons, or gain or lose electrons in order to satisfy this octet rule compounds are fo ...
... atoms tend to be stable when the outer energy level is full of electrons the octet rule states that atoms bond in a way to have a full valence energy level (there are exceptions) atoms will either share electrons, or gain or lose electrons in order to satisfy this octet rule compounds are fo ...
Key Concept Summary - Bellingham High School
... Dalton’s theory enables us to set up a scale of relative atomic masses. He cannot measure the exact mass of atoms but relative mass. E.g. Consider calcium sulfide, which consists of 55.6% calcium by mass and 44.4% sulfur by mass. Suppose there is one calcium atom for each sulfur atom in calcium sulf ...
... Dalton’s theory enables us to set up a scale of relative atomic masses. He cannot measure the exact mass of atoms but relative mass. E.g. Consider calcium sulfide, which consists of 55.6% calcium by mass and 44.4% sulfur by mass. Suppose there is one calcium atom for each sulfur atom in calcium sulf ...
CHAPTER 2: ATOMS, MOLECULES AND IONS ULES AND IONS
... 1. From left to right (row of periodic table) the atomic number (Number of protons) increases. 2. From top to bottom (vertical column of periodic table), the elements have similar chemical properties. ...
... 1. From left to right (row of periodic table) the atomic number (Number of protons) increases. 2. From top to bottom (vertical column of periodic table), the elements have similar chemical properties. ...
Chapter 4 Atoms and Elements
... • The properties of atoms determine the properties of matter. • An atom is the smallest identifiable unit of an element. • An element is a substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances. • There are about 91 different elements in nature, and consequently about 91 different kinds of ato ...
... • The properties of atoms determine the properties of matter. • An atom is the smallest identifiable unit of an element. • An element is a substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances. • There are about 91 different elements in nature, and consequently about 91 different kinds of ato ...
Mass/Mole Conversions
... • Neutrons are _____________ neutral. • P+ and no have almost ____________ masses, electrons weigh 1836 times ______. ...
... • Neutrons are _____________ neutral. • P+ and no have almost ____________ masses, electrons weigh 1836 times ______. ...
Hands-On Chemistry Unit
... 7. Activities and Worksheets .................................................................................................................... 8 7.1. Introduction to Chemistry .............................................................................................................. 8 7.2. Exa ...
... 7. Activities and Worksheets .................................................................................................................... 8 7.1. Introduction to Chemistry .............................................................................................................. 8 7.2. Exa ...
www.xtremepapers.net
... Point out that the more outer-shell electrons, the more electrons are delocalised and the stronger the attraction (e.g. m.pt. Al > Mg > Na). ...
... Point out that the more outer-shell electrons, the more electrons are delocalised and the stronger the attraction (e.g. m.pt. Al > Mg > Na). ...
chemistry 1
... a chemical formula. Water, which contains two atoms of hydrogen for each atom of oxygen, has the chemical formula H2O. The formula for table salt, NaCl, indicates that the elements that make up table salt—sodium and chlorine—combine in a 1:1 ratio. ...
... a chemical formula. Water, which contains two atoms of hydrogen for each atom of oxygen, has the chemical formula H2O. The formula for table salt, NaCl, indicates that the elements that make up table salt—sodium and chlorine—combine in a 1:1 ratio. ...
Chapter 2 – Atoms, Ions and Compounds
... 2.5 Trends in Compound Formation Chemical bond: holds atoms or ions together in a compound COVALENT BOND and MOLECULES • Covalent bond: sharing of a pair of electrons by 2 nonmetal atoms • Two or more covalently bonded atoms form a molecule • Molecule: basic unit of a compound of covalently bonded ...
... 2.5 Trends in Compound Formation Chemical bond: holds atoms or ions together in a compound COVALENT BOND and MOLECULES • Covalent bond: sharing of a pair of electrons by 2 nonmetal atoms • Two or more covalently bonded atoms form a molecule • Molecule: basic unit of a compound of covalently bonded ...
ite and - Smithycroft Secondary School
... I can explain what an atomic number and a mass number are in an atom I can state the mass of subatomic particles Look at the periodic table on page 8 of chemistry data book. Notice that each element has a number above it - this is its unique ATOMIC NUMBER. The atomic number used to be called the pro ...
... I can explain what an atomic number and a mass number are in an atom I can state the mass of subatomic particles Look at the periodic table on page 8 of chemistry data book. Notice that each element has a number above it - this is its unique ATOMIC NUMBER. The atomic number used to be called the pro ...
Name: (1 of 2) Math Set # 13 Protons,
... The number of protons is ALWAYS the same for an atom of a specific element. Germanium ALWAYS has 32 protons. If you add a proton it is no longer Germanium but becomes Arsenic. ...
... The number of protons is ALWAYS the same for an atom of a specific element. Germanium ALWAYS has 32 protons. If you add a proton it is no longer Germanium but becomes Arsenic. ...