PPT
... Valence Shell : Outermost, highest energy shell of an atom. Valence electrons: An electron in an outermost shell of an atom. These electrons are loosely held, they are most important in determining an element’s properties. ...
... Valence Shell : Outermost, highest energy shell of an atom. Valence electrons: An electron in an outermost shell of an atom. These electrons are loosely held, they are most important in determining an element’s properties. ...
Name: Period:______ Table Number:______
... 51. Each element found on the periodic table of elements has a unique single letter (Hydrogen – H), two letter (Helium – He ) or three letter (Unnilquadiam – Unq) abbreviation which is called the CHEMICAL SYMBOL of that element. P. 83, Bill Nye the Science Guy Video 52. JONS BERZELIUS created the un ...
... 51. Each element found on the periodic table of elements has a unique single letter (Hydrogen – H), two letter (Helium – He ) or three letter (Unnilquadiam – Unq) abbreviation which is called the CHEMICAL SYMBOL of that element. P. 83, Bill Nye the Science Guy Video 52. JONS BERZELIUS created the un ...
Chemistry - Beachwood City Schools
... metals lose this s electron, they acquire noble gas electron configurations which end in completed energy levels. They have a strong tendency, therefore, to lose their final single s electrons. This makes them extremely reactive and the metals with the greatest tendency to lose electrons. Group 17 e ...
... metals lose this s electron, they acquire noble gas electron configurations which end in completed energy levels. They have a strong tendency, therefore, to lose their final single s electrons. This makes them extremely reactive and the metals with the greatest tendency to lose electrons. Group 17 e ...
Chemistry SOL Review
... •Control experiment: experiment where the independent variable is set to zero •Constants: variables that are kept constant during a set of trials Analyze the following experiment and identify the control experiment, independent variable, dependent variable, and constants. ...
... •Control experiment: experiment where the independent variable is set to zero •Constants: variables that are kept constant during a set of trials Analyze the following experiment and identify the control experiment, independent variable, dependent variable, and constants. ...
atom
... identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds In chemical reactions, atoms are comb ...
... identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds In chemical reactions, atoms are comb ...
Chapter 20 Resource: Chemical Bonds
... B. An ionic compound is held together by the ___________________—the force of attraction between opposite charges of the ions. 1. The result of this bond is a(n) ________________ compound. 2. The sum of the charges on the ions in a unit of the compound is _____________. C. __________________ are neu ...
... B. An ionic compound is held together by the ___________________—the force of attraction between opposite charges of the ions. 1. The result of this bond is a(n) ________________ compound. 2. The sum of the charges on the ions in a unit of the compound is _____________. C. __________________ are neu ...
Chapter 4 Presentation - Spearfish School District
... • To test the polarity of the cathode ray, Thompson replaced the paddle-wheel with another pair of electrodes. • When the current was passed through this new apparatus, Thompson found that the cathoderay was "bent" towards the positive electrode and repelled by the negative electrode. • Thompson at ...
... • To test the polarity of the cathode ray, Thompson replaced the paddle-wheel with another pair of electrodes. • When the current was passed through this new apparatus, Thompson found that the cathoderay was "bent" towards the positive electrode and repelled by the negative electrode. • Thompson at ...
(a) Atoms - Warren County Schools
... more of the entire unit it appears in front of. The coefficient used in this example shows that, in the left reactant, there are 4 hydrogen, and in the product, there are 4 hydrogen and 2 oxygen. • The coefficient does not effect the oxygen in the reactant because it is not a compound with hydrogen ...
... more of the entire unit it appears in front of. The coefficient used in this example shows that, in the left reactant, there are 4 hydrogen, and in the product, there are 4 hydrogen and 2 oxygen. • The coefficient does not effect the oxygen in the reactant because it is not a compound with hydrogen ...
The Mole - My CCSD
... We come here to be philosophers, and I hope you will always remember that whenever a result happens, especially if it be new, you should say, “What is the cause? Why does it occur?” and you will, in the course of time, find out the reason. -Michael Faraday Bires, 2010 ...
... We come here to be philosophers, and I hope you will always remember that whenever a result happens, especially if it be new, you should say, “What is the cause? Why does it occur?” and you will, in the course of time, find out the reason. -Michael Faraday Bires, 2010 ...
ch3 - Otterville R-VI School District
... Discovery of Nucleus Characteristics of “Powerful Force”: 1. dense- since it was strong enough to deflect particle 2. small- only 1/8000 hit the force dead on and bounced back 3. positively charged- since there was a repulsion between force and alpha particles ...
... Discovery of Nucleus Characteristics of “Powerful Force”: 1. dense- since it was strong enough to deflect particle 2. small- only 1/8000 hit the force dead on and bounced back 3. positively charged- since there was a repulsion between force and alpha particles ...
Chapter 3
... D. an atom or group of atoms with a net positive charge. 34. An cation is defined as A. a charged atom or group of atoms with a net negative charge. B. a stable atom. C. a group of stable atoms. D. an atom or group of atoms with a net positive charge. 35. Atoms of the same element with different mas ...
... D. an atom or group of atoms with a net positive charge. 34. An cation is defined as A. a charged atom or group of atoms with a net negative charge. B. a stable atom. C. a group of stable atoms. D. an atom or group of atoms with a net positive charge. 35. Atoms of the same element with different mas ...
PPTB&W - Gmu - George Mason University
... Li3PO4, in water is much more difficult than similar salts of sodium (Na) and Potassium (K) Only member of Alkali group that forms simple Oxide and Nitride, Li2O & Li3N, on reaction with O2 & N2 in air Only Lithium forms organo-metalic molecular compounds with hydrocarbon groups from organic Hal ...
... Li3PO4, in water is much more difficult than similar salts of sodium (Na) and Potassium (K) Only member of Alkali group that forms simple Oxide and Nitride, Li2O & Li3N, on reaction with O2 & N2 in air Only Lithium forms organo-metalic molecular compounds with hydrocarbon groups from organic Hal ...
AP CHEMISTRY SUMMER ASSIGNMENT
... If you can count separate units of a substance, you can get an exact number. For example, you can count that you have 12 pencils or 25 bottles of soda or 150 marbles. When you measure something, however, you obtain a number that is not exact. For example, you can determine that a beaker has a mass o ...
... If you can count separate units of a substance, you can get an exact number. For example, you can count that you have 12 pencils or 25 bottles of soda or 150 marbles. When you measure something, however, you obtain a number that is not exact. For example, you can determine that a beaker has a mass o ...
atomic number, mass, isotopes
... • Electrons with different amounts of energy exist in different energy levels • Many possible energy levels an electron can occupy • Number of energy levels depends on the number of electrons ...
... • Electrons with different amounts of energy exist in different energy levels • Many possible energy levels an electron can occupy • Number of energy levels depends on the number of electrons ...
mass number
... Relative => means with respect to each other About 1864 ( 2000) electrons = 1 proton ...
... Relative => means with respect to each other About 1864 ( 2000) electrons = 1 proton ...
File
... Matter is separated into two major categories: 1) Pure substance cannot be separated into different kinds of matter by physical means and are made up of one single chemical throughout 2) Mixtures are made up of multiple substances Most matter in the world around us are mixtures ...
... Matter is separated into two major categories: 1) Pure substance cannot be separated into different kinds of matter by physical means and are made up of one single chemical throughout 2) Mixtures are made up of multiple substances Most matter in the world around us are mixtures ...
PPT - George Mason University
... Boron-Nitrogen compounds are similar in structure to elemental Carbon and some of its organic compounds Size, Ionization Energy, Electronegativity of Carbon is between Boron & Nitrogen Ethane & Amine – Borane have the same number & electron configuration ...
... Boron-Nitrogen compounds are similar in structure to elemental Carbon and some of its organic compounds Size, Ionization Energy, Electronegativity of Carbon is between Boron & Nitrogen Ethane & Amine – Borane have the same number & electron configuration ...
Atomic Nature of Matter
... Atomic and Nuclear Radii The size of an atom is difficult to define exactly due to the fact that the electron cloud, formed by the electrons moving in their various orbitals, does not have a distinct outer edge. A reasonable measure of atomic size is given by the average distance of the outermost el ...
... Atomic and Nuclear Radii The size of an atom is difficult to define exactly due to the fact that the electron cloud, formed by the electrons moving in their various orbitals, does not have a distinct outer edge. A reasonable measure of atomic size is given by the average distance of the outermost el ...
Chapter 3
... D. 6 31. How many grams of NO2 are there in 1.55 mol of NO2 ? A. 71.32 g * B. 199 g C. 80.01 g D. 200 g 32. Calculate the percent of nitrogen in Mg(NO3)2 A. 18.89% * B. 9.44% C. 17.10% D. 16% 33. Which of the following is an empirical formula ? A. CO2 * B. C6H12O6 C. S8 D. O2 ...
... D. 6 31. How many grams of NO2 are there in 1.55 mol of NO2 ? A. 71.32 g * B. 199 g C. 80.01 g D. 200 g 32. Calculate the percent of nitrogen in Mg(NO3)2 A. 18.89% * B. 9.44% C. 17.10% D. 16% 33. Which of the following is an empirical formula ? A. CO2 * B. C6H12O6 C. S8 D. O2 ...
File
... contains as many particles as there are atoms in exactly 12 g of carbon-12. • A mole is the SI unit for the amount of a ...
... contains as many particles as there are atoms in exactly 12 g of carbon-12. • A mole is the SI unit for the amount of a ...
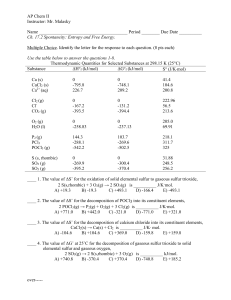
AP Chem II Instructor: Mr. Malasky Name Period ______ Due Date
... ____ 5. The value of ΔG˚ at 25˚C for the decomposition of gaseous sulfur dioxide to solid elemental sulfur and gaseous oxygen, SO2(g) → 2 S (s,rhombic) + O2(g) is __________ kJ/mol. A) +395.2 B) +269.9 C) -269.9 D) +300.4 E) -300.4 ____ 6. The value of ΔG˚ at 25˚C for the formation of POCl3 from it ...
... ____ 5. The value of ΔG˚ at 25˚C for the decomposition of gaseous sulfur dioxide to solid elemental sulfur and gaseous oxygen, SO2(g) → 2 S (s,rhombic) + O2(g) is __________ kJ/mol. A) +395.2 B) +269.9 C) -269.9 D) +300.4 E) -300.4 ____ 6. The value of ΔG˚ at 25˚C for the formation of POCl3 from it ...
Hewitt/Lyons/Suchocki/Yeh, Conceptual Integrated Science
... observed collisions between visible particles and invisible atoms (Brownian motion)—later confirmed by Einstein as evidence for the existence of atoms. ...
... observed collisions between visible particles and invisible atoms (Brownian motion)—later confirmed by Einstein as evidence for the existence of atoms. ...
Atomic Theory - Northwest ISD Moodle
... Sub-Atomic Particles Thomson made the following observations: 1. The cathode rays had the same properties regardless of the metal used for the cathode. 2. The rays traveled from the cathode (- charged) to the anode (+ charged). 3. The rays were attracted to the positive plate of an external electri ...
... Sub-Atomic Particles Thomson made the following observations: 1. The cathode rays had the same properties regardless of the metal used for the cathode. 2. The rays traveled from the cathode (- charged) to the anode (+ charged). 3. The rays were attracted to the positive plate of an external electri ...