Atom - Malibu High School
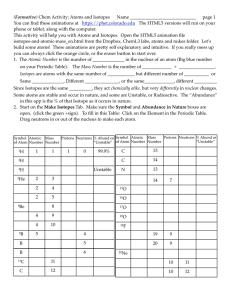
... therefore 1 proton or 1 neutron = ~1 amu 1 amu = 1.6606 x 10 -24 grams Since the mass mostly depends on # protons and # neutrons, you’d think atomic mass would be a whole number, but it isn’t. How come? ...
... therefore 1 proton or 1 neutron = ~1 amu 1 amu = 1.6606 x 10 -24 grams Since the mass mostly depends on # protons and # neutrons, you’d think atomic mass would be a whole number, but it isn’t. How come? ...
Chapter 2 - Phillips Scientific Methods
... • The chemical behavior of an atom is mostly determined by the valence electrons. • Elements with a full valence shell are chemically inert. ...
... • The chemical behavior of an atom is mostly determined by the valence electrons. • Elements with a full valence shell are chemically inert. ...
The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central
... The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons (except in the case of hydrogen-1, which is the only stable nuclide wit ...
... The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons (except in the case of hydrogen-1, which is the only stable nuclide wit ...
CHAPTER-4 STRUCTURE OF THE ATOM
... Ans: The valency of an element is the combining capacity of that element. The valency of an element is determined by the number of valence electrons present in the atom of that element. If the number of valence electrons of the atom of an element is less than or equal to four, then the valency of th ...
... Ans: The valency of an element is the combining capacity of that element. The valency of an element is determined by the number of valence electrons present in the atom of that element. If the number of valence electrons of the atom of an element is less than or equal to four, then the valency of th ...
Atoms and nukes packet 2016
... 3. Why does flying in an airplane increase your radiation dose? 4. What is the purpose of Pu in a pacemaker? 5. What radioactive isotope is in a smoke detector? ________ 6. How much radiation comes from smoking a pack of cigarettes a day? _____________ What isotopes produce this radiation? _________ ...
... 3. Why does flying in an airplane increase your radiation dose? 4. What is the purpose of Pu in a pacemaker? 5. What radioactive isotope is in a smoke detector? ________ 6. How much radiation comes from smoking a pack of cigarettes a day? _____________ What isotopes produce this radiation? _________ ...
atoms II - Doral Academy Preparatory
... •Every atom is made up of a nucleus (which contains protons and neutrons). •The nucleus is the center, and it contains most of the mass of the atom. •Outside the nucleus there are electrons, which are extremely small, and which move around the nucleus very quickly. •The electrons are segregated into ...
... •Every atom is made up of a nucleus (which contains protons and neutrons). •The nucleus is the center, and it contains most of the mass of the atom. •Outside the nucleus there are electrons, which are extremely small, and which move around the nucleus very quickly. •The electrons are segregated into ...
Chemistry Final Exam Practice Test
... 91. The periodic law states that there is a periodic repetition of the physical and chemical properties of elements _____. a) When they are arranged in order of increasing atomic mass b) If only metals are considered c) When they are arranged in order of increasing atomic radii d) When they are arra ...
... 91. The periodic law states that there is a periodic repetition of the physical and chemical properties of elements _____. a) When they are arranged in order of increasing atomic mass b) If only metals are considered c) When they are arranged in order of increasing atomic radii d) When they are arra ...
Unit 2: Atoms, Moles and The Periodic Table Notes (answers)
... Atomic Number and Mass Number: Recall from the Dalton’s Atomic Theory, one of its points is that different elements have different atoms. For a long time, it was believed that the main difference between atoms of different elements is the mass number (the total mass of an atom). This is the mass cha ...
... Atomic Number and Mass Number: Recall from the Dalton’s Atomic Theory, one of its points is that different elements have different atoms. For a long time, it was believed that the main difference between atoms of different elements is the mass number (the total mass of an atom). This is the mass cha ...
ch2 - sscyr11chemistry
... by their atomic number and not by their mass number. A26. Most elements have more than one isotope, so they will have more than one mass number. All bromine atoms have 35 protons in their nuclei. No other type of atom has 35 protons in its nucleus (i.e. no other atom has an atomic number of 35). Iso ...
... by their atomic number and not by their mass number. A26. Most elements have more than one isotope, so they will have more than one mass number. All bromine atoms have 35 protons in their nuclei. No other type of atom has 35 protons in its nucleus (i.e. no other atom has an atomic number of 35). Iso ...
10/2/2013 1 5 Early Atomic Theory and Structure Chapter Outline
... Dalton’s theory of atoms, proposed in the early 1800s, states: 1. Elements are composed of small, indivisible particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are identical in mass and size. 3. Atoms of different elements differ in their mass and size. 4. Compounds are formed by combining two or ...
... Dalton’s theory of atoms, proposed in the early 1800s, states: 1. Elements are composed of small, indivisible particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are identical in mass and size. 3. Atoms of different elements differ in their mass and size. 4. Compounds are formed by combining two or ...
Chapter 5
... Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus. Electrons are dispersed throughout the remainder of the atom (mainly open space). Neutral atoms contain the same number of protons and neutrons to maintain charge balance. © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. ...
... Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus. Electrons are dispersed throughout the remainder of the atom (mainly open space). Neutral atoms contain the same number of protons and neutrons to maintain charge balance. © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. ...
1 - Atomic Theory - Crestwood Local Schools
... An ISOTOPE is an atom with a different number of Neutrons and therefore a different atomic mass. ...
... An ISOTOPE is an atom with a different number of Neutrons and therefore a different atomic mass. ...
periodic table - Mesa Community College
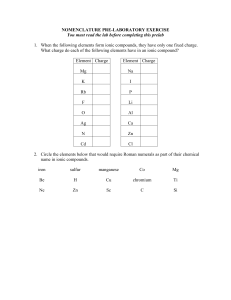
... language. These rules make it possible to recognize thousands of compounds without memorizing all the formulas and names. The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) is the international group that governs nomenclature for all branches of chemistry in all countries, so that a chemi ...
... language. These rules make it possible to recognize thousands of compounds without memorizing all the formulas and names. The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) is the international group that governs nomenclature for all branches of chemistry in all countries, so that a chemi ...
Reading 2.1 A Return to Isotopes
... nature, only certain isotopes exist. For instance, stable lithium exists as an isotope with 3 neutrons and as an isotope with 4 neutrons, but there are no stable lithium isotopes with 2 neutrons or 5 neutrons. This whole discussion of isotopes brings us back to Dalton’s atomic theory. According to D ...
... nature, only certain isotopes exist. For instance, stable lithium exists as an isotope with 3 neutrons and as an isotope with 4 neutrons, but there are no stable lithium isotopes with 2 neutrons or 5 neutrons. This whole discussion of isotopes brings us back to Dalton’s atomic theory. According to D ...
Document
... 9) The number of electrons found in a zinc atom is _________________. 10) The name of the element with 82 protons is _________________________________. ...
... 9) The number of electrons found in a zinc atom is _________________. 10) The name of the element with 82 protons is _________________________________. ...
Mystery Isotopes
... Lesson Plan Template: General Lesson Plan Learning Objectives: What should students know and be able to do as a result of this lesson? Students will be able to create a Bohr Model of Nitrogen and Carbon isotopes. Students will be able to identify and name isotopes through analyzing structure (arrang ...
... Lesson Plan Template: General Lesson Plan Learning Objectives: What should students know and be able to do as a result of this lesson? Students will be able to create a Bohr Model of Nitrogen and Carbon isotopes. Students will be able to identify and name isotopes through analyzing structure (arrang ...
Atomic Theory
... in the star merge to form neutrons and neutrinos. The neutrons form the neutron star, which is usually around 20 km in diameter, but can be over twice the mass of the sun. Nuclear fission reactions occur when a free neutron hits an atom's nucleus causing it to break apart into two different nuclei, ...
... in the star merge to form neutrons and neutrinos. The neutrons form the neutron star, which is usually around 20 km in diameter, but can be over twice the mass of the sun. Nuclear fission reactions occur when a free neutron hits an atom's nucleus causing it to break apart into two different nuclei, ...
Isotopes of Hydrogen
... Isotopes are atoms of the same elements that have different masses. The isotopes of a particular element all have the same number of protons and electrons but different numbers of neutrons. SECTION 3-3 OBJECTIVE 2 Define atomic number and mass number, and describe how they apply to isotopes. The Ato ...
... Isotopes are atoms of the same elements that have different masses. The isotopes of a particular element all have the same number of protons and electrons but different numbers of neutrons. SECTION 3-3 OBJECTIVE 2 Define atomic number and mass number, and describe how they apply to isotopes. The Ato ...
Chapter 2
... The different states of potential energy that the electrons of an atom can have are called electron shells. o The first shell, closest to the nucleus, has the lowest potential energy. o Electrons in outer shells have higher potential energy. o Electrons can change their position only if they absorb ...
... The different states of potential energy that the electrons of an atom can have are called electron shells. o The first shell, closest to the nucleus, has the lowest potential energy. o Electrons in outer shells have higher potential energy. o Electrons can change their position only if they absorb ...
Units and Unit Conversions 6. Define the problem: If the nucleus
... Develop a plan: Look up the symbol for cobalt and find that symbol on the periodic table. The periodic table gives the atomic number. The atomic number is the number of protons. The number of electrons is equal to the number of protons since the atom has no charge. The number of neutrons is the diff ...
... Develop a plan: Look up the symbol for cobalt and find that symbol on the periodic table. The periodic table gives the atomic number. The atomic number is the number of protons. The number of electrons is equal to the number of protons since the atom has no charge. The number of neutrons is the diff ...
Chapter 4, 5, 6 - Campbell County Schools
... Target 2 - Identify the atomic number and the atomic mass of all elements and explain what they mean. A. All of the elements are listed on the ___________________________ of Elements. B. Elements are different kinds of atoms with a name, symbol, and unique properties. C. The Periodic Table lists the ...
... Target 2 - Identify the atomic number and the atomic mass of all elements and explain what they mean. A. All of the elements are listed on the ___________________________ of Elements. B. Elements are different kinds of atoms with a name, symbol, and unique properties. C. The Periodic Table lists the ...
Aleksander Herman
... approach above, it may be of particular importance to examine the computed properties of atoms in comparison with accurate Hartree-Fock results [6, 7]. The questions are how our total binding energy values compare with results of accurate Hartree-Fock calculations, and what happens with radial expec ...
... approach above, it may be of particular importance to examine the computed properties of atoms in comparison with accurate Hartree-Fock results [6, 7]. The questions are how our total binding energy values compare with results of accurate Hartree-Fock calculations, and what happens with radial expec ...
10.1 RG and answer key
... 2. Sample: I did not use sight and taste because I could not see or taste the object through the box. 3. The object must be smaller than the box because it fits inside the box. 4. Sample: The object would make soft sounds when the box is shaken, the box would be light. ...
... 2. Sample: I did not use sight and taste because I could not see or taste the object through the box. 3. The object must be smaller than the box because it fits inside the box. 4. Sample: The object would make soft sounds when the box is shaken, the box would be light. ...
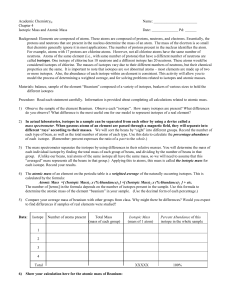
In actual laboratories, isotopes in a sample can be
... neutrons. Atoms of the same element (i.e., with same number of protons) that have a different number of neutrons are called isotopes. One isotope of chlorine has 18 neutrons and a different isotope has 20 neutrons. These atoms would be considered isotopes of chlorine. The masses of isotopes vary due ...
... neutrons. Atoms of the same element (i.e., with same number of protons) that have a different number of neutrons are called isotopes. One isotope of chlorine has 18 neutrons and a different isotope has 20 neutrons. These atoms would be considered isotopes of chlorine. The masses of isotopes vary due ...