Chapter 2 Elements and Compounds 2.1 The Structure of the Atom
... Every carbon atom has six protons, and the mass of electrons is negligible; this means we can conclude that the carbon atoms shown in Interactive Figure 2.1.2 have different mass numbers because each has a different number of neutrons. Atoms that have the same atomic number (Z) but different mass nu ...
... Every carbon atom has six protons, and the mass of electrons is negligible; this means we can conclude that the carbon atoms shown in Interactive Figure 2.1.2 have different mass numbers because each has a different number of neutrons. Atoms that have the same atomic number (Z) but different mass nu ...
chapter2.1
... 2. Identify the characteristics of protons, neutrons, and electrons. (Section 2.2; Exercises 2.10 and 2.12) 3. Use the concepts of atomic number and mass number to determine the number of subatomic particles in isotopes and to write correct symbols for isotopes. (Section 2.3; Exercises 2.16 and 2.22 ...
... 2. Identify the characteristics of protons, neutrons, and electrons. (Section 2.2; Exercises 2.10 and 2.12) 3. Use the concepts of atomic number and mass number to determine the number of subatomic particles in isotopes and to write correct symbols for isotopes. (Section 2.3; Exercises 2.16 and 2.22 ...
Regents Chemistry Topic Review Packet
... You can recognize an excited state electron configuration. If the configuration does not match that on the Periodic Table for that number of electrons, then it is an excited state. 9. When an electron returns from a higher energy state to a lower energy state, it emits a specific amount of energy ...
... You can recognize an excited state electron configuration. If the configuration does not match that on the Periodic Table for that number of electrons, then it is an excited state. 9. When an electron returns from a higher energy state to a lower energy state, it emits a specific amount of energy ...
CHAPTER 1
... Key Terms mass matter atom element compound extensive property intensive property physical property ...
... Key Terms mass matter atom element compound extensive property intensive property physical property ...
Chem 101 Test #1 review questions. Please don`t look at the
... Since the temperature in Paris is 18°C, it must be less than the freezing point. The state of the substance must be that of a solid. (if it were higher than the freezing point, it would have been a liquid, right??). ...
... Since the temperature in Paris is 18°C, it must be less than the freezing point. The state of the substance must be that of a solid. (if it were higher than the freezing point, it would have been a liquid, right??). ...
Electrochemistry
... A. Chemists assign a number to each element in a reaction called an _________________ state that allows him/her to determine the electron flow in the reaction. 1. Even though they look like them, oxidation states are not _________ charges! 2. Oxidation numbers can be assigned to each atom in an elem ...
... A. Chemists assign a number to each element in a reaction called an _________________ state that allows him/her to determine the electron flow in the reaction. 1. Even though they look like them, oxidation states are not _________ charges! 2. Oxidation numbers can be assigned to each atom in an elem ...
Chapter 7
... • First I add a 2 to the product to end with 2 bromine atoms, but now I am also ending with 2 potassium atoms. • 2K + Br2 → 2KBr • Adding a 2 in front of potassium fixes this. ...
... • First I add a 2 to the product to end with 2 bromine atoms, but now I am also ending with 2 potassium atoms. • 2K + Br2 → 2KBr • Adding a 2 in front of potassium fixes this. ...
Lesson 4: Atomic Structure
... charge he measured must be balanced by a particle of positive charge, since there was no overall charge on an atom. Thomson devised his own model of the atom, which is often described as the blueberry muffin model: he pictured an atom as a uniform ball of positive charge, with the electrons scattere ...
... charge he measured must be balanced by a particle of positive charge, since there was no overall charge on an atom. Thomson devised his own model of the atom, which is often described as the blueberry muffin model: he pictured an atom as a uniform ball of positive charge, with the electrons scattere ...
atom - Social Circle City Schools
... • Atoms that contain too many or two few neutrons are unstable and lose energy through radioactive decay to form a stable nucleus. • Few exist in nature—most have already decayed to stable forms. ...
... • Atoms that contain too many or two few neutrons are unstable and lose energy through radioactive decay to form a stable nucleus. • Few exist in nature—most have already decayed to stable forms. ...
mineral
... 1. An __________ is a substance that can not be broken down into simpler substance by chemical or physical means. atom is the smallest particle of matter that contains the 2. An _____ characteristics of an element. protons 3. The number of __________ in a nucleus of an atom is called the atomic numb ...
... 1. An __________ is a substance that can not be broken down into simpler substance by chemical or physical means. atom is the smallest particle of matter that contains the 2. An _____ characteristics of an element. protons 3. The number of __________ in a nucleus of an atom is called the atomic numb ...
2005/6 - SAASTA
... The project offers learners in grades 10-12 an exciting opportunity to compete in the science arena with fellow learners from all the nine provinces and SADC countries, such as Namibia and Lesotho. The competition comprises an annual examination in science, and top learners and top schools stand a c ...
... The project offers learners in grades 10-12 an exciting opportunity to compete in the science arena with fellow learners from all the nine provinces and SADC countries, such as Namibia and Lesotho. The competition comprises an annual examination in science, and top learners and top schools stand a c ...
XIX. Chemistry, High School
... Reference Materials and Tools Each student taking the high school Chemistry test was provided with a Chemistry Formula and Constants Sheet/Periodic Table of the Elements. Copies of both sides of this formula sheet follow the final question in this chapter. Each student also had sole access to a calc ...
... Reference Materials and Tools Each student taking the high school Chemistry test was provided with a Chemistry Formula and Constants Sheet/Periodic Table of the Elements. Copies of both sides of this formula sheet follow the final question in this chapter. Each student also had sole access to a calc ...
aq - Wikispaces
... If there is NO decimal, the situation is ambiguous, and a bit of a JUDGEMENT CALL. If you trust the source to be precise, then you count all the zeros at the end. If you have reason to believe the person was estimating, then you don’t count the zeros at the end. ...
... If there is NO decimal, the situation is ambiguous, and a bit of a JUDGEMENT CALL. If you trust the source to be precise, then you count all the zeros at the end. If you have reason to believe the person was estimating, then you don’t count the zeros at the end. ...
zum_ic6e_ch04_lecture_ppt_23
... • Each element is represented by its symbol. • The number of each type of atom is indicated by a subscript written to the right of the element symbol. • If only one atom is present, do not include a subscript. • If polyatomic groups are present in the molecule, they are written inside parentheses if ...
... • Each element is represented by its symbol. • The number of each type of atom is indicated by a subscript written to the right of the element symbol. • If only one atom is present, do not include a subscript. • If polyatomic groups are present in the molecule, they are written inside parentheses if ...
Chapter 2
... An element is a substance that cannot be broken down into two or more simpler substances by any means. Examples: gold, oxygen, helium ...
... An element is a substance that cannot be broken down into two or more simpler substances by any means. Examples: gold, oxygen, helium ...
atom
... Determine (a) the number of moles of C in 25.00 g of carbon, (b) the number of moles of He in 10.50 g of helium, and (c) the number of moles of Na in 15.75 g of sodium. Strategy Molar mass of an element is numerically equal to its average atomic mass. Use the molar mass for each element to convert f ...
... Determine (a) the number of moles of C in 25.00 g of carbon, (b) the number of moles of He in 10.50 g of helium, and (c) the number of moles of Na in 15.75 g of sodium. Strategy Molar mass of an element is numerically equal to its average atomic mass. Use the molar mass for each element to convert f ...
ppt
... including C, S, Cu, Ag, Au, Fe, Sn, Sb and Pb. The names of most of these are from the Latin words. ...
... including C, S, Cu, Ag, Au, Fe, Sn, Sb and Pb. The names of most of these are from the Latin words. ...
Acquiring the Foundation: The Periodic Table for Middle
... animated periodic table of the first eighteen elements on the periodic table of elements. The animated periodic table of elements will be organized according to the same principles Mendeleyev used when he placed elements in the original periodic table. This unit will help students build a strong fou ...
... animated periodic table of the first eighteen elements on the periodic table of elements. The animated periodic table of elements will be organized according to the same principles Mendeleyev used when he placed elements in the original periodic table. This unit will help students build a strong fou ...
atoms - ChilhowieMiddleSchool
... Matter is made up of atoms Atoms cannot be divided. All atoms of the same element are alike. Different elements are made of different atoms. ...
... Matter is made up of atoms Atoms cannot be divided. All atoms of the same element are alike. Different elements are made of different atoms. ...
LIQUIDS
... This theory assumes that all elements are made up of "atoms". If you were to divide a lump of an element into smaller and smaller pieces you would eventually come to a piece that could not be divided any further - a single ATOM of the element. Atoms are therefore very small. We can see this if we di ...
... This theory assumes that all elements are made up of "atoms". If you were to divide a lump of an element into smaller and smaller pieces you would eventually come to a piece that could not be divided any further - a single ATOM of the element. Atoms are therefore very small. We can see this if we di ...
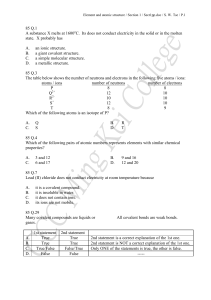
85 Q.1 A substance X melts at 1600oC. Its does
... M is an element in the third period of the Periodic Table. M forms a sulphate which has the formula M2(SO4)3. The formula of the nitrate of M is A. C. ...
... M is an element in the third period of the Periodic Table. M forms a sulphate which has the formula M2(SO4)3. The formula of the nitrate of M is A. C. ...
Chemistry 11 – Course Review
... Element “X” is composed of the following naturally occurring isotopes: Isotope ...
... Element “X” is composed of the following naturally occurring isotopes: Isotope ...
Atomic Structure Powerpoints - Warren County Public Schools
... • I can recognize that the periodic table is organized by an element’s atomic number. • I can divide the elements in the periodic table into periods and groups. • I can identify and distinguish between metals, nonmetals, and metalloids on the periodic table. • I can determine if an atom is neutral o ...
... • I can recognize that the periodic table is organized by an element’s atomic number. • I can divide the elements in the periodic table into periods and groups. • I can identify and distinguish between metals, nonmetals, and metalloids on the periodic table. • I can determine if an atom is neutral o ...
Bohr, Niels Henrik David
... their atoms and that only the atomic weight and possible radioactive behaviour are determined by the small but massive nucleus itself. Rutherford's nuclear atom was both mechanically and electromagnetically unstable, but Bohr imposed stability on it by introducing the new and not yet clarified idea ...
... their atoms and that only the atomic weight and possible radioactive behaviour are determined by the small but massive nucleus itself. Rutherford's nuclear atom was both mechanically and electromagnetically unstable, but Bohr imposed stability on it by introducing the new and not yet clarified idea ...