EXPERIMENT 4 – The Periodic Table
... In this experiment, you will be looking at some elements in the laboratory display. Some look different from each other, while others look similar. Elements can be categorized in several ways. In this experiment, you are going to group elements by similarities in their physical properties. Elements ...
... In this experiment, you will be looking at some elements in the laboratory display. Some look different from each other, while others look similar. Elements can be categorized in several ways. In this experiment, you are going to group elements by similarities in their physical properties. Elements ...
Atomic Timeline - Ms Brown`s Chemistry Page
... Atoms, Ions and Isotopes • The number of protons in an atom NEVER changes. This is how you identify an element. If the number of protons are changed, you have a whole new element. Atoms are electrically neutral (protons = electrons). • If an atom is heavier/lighter than expected (greater or lower a ...
... Atoms, Ions and Isotopes • The number of protons in an atom NEVER changes. This is how you identify an element. If the number of protons are changed, you have a whole new element. Atoms are electrically neutral (protons = electrons). • If an atom is heavier/lighter than expected (greater or lower a ...
Foldable - Georgetown ISD
... Ions: when an atom has lost or gained electrons it becomes an ion. Ions have either a positive or negative charge. Atoms do not have a charge because in an ATOM the #protons = #electrons. To calculate the charge of an ion = #protons - #electrons Example: Write the nuclear symbol for an ion with 10 e ...
... Ions: when an atom has lost or gained electrons it becomes an ion. Ions have either a positive or negative charge. Atoms do not have a charge because in an ATOM the #protons = #electrons. To calculate the charge of an ion = #protons - #electrons Example: Write the nuclear symbol for an ion with 10 e ...
EXPERIMENT 4 – The Periodic Table
... In this experiment, you will be looking at some elements in the laboratory display. Some look different from each other, while others look similar. Elements can be categorized in several ways. In this experiment, you are going to group elements by similarities in their physical properties. Elements ...
... In this experiment, you will be looking at some elements in the laboratory display. Some look different from each other, while others look similar. Elements can be categorized in several ways. In this experiment, you are going to group elements by similarities in their physical properties. Elements ...
Name: Date: ______ Period: Unit 3 – Atomic Structure Review
... 1. Who was the ancient Greek philosopher who first proposed the notion of the atom? Democritus 2. What was Dalton’s atomic model called? Billard ball model 3. Who’s model first introduced the concept of energy levels? Bohr 4. What were the major problems of Dalton’s atomic theory? Did not have an in ...
... 1. Who was the ancient Greek philosopher who first proposed the notion of the atom? Democritus 2. What was Dalton’s atomic model called? Billard ball model 3. Who’s model first introduced the concept of energy levels? Bohr 4. What were the major problems of Dalton’s atomic theory? Did not have an in ...
HighFour Chemistry Round 1 Category C: Grades 9 – 10 Thursday
... equivalent to the atomic number because the number of protons remains unchanged during reactions. Referring to Table 24 (Periodic Table) of the Chemistry Data Booklet, the element with an atomic number of 15 is phosphorus, P. ...
... equivalent to the atomic number because the number of protons remains unchanged during reactions. Referring to Table 24 (Periodic Table) of the Chemistry Data Booklet, the element with an atomic number of 15 is phosphorus, P. ...
Chapter 4 Cornell Notes
... ____________________ of large atoms into smaller pieces) and nuclear ____________________ (the ____________________ of small atoms into one large one), but on earth these reactions do not occur naturally. 2) Naturally occurring nuclear reactions result from the unusual number of neutrons of an isoto ...
... ____________________ of large atoms into smaller pieces) and nuclear ____________________ (the ____________________ of small atoms into one large one), but on earth these reactions do not occur naturally. 2) Naturally occurring nuclear reactions result from the unusual number of neutrons of an isoto ...
Early Atomic Theory - Columbia University
... a calcium ion It is 58.69 / 10.81 = 5.29 times as heavy as a boron ion Element ...
... a calcium ion It is 58.69 / 10.81 = 5.29 times as heavy as a boron ion Element ...
atom - Images
... protons and neutrons are about same size electrons are much smaller nuclear force- when particles in the nucleus get very close, they have a strong attraction ...
... protons and neutrons are about same size electrons are much smaller nuclear force- when particles in the nucleus get very close, they have a strong attraction ...
Atomic Structure
... isotopes. Isotopes will have the same atomic number as other atoms of the same element. However, they will have a different atomic mass due to the different number of neutrons. Isotopes of a specific element will have different properties. To account for the different masses of an element's isotopes ...
... isotopes. Isotopes will have the same atomic number as other atoms of the same element. However, they will have a different atomic mass due to the different number of neutrons. Isotopes of a specific element will have different properties. To account for the different masses of an element's isotopes ...
Chapter 5: Atomic Structure & The Periodic Table
... experimental support because scientific testing was unknown at the time. 2000 years after Democritus, the real nature of atoms and observable changes at the atomic level were established. John Dalton (1766-1844)—English school teacher, performed experiments to test and correct his atomic theory. ...
... experimental support because scientific testing was unknown at the time. 2000 years after Democritus, the real nature of atoms and observable changes at the atomic level were established. John Dalton (1766-1844)—English school teacher, performed experiments to test and correct his atomic theory. ...
Chapter 4 Review
... atoms of the same element have the same _____. Know Dalton’s Atomic Theory. An element has an atomic number of 76. What is the number of protons and electrons in a neutral atom of this element? How is the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom calculated? ...
... atoms of the same element have the same _____. Know Dalton’s Atomic Theory. An element has an atomic number of 76. What is the number of protons and electrons in a neutral atom of this element? How is the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom calculated? ...
Chapter Two Atoms & The Periodic Table
... The atomic masses of two stable isotopes of copper, copper-63 and copper 65, are 62.929599 and 64.927793 amu, respectively. If copper-63 is 69.17% and copper-65 is 30.83%, what is the average atomic mass of ...
... The atomic masses of two stable isotopes of copper, copper-63 and copper 65, are 62.929599 and 64.927793 amu, respectively. If copper-63 is 69.17% and copper-65 is 30.83%, what is the average atomic mass of ...
Chapter 2 Lect. 1
... 2. Sizes: Nucleus = ball bearing; Atom = football stadium 3. Mass: essentially all the mass is at the nucleus (7300:1 ratio proton to electron mass) 4. The chemistry of the atom is primarily due to the electrons a. Different elements have different numbers of protons and electrons b. This leads to ...
... 2. Sizes: Nucleus = ball bearing; Atom = football stadium 3. Mass: essentially all the mass is at the nucleus (7300:1 ratio proton to electron mass) 4. The chemistry of the atom is primarily due to the electrons a. Different elements have different numbers of protons and electrons b. This leads to ...
Ch 2 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... - The formula is a type of notation using atomic symbols and integer subscripts. - A molecule is a finite arrangement of atoms chemically bonded together. The molecule has particular chemical bonds, as well a 3D structure. Generally, all of the atoms in a molecule are nonmetals. - The molecular form ...
... - The formula is a type of notation using atomic symbols and integer subscripts. - A molecule is a finite arrangement of atoms chemically bonded together. The molecule has particular chemical bonds, as well a 3D structure. Generally, all of the atoms in a molecule are nonmetals. - The molecular form ...
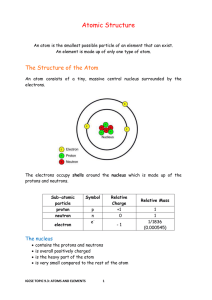
9.3 Atoms and Elements notes
... number of electrons in an atom = number of protons Electrons are arranged in energy levels (also known as shells) around the nucleus. The lowest energy levels are always filled first. These are closer to the nucleus and hold the least numbers of electrons. The first energy level can only hold 2 el ...
... number of electrons in an atom = number of protons Electrons are arranged in energy levels (also known as shells) around the nucleus. The lowest energy levels are always filled first. These are closer to the nucleus and hold the least numbers of electrons. The first energy level can only hold 2 el ...
CHAPTER 4: ATOMS AND ELEMENTS
... Nuclear Symbol (also called “Atomic Notation”): – shorthand for keeping track of number of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus atomic number: whole number of protons = number of electrons in a neutral atom mass number: # of protons + # of neutrons in an atom’s nucleus # of protons + # of neutr ...
... Nuclear Symbol (also called “Atomic Notation”): – shorthand for keeping track of number of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus atomic number: whole number of protons = number of electrons in a neutral atom mass number: # of protons + # of neutrons in an atom’s nucleus # of protons + # of neutr ...
Atomic Model
... – Electrons are in probability zones called “orbitals”, not orbits and the location cannot be pinpointed – Electrons are particles and waves at the same time – Developed quantum numbers based on theories of Einstein and Planck ...
... – Electrons are in probability zones called “orbitals”, not orbits and the location cannot be pinpointed – Electrons are particles and waves at the same time – Developed quantum numbers based on theories of Einstein and Planck ...
Topic one midterm review
... Location of Electrons • Energy levels – The orbitals in an atom form a series of energy levels in which electrons may be found. – Each electron in an atom has its own distinct amount of energy that corresponds to the energy level that it occupies. • Electrons can gain or lose energy and move to dif ...
... Location of Electrons • Energy levels – The orbitals in an atom form a series of energy levels in which electrons may be found. – Each electron in an atom has its own distinct amount of energy that corresponds to the energy level that it occupies. • Electrons can gain or lose energy and move to dif ...
Chemical Bond – a force that holds two atoms together, the bond
... Metallic Bond – is the attraction of a metallic cation for delocalized electrons; electrons are not localized to one metallic atom. Delocalized Electrons – electrons that freely move from one metallic atom to another metallic atom. Covalent Bond – a chemical bond between two different atomic elemen ...
... Metallic Bond – is the attraction of a metallic cation for delocalized electrons; electrons are not localized to one metallic atom. Delocalized Electrons – electrons that freely move from one metallic atom to another metallic atom. Covalent Bond – a chemical bond between two different atomic elemen ...
atomic number - Teacher Pages
... – Group Two – Alkaline Earth Metals: reactive, but not as reactive as alkali metals, also not found uncombined in nature. – Group 3 – Group 12 – Transition Metals: They form a bridge between the very reactive metals on the left and the less reactive metals on the right. – Group 13-16 – includes meta ...
... – Group Two – Alkaline Earth Metals: reactive, but not as reactive as alkali metals, also not found uncombined in nature. – Group 3 – Group 12 – Transition Metals: They form a bridge between the very reactive metals on the left and the less reactive metals on the right. – Group 13-16 – includes meta ...
Atomic Structure Worksheet
... Look at the atomic weights of a few different elements on your periodic table. Do you notice that very few of the elements have atomic weights that are close to being nice whole numbers? Do you know why this is? After all, for our purposes, the mass of both the proton and the neutron are almost exac ...
... Look at the atomic weights of a few different elements on your periodic table. Do you notice that very few of the elements have atomic weights that are close to being nice whole numbers? Do you know why this is? After all, for our purposes, the mass of both the proton and the neutron are almost exac ...
document
... • All atoms in Group 1A have one valence electron, Group 2A have 2 valence electrons, Group 3A have 3 valence electrons etc… • Valence electrons are typically represented in one of two ways: electron configuration (not covered in this class) and Lewis dot symbols (also called electron-dot symbols). ...
... • All atoms in Group 1A have one valence electron, Group 2A have 2 valence electrons, Group 3A have 3 valence electrons etc… • Valence electrons are typically represented in one of two ways: electron configuration (not covered in this class) and Lewis dot symbols (also called electron-dot symbols). ...
Mileposts on the road to the atom (download)
... Proposed that atoms of heavier elements were made from hydrogen atoms Implication that larger atoms comprise smaller units Partial truth: there are common factors between atoms of different elements But they are not H atoms… ...
... Proposed that atoms of heavier elements were made from hydrogen atoms Implication that larger atoms comprise smaller units Partial truth: there are common factors between atoms of different elements But they are not H atoms… ...