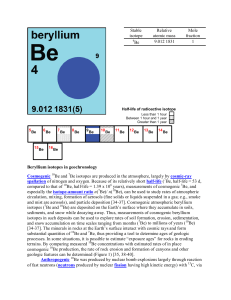
Beryllium isotopes in geochronology Cosmogenic Be and Be
... cosmic rays – extremely high-energy radiation, mainly originating outside the Solar System, consisting of one or more charged particles, such as protons, alpha particles, and larger atomic nuclei. [return] cosmogenic – produced by the interaction of Earth materials (soil, rock, and atmosphere) and m ...
... cosmic rays – extremely high-energy radiation, mainly originating outside the Solar System, consisting of one or more charged particles, such as protons, alpha particles, and larger atomic nuclei. [return] cosmogenic – produced by the interaction of Earth materials (soil, rock, and atmosphere) and m ...
Dalton`s Atomic Theory
... Atoms have very small masses - the heaviest known atom is about 4 x 10−22 g Therefore, atomic mass unit (amu) is used to describe the mass of an individual atom The proton and neutron have nearly identical mass, and are much heavier than the electron (1 proton has same mass as 1836 electrons) ...
... Atoms have very small masses - the heaviest known atom is about 4 x 10−22 g Therefore, atomic mass unit (amu) is used to describe the mass of an individual atom The proton and neutron have nearly identical mass, and are much heavier than the electron (1 proton has same mass as 1836 electrons) ...
Slide 1
... atom, its protons and neutrons. • A single atom of lithium contains 3 protons and 4 neutrons and thus has a mass number of 7. • In almost all elements there exists a small fraction of atoms of the element that have different numbers of neutrons • Atoms with the same number of protons but different n ...
... atom, its protons and neutrons. • A single atom of lithium contains 3 protons and 4 neutrons and thus has a mass number of 7. • In almost all elements there exists a small fraction of atoms of the element that have different numbers of neutrons • Atoms with the same number of protons but different n ...
chapter 2 - Columbia University
... Mass Number, A Atoms of the same element can differ in mass number A = number of protons + number of neutrons Isotope ...
... Mass Number, A Atoms of the same element can differ in mass number A = number of protons + number of neutrons Isotope ...
Ch. 6 Vocabulary
... • atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons ...
... • atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons ...
Chapter 14 Inside the Atom Notes
... nucleus of an atom. 1. Isotopes of an atom have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons (pg. 415). 2. Mass number is the number of neutrons plus the number of protons. 3. Average atomic mass – the average mass of the mixture of an element’s isotopes ...
... nucleus of an atom. 1. Isotopes of an atom have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons (pg. 415). 2. Mass number is the number of neutrons plus the number of protons. 3. Average atomic mass – the average mass of the mixture of an element’s isotopes ...
File
... 13. What does the quantum mechanical model determine about electrons in atoms? 14. How do two sublevels of the same principal energy level differ from each other? 15. What are the three rules for writing the electron configuration of elements? 16. Explain why the actual electron configurations for s ...
... 13. What does the quantum mechanical model determine about electrons in atoms? 14. How do two sublevels of the same principal energy level differ from each other? 15. What are the three rules for writing the electron configuration of elements? 16. Explain why the actual electron configurations for s ...
Chemistry is a material science
... definition of matter leads to a common property of matter, namely, _______. Density is equal to the mass divided by the volume. The “__________” of matter is its composition. This addresses the question what ______ of atoms and molecules are present in this matter. Matter composed of _______ kind of ...
... definition of matter leads to a common property of matter, namely, _______. Density is equal to the mass divided by the volume. The “__________” of matter is its composition. This addresses the question what ______ of atoms and molecules are present in this matter. Matter composed of _______ kind of ...
Test Review - Alvinisd.net
... 1. Which of John Dalton’s postulates are still considered to be true today? 2. Which of John Dalton’s postulates are NOT considered to be true today? 3. What was discovered in the cathode ray tube experiment? 4. What did Ernest Rutherford’s gold foil experiment discover? (actually 4 discoveries) 5. ...
... 1. Which of John Dalton’s postulates are still considered to be true today? 2. Which of John Dalton’s postulates are NOT considered to be true today? 3. What was discovered in the cathode ray tube experiment? 4. What did Ernest Rutherford’s gold foil experiment discover? (actually 4 discoveries) 5. ...
Atomic Mass Lab (Flaskum)
... The atomic mass of an atom is equal to the sum of the protons and neutrons in the atom’s nucleus. Since both the proton and neutron have a mass of 1 amu, the mass of an atom is measured in atomic mass units. Because atoms are so small, it is impossible to count the number of protons and neutrons in ...
... The atomic mass of an atom is equal to the sum of the protons and neutrons in the atom’s nucleus. Since both the proton and neutron have a mass of 1 amu, the mass of an atom is measured in atomic mass units. Because atoms are so small, it is impossible to count the number of protons and neutrons in ...
1st Term Review
... 11. What element has the following electron configuration? 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p65s24d5 12. Dalton believed that all atoms of the same element are exactly alike. What discovery has since proved that untrue? 13. What is the mass of grams of 0.500 moles of Au? 14. Based on the gold foil experiment, ...
... 11. What element has the following electron configuration? 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p65s24d5 12. Dalton believed that all atoms of the same element are exactly alike. What discovery has since proved that untrue? 13. What is the mass of grams of 0.500 moles of Au? 14. Based on the gold foil experiment, ...
The Basics of Atomic Structure
... – Cation is a positive ion (created when an atom loses electrons) – Anion is an negative ion (created when an atom gains electrons) Notice: it’s the number of electrons and neutrons that change, not the atomic number! ...
... – Cation is a positive ion (created when an atom loses electrons) – Anion is an negative ion (created when an atom gains electrons) Notice: it’s the number of electrons and neutrons that change, not the atomic number! ...
Isotopes - Cloudfront.net
... Apply the Law of Conservation of Mass to get the same number of atoms of every element on each side of the equation. Start by balancing an element that appears in only one reactant ...
... Apply the Law of Conservation of Mass to get the same number of atoms of every element on each side of the equation. Start by balancing an element that appears in only one reactant ...
Matter Review
... – The number of electrons on the outer most shell (valence electrons) – Draw the atoms for each ...
... – The number of electrons on the outer most shell (valence electrons) – Draw the atoms for each ...
Models of the Atom: A Historical perspective
... • Most particles passed through • So, atoms are mostly empty space ...
... • Most particles passed through • So, atoms are mostly empty space ...
ATOMIC THEORY Philosophical Idea to Scientific Theory
... 1. All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms which cannot be subdivided, created or destroyed. ...
... 1. All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms which cannot be subdivided, created or destroyed. ...
NOTES – 14.1 – Structure of the Atom (FPS3)
... We say an object is electrically neutral when its total electric charge is zero. Atoms are normally neutral, but the things that make them up are charged. ...
... We say an object is electrically neutral when its total electric charge is zero. Atoms are normally neutral, but the things that make them up are charged. ...
Name Class Block ______ Directions: Read the following article
... The Greek philosopher Democritus named the tiny particles everything was made of “atoms.” Although Democritus had no way to test his theory, he was correct. Today, we know atoms are the building blocks of matter. Because scientists did not have instruments to see atoms, Democritus’ ideas were forgot ...
... The Greek philosopher Democritus named the tiny particles everything was made of “atoms.” Although Democritus had no way to test his theory, he was correct. Today, we know atoms are the building blocks of matter. Because scientists did not have instruments to see atoms, Democritus’ ideas were forgot ...
Element Blocks Project
... Your assignment is to produce an element block that will have six sides, each having different information about your element. Elements will be assigned randomly. Your teacher will show you how to make the block after you have researched and obtained all the information that will go onto you block. ...
... Your assignment is to produce an element block that will have six sides, each having different information about your element. Elements will be assigned randomly. Your teacher will show you how to make the block after you have researched and obtained all the information that will go onto you block. ...
Chemistry - Rainhill High School
... MEDIA ARTS COLLEGE YEAR 9 CHEMISTRY HALF-TERM 1 This half term I will learn: The structure of the atom in terms of its sub atomic particles. How they make elements compounds and mixture and how they are separated. Groups and periods and how electronic configuration contributes to simple bonding mode ...
... MEDIA ARTS COLLEGE YEAR 9 CHEMISTRY HALF-TERM 1 This half term I will learn: The structure of the atom in terms of its sub atomic particles. How they make elements compounds and mixture and how they are separated. Groups and periods and how electronic configuration contributes to simple bonding mode ...
Test 1
... The mass of an atom in amu is approximated as the number of photons plus the number of neutrons present in the nucleus. Atoms can be split into a nucleus and the electrons, and the electrons move around the nucleus. Different isotopes of an element contain different numbers of neutrons. The three pr ...
... The mass of an atom in amu is approximated as the number of photons plus the number of neutrons present in the nucleus. Atoms can be split into a nucleus and the electrons, and the electrons move around the nucleus. Different isotopes of an element contain different numbers of neutrons. The three pr ...
I. Structure of the Atom
... • Round off the atomic mass listed on the table and subtract the atomic # to find the # of neutrons. • Abbreviate the # of ‘p’ and ‘n’ in the nucleus. Have a partner check your drawing. Repeat with a new element. ...
... • Round off the atomic mass listed on the table and subtract the atomic # to find the # of neutrons. • Abbreviate the # of ‘p’ and ‘n’ in the nucleus. Have a partner check your drawing. Repeat with a new element. ...
Chemical element
A chemical element (or element) is a chemical substance consisting of atoms having the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei (i.e. the same atomic number, Z). There are 118 elements that have been identified, of which the first 94 occur naturally on Earth with the remaining 24 being synthetic elements. There are 80 elements that have at least one stable isotope and 38 that have exclusively radioactive isotopes, which decay over time into other elements. Iron is the most abundant element (by mass) making up the Earth, while oxygen is the most common element in the crust of the earth.Chemical elements constitute approximately 15% of the matter in the universe: the remainder is dark matter, the composition of it is unknown, but it is not composed of chemical elements.The two lightest elements, hydrogen and helium were mostly formed in the Big Bang and are the most common elements in the universe. The next three elements (lithium, beryllium and boron) were formed mostly by cosmic ray spallation, and are thus more rare than those that follow. Formation of elements with from six to twenty six protons occurred and continues to occur in main sequence stars via stellar nucleosynthesis. The high abundance of oxygen, silicon, and iron on Earth reflects their common production in such stars. Elements with greater than twenty six protons are formed by supernova nucleosynthesis in supernovae, which, when they explode, blast these elements far into space as planetary nebulae, where they may become incorporated into planets when they are formed.When different elements are chemically combined, with the atoms held together by chemical bonds, they form chemical compounds. Only a minority of elements are found uncombined as relatively pure minerals. Among the more common of such ""native elements"" are copper, silver, gold, carbon (as coal, graphite, or diamonds), and sulfur. All but a few of the most inert elements, such as noble gases and noble metals, are usually found on Earth in chemically combined form, as chemical compounds. While about 32 of the chemical elements occur on Earth in native uncombined forms, most of these occur as mixtures. For example, atmospheric air is primarily a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and argon, and native solid elements occur in alloys, such as that of iron and nickel.The history of the discovery and use of the elements began with primitive human societies that found native elements like carbon, sulfur, copper and gold. Later civilizations extracted elemental copper, tin, lead and iron from their ores by smelting, using charcoal. Alchemists and chemists subsequently identified many more, with almost all of the naturally-occurring elements becoming known by 1900. The properties of the chemical elements are summarized on the periodic table, which organizes the elements by increasing atomic number into rows (""periods"") in which the columns (""groups"") share recurring (""periodic"") physical and chemical properties. Save for unstable radioactive elements with short half-lives, all of the elements are available industrially, most of them in high degrees of purity.























