1. All matter is made up of
... 3. What is the atomic mass for Argon? 4. How many electrons does an atom of H have? 5. How many neutrons are in an atom of Li? 6. How many electrons are in an atom of Si? 7. How many protons and neutrons are in an atom of Argon? ...
... 3. What is the atomic mass for Argon? 4. How many electrons does an atom of H have? 5. How many neutrons are in an atom of Li? 6. How many electrons are in an atom of Si? 7. How many protons and neutrons are in an atom of Argon? ...
Name: : ______ Chemistry—Matter, Atoms, and More Visit the
... _________________. Matter is anything that has a _________________. As of ___________ scientists have identified ___________________ states of matter. 12. You should know about ______________, _______________, _______________, and plasmas, and a new one called ________________-__________________ __ ...
... _________________. Matter is anything that has a _________________. As of ___________ scientists have identified ___________________ states of matter. 12. You should know about ______________, _______________, _______________, and plasmas, and a new one called ________________-__________________ __ ...
Chapter 3 pages 65
... same two elements, then the ratio of the masses of the second element combined with a certain mass of the first element is always a ratio of small whole numbers Daltons Atomic Theory 1) All matter made up of atoms 2) Atoms of same element have same size, mass, and other properties 3) Atoms cannot be ...
... same two elements, then the ratio of the masses of the second element combined with a certain mass of the first element is always a ratio of small whole numbers Daltons Atomic Theory 1) All matter made up of atoms 2) Atoms of same element have same size, mass, and other properties 3) Atoms cannot be ...
Atoms and isotopes MS
... Correct formulas [1], balancing of correct equation [1]. 2Na + 2T2O 2NaOT + T2; Correct formulas [1], balancing of correct equation [1]. If H is used instead of T in any of the equations [3 max]. Accept any other suitable equation for both parts. ...
... Correct formulas [1], balancing of correct equation [1]. 2Na + 2T2O 2NaOT + T2; Correct formulas [1], balancing of correct equation [1]. If H is used instead of T in any of the equations [3 max]. Accept any other suitable equation for both parts. ...
Atom through Periodic Table Study Guide
... 16. Periods go ____(which way) on the periodic table, while rows go ____(which way). 17. Which family has elements that are highly reactive non-metals and has 7 valence electrons? 18. The noble gases are found in which column of the periodic table? 19. The noble gases are non-reactive- they won’t b ...
... 16. Periods go ____(which way) on the periodic table, while rows go ____(which way). 17. Which family has elements that are highly reactive non-metals and has 7 valence electrons? 18. The noble gases are found in which column of the periodic table? 19. The noble gases are non-reactive- they won’t b ...
CHE111-2 Atoms Molecules Ions
... The Greek Philosopher Democritus expressed the belief that all matter consists of tiny, indivisible particles. He named these particles atomos, which means indivisible. In 1808, John Dalton formulated a definition of the atom and thus Dalton’s Atomic theory says this: 1)-Elements are made up of extr ...
... The Greek Philosopher Democritus expressed the belief that all matter consists of tiny, indivisible particles. He named these particles atomos, which means indivisible. In 1808, John Dalton formulated a definition of the atom and thus Dalton’s Atomic theory says this: 1)-Elements are made up of extr ...
Inside the Atom 1. Atom – greek for cannot be divided. Democritus
... b. Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons = isotopes c. The nucleus can become unstable if there are too many neutrons for the number of protons creating a radioactive isotope 2. Radioactive isotopes a. Give off radiation in the form of alpha, beta, and gamma particles b. ...
... b. Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons = isotopes c. The nucleus can become unstable if there are too many neutrons for the number of protons creating a radioactive isotope 2. Radioactive isotopes a. Give off radiation in the form of alpha, beta, and gamma particles b. ...
100610 chem a GALL
... The atomic number is the number of protons. The mass number is the average sum of the protons and neutrons. For example, Hydrogen has an atomic number of one because it has one proton. Hydrogen only SOMETIMES has a neutron... The average mass of a hydrogen atom is 1.0079 amu. ...
... The atomic number is the number of protons. The mass number is the average sum of the protons and neutrons. For example, Hydrogen has an atomic number of one because it has one proton. Hydrogen only SOMETIMES has a neutron... The average mass of a hydrogen atom is 1.0079 amu. ...
Atomic Theory Notes
... All atoms of the same element are identical in mass and properties All atoms of different elements are different in mass and properties ...
... All atoms of the same element are identical in mass and properties All atoms of different elements are different in mass and properties ...
Outline Chapter 10 The Periodic Law
... 10-13. Ionic Bond Ionic bond = formed when electrons are transferred between two or more atoms and the resulting ions of opposite charge attract each other. 10-14. Ionic Compounds When a metal atom combines with a nonmetal atom to form an ionic compound, the chemical formula of the ionic compound fo ...
... 10-13. Ionic Bond Ionic bond = formed when electrons are transferred between two or more atoms and the resulting ions of opposite charge attract each other. 10-14. Ionic Compounds When a metal atom combines with a nonmetal atom to form an ionic compound, the chemical formula of the ionic compound fo ...
Copy of 427
... particular significance in this course. Hydrogen has three isotopes shown in Figure 1.2. The first two occur naturally, although deuterium is only 0.015% abundant (about one atom in every 7000). Unfortunately we need deuterium in the form of heavy water (D 2 0) to make the CANDU reactor work. This r ...
... particular significance in this course. Hydrogen has three isotopes shown in Figure 1.2. The first two occur naturally, although deuterium is only 0.015% abundant (about one atom in every 7000). Unfortunately we need deuterium in the form of heavy water (D 2 0) to make the CANDU reactor work. This r ...
Chapter 2 Law of
... neutrons in an atom. • Isotopes of the same element have the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons. ...
... neutrons in an atom. • Isotopes of the same element have the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons. ...
Slide 1
... Postulates of Dalton’s Atomic Theory Atoms are the smallest unit of matter. An atom is an extremely small particle of matter that retains its identity during chemical reactions. Atoms of Element A cannot be converted to Atoms of element B Atoms of the same element are identical. Each atom of an elem ...
... Postulates of Dalton’s Atomic Theory Atoms are the smallest unit of matter. An atom is an extremely small particle of matter that retains its identity during chemical reactions. Atoms of Element A cannot be converted to Atoms of element B Atoms of the same element are identical. Each atom of an elem ...
Atoms and Atomic Theory
... So what does it mean, and where does the 0.5 come from? Here is the explanation. The non integer values mean that there is more than one isotope of chlorine that exists in nature, in this case 35Cl and 37Cl. A quick calculation will tell you that these two species have the same number of protons and ...
... So what does it mean, and where does the 0.5 come from? Here is the explanation. The non integer values mean that there is more than one isotope of chlorine that exists in nature, in this case 35Cl and 37Cl. A quick calculation will tell you that these two species have the same number of protons and ...
Inside the Atom connections to the lower secondary (KS3
... Atoms, elements and compounds. Pupils are taught about: • a simple (Dalton) atomic model • differences between atoms, elements and compounds • chemical symbols and formulae for elements and compounds • conservation of mass changes of state and chemical reactions. Most of the nuclear physics rela ...
... Atoms, elements and compounds. Pupils are taught about: • a simple (Dalton) atomic model • differences between atoms, elements and compounds • chemical symbols and formulae for elements and compounds • conservation of mass changes of state and chemical reactions. Most of the nuclear physics rela ...
Modern Atomic Theory and The Periodic Table
... –This periodic table now contains information regarding the chemical symbol, atomic number, average atomic mass, physical state of each element, group’s numbers, electron configurations, as well as many other useful characteristics. –Recently accepted names for elements 104-109 have been added. –Thi ...
... –This periodic table now contains information regarding the chemical symbol, atomic number, average atomic mass, physical state of each element, group’s numbers, electron configurations, as well as many other useful characteristics. –Recently accepted names for elements 104-109 have been added. –Thi ...
A quick summary about atoms: Atomic masses and/or hydrogen
... Atoms were used by John Dalton (1804) to explain the Law of Definite Proportions: if elements combine only in definite proportions by weight, the simplest explanation is that whole numbers of atoms combine into specific molecules. Atoms were considered to be indivisible, the smallest possible pieces ...
... Atoms were used by John Dalton (1804) to explain the Law of Definite Proportions: if elements combine only in definite proportions by weight, the simplest explanation is that whole numbers of atoms combine into specific molecules. Atoms were considered to be indivisible, the smallest possible pieces ...
the Atom
... tiny, indivisible, indestructible particles. Each one has a certain mass, size, and chemical behavior that was determined by what kind of element they were. A Summary of Dalton’s Atomic Theory: ...
... tiny, indivisible, indestructible particles. Each one has a certain mass, size, and chemical behavior that was determined by what kind of element they were. A Summary of Dalton’s Atomic Theory: ...
Zumdahl`s Chapter 2
... tissue proving protons (p+) in nucleus F.A. Aston (1919) “weighs” atomic ions J. Chadwick (1939) observes neutrons (no charge) by decomposition (to p+, e–, and ). ...
... tissue proving protons (p+) in nucleus F.A. Aston (1919) “weighs” atomic ions J. Chadwick (1939) observes neutrons (no charge) by decomposition (to p+, e–, and ). ...
Chemistry Content Standards
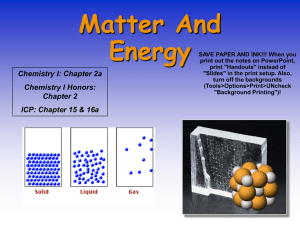
... physical processes. a. Compare and contrast atomic/molecular motion in solids, liquids, gases, and plasmas. b. Collect data and calculate the amount of heat given off or taken in by chemical or physical processes. c. Analyzing (both conceptually and quantitatively) flow of energy during change of st ...
... physical processes. a. Compare and contrast atomic/molecular motion in solids, liquids, gases, and plasmas. b. Collect data and calculate the amount of heat given off or taken in by chemical or physical processes. c. Analyzing (both conceptually and quantitatively) flow of energy during change of st ...
Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
... Scientists once thought these metals were available only in tiny amounts on the Earth ...
... Scientists once thought these metals were available only in tiny amounts on the Earth ...
atoms and elements
... An atom is the smallest particle into which an element can be divided and still maintain the properties of that element. All elements are made of atoms. So what’s an element? What makes one element different from another? Let’s find out! Vocabulary: First things first, let’s look at the structure of ...
... An atom is the smallest particle into which an element can be divided and still maintain the properties of that element. All elements are made of atoms. So what’s an element? What makes one element different from another? Let’s find out! Vocabulary: First things first, let’s look at the structure of ...
Discovery Education Science Connection
... make compounds. Why would some elements react explosively? Why would some elements not react at all? The Development of the Atomic Model To answer these questions, scientists returned to the atomic model. John Dalton, a 19th-century English chemist, proposed that all elements were made of atoms. His ...
... make compounds. Why would some elements react explosively? Why would some elements not react at all? The Development of the Atomic Model To answer these questions, scientists returned to the atomic model. John Dalton, a 19th-century English chemist, proposed that all elements were made of atoms. His ...
Chemical element
A chemical element (or element) is a chemical substance consisting of atoms having the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei (i.e. the same atomic number, Z). There are 118 elements that have been identified, of which the first 94 occur naturally on Earth with the remaining 24 being synthetic elements. There are 80 elements that have at least one stable isotope and 38 that have exclusively radioactive isotopes, which decay over time into other elements. Iron is the most abundant element (by mass) making up the Earth, while oxygen is the most common element in the crust of the earth.Chemical elements constitute approximately 15% of the matter in the universe: the remainder is dark matter, the composition of it is unknown, but it is not composed of chemical elements.The two lightest elements, hydrogen and helium were mostly formed in the Big Bang and are the most common elements in the universe. The next three elements (lithium, beryllium and boron) were formed mostly by cosmic ray spallation, and are thus more rare than those that follow. Formation of elements with from six to twenty six protons occurred and continues to occur in main sequence stars via stellar nucleosynthesis. The high abundance of oxygen, silicon, and iron on Earth reflects their common production in such stars. Elements with greater than twenty six protons are formed by supernova nucleosynthesis in supernovae, which, when they explode, blast these elements far into space as planetary nebulae, where they may become incorporated into planets when they are formed.When different elements are chemically combined, with the atoms held together by chemical bonds, they form chemical compounds. Only a minority of elements are found uncombined as relatively pure minerals. Among the more common of such ""native elements"" are copper, silver, gold, carbon (as coal, graphite, or diamonds), and sulfur. All but a few of the most inert elements, such as noble gases and noble metals, are usually found on Earth in chemically combined form, as chemical compounds. While about 32 of the chemical elements occur on Earth in native uncombined forms, most of these occur as mixtures. For example, atmospheric air is primarily a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and argon, and native solid elements occur in alloys, such as that of iron and nickel.The history of the discovery and use of the elements began with primitive human societies that found native elements like carbon, sulfur, copper and gold. Later civilizations extracted elemental copper, tin, lead and iron from their ores by smelting, using charcoal. Alchemists and chemists subsequently identified many more, with almost all of the naturally-occurring elements becoming known by 1900. The properties of the chemical elements are summarized on the periodic table, which organizes the elements by increasing atomic number into rows (""periods"") in which the columns (""groups"") share recurring (""periodic"") physical and chemical properties. Save for unstable radioactive elements with short half-lives, all of the elements are available industrially, most of them in high degrees of purity.