CHEM 1405 Practice Exam #2 (2015)
... 10) How many valence electrons does the representative element with the electron configuration 1s22s22p63s23p5 possess? A) 5 B) 6 11) The compound Au2Se3 is classified as which of the following? A) binary ionic B) ternary ionic C) 7 D) 2 C) binary molecular D) binary acid 12) Which of the following ...
... 10) How many valence electrons does the representative element with the electron configuration 1s22s22p63s23p5 possess? A) 5 B) 6 11) The compound Au2Se3 is classified as which of the following? A) binary ionic B) ternary ionic C) 7 D) 2 C) binary molecular D) binary acid 12) Which of the following ...
Build an Atom Scripted
... but they would eventually become known as electrons. Since the metal atoms themselves were electrically neutral, the negative charge on the electrons meant that there must also be some kind of positively charged particles within an atom, which led to the 1917 discovery of the proton, and in turn to ...
... but they would eventually become known as electrons. Since the metal atoms themselves were electrically neutral, the negative charge on the electrons meant that there must also be some kind of positively charged particles within an atom, which led to the 1917 discovery of the proton, and in turn to ...
Build an Atom Scripted - UTeach Outreach
... charged particles from samples of metal. No matter which metal Thomson used, the tiny negative particles that were released were identical. Thomson referred to these particles as “corpuscles,” but they would eventually become known as electrons. Since the metal atoms themselves were electrically ne ...
... charged particles from samples of metal. No matter which metal Thomson used, the tiny negative particles that were released were identical. Thomson referred to these particles as “corpuscles,” but they would eventually become known as electrons. Since the metal atoms themselves were electrically ne ...
Document
... What is the atomic number of boron, B? 5 What is the atomic mass of silicon, Si? 28.09 amu How many protons does a chlorine atom have? 17 How many electrons does a neutral neon atom have? 10 Will an atom with 6 protons, 6 neutrons and 6 electrons be electrically neutral? Yes • Will an atom with 27 p ...
... What is the atomic number of boron, B? 5 What is the atomic mass of silicon, Si? 28.09 amu How many protons does a chlorine atom have? 17 How many electrons does a neutral neon atom have? 10 Will an atom with 6 protons, 6 neutrons and 6 electrons be electrically neutral? Yes • Will an atom with 27 p ...
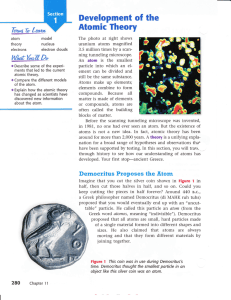
Development of the Atomic Theory
... learned how the atomic theory developed through centuries of observation and experimentation. Now it's time to learn about the atom itself. In this section, you'll learn about the particles inside the atom, and you'll learn about the forces that act on those particles. But first you'll find out just ...
... learned how the atomic theory developed through centuries of observation and experimentation. Now it's time to learn about the atom itself. In this section, you'll learn about the particles inside the atom, and you'll learn about the forces that act on those particles. But first you'll find out just ...
FREE Sample Here
... d. When two molecules combine, they do so in definite proportions by weight e. When two different elements combine to form a mixture, they do so in definite proportions by weight Section 2.1 3. The relative number of atoms of each element in a particular compound a. b. c. * d. e. ...
... d. When two molecules combine, they do so in definite proportions by weight e. When two different elements combine to form a mixture, they do so in definite proportions by weight Section 2.1 3. The relative number of atoms of each element in a particular compound a. b. c. * d. e. ...
FREE Sample Here - We can offer most test bank and
... d. When two molecules combine, they do so in definite proportions by weight e. When two different elements combine to form a mixture, they do so in definite proportions by weight Section 2.1 3. The relative number of atoms of each element in a particular compound a. b. c. * d. e. ...
... d. When two molecules combine, they do so in definite proportions by weight e. When two different elements combine to form a mixture, they do so in definite proportions by weight Section 2.1 3. The relative number of atoms of each element in a particular compound a. b. c. * d. e. ...
CHEMISTRY 123-07 Midterm #1 – Answer key October 14, 2010
... PART VI: CALCULATION PROBLEMS (Show your work in its entirety. Do not provide just a single number!). 44. (7 pts) Potassium superoxide, KO2, is used in re-breathing gas masks to generate oxygen according to the equation: 4 KO2 (s) + a. ...
... PART VI: CALCULATION PROBLEMS (Show your work in its entirety. Do not provide just a single number!). 44. (7 pts) Potassium superoxide, KO2, is used in re-breathing gas masks to generate oxygen according to the equation: 4 KO2 (s) + a. ...
atm-atomic structure - Discovery Education
... observation of atoms and the particles that compose them. Democritus was the first to realize that the forces that hold together the atom cannot be divided except by the most powerful reactions. When the nucleus of an atom is split apart in a process called fission, tremendous energy is released. Th ...
... observation of atoms and the particles that compose them. Democritus was the first to realize that the forces that hold together the atom cannot be divided except by the most powerful reactions. When the nucleus of an atom is split apart in a process called fission, tremendous energy is released. Th ...
High School Knowledge Exam – Study Guide
... something), color change (caused by reaction b/w chemicals) Dalton’s Atomic Theory 1) All matter is made up of very small, discrete particles called atoms 2) All atoms of a given element are identical, and the atoms of a given element are different from those of any other element (Incorrect – all at ...
... something), color change (caused by reaction b/w chemicals) Dalton’s Atomic Theory 1) All matter is made up of very small, discrete particles called atoms 2) All atoms of a given element are identical, and the atoms of a given element are different from those of any other element (Incorrect – all at ...
0 Review Presentations
... ▸ “Atoms comes from Greek word “Atomos,”meaning “indivisible.” ▸ In 1897, J.J. Thompson created the Cathrode Ray Tube that discovered the ...
... ▸ “Atoms comes from Greek word “Atomos,”meaning “indivisible.” ▸ In 1897, J.J. Thompson created the Cathrode Ray Tube that discovered the ...
Chap4 Review - armstrongchemistry
... average mass of the isotopes of that element. Based on this definition, which of these does NOT show the correct atomic mass for an element? A ...
... average mass of the isotopes of that element. Based on this definition, which of these does NOT show the correct atomic mass for an element? A ...
4.1 Studying Atoms
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory Evidence for Atoms John Dalton studied the behavior of gases in air. Based on the way gases exert pressure, Dalton correctly concluded that a gas consists of individual particles. Dalton measured masses of elements that combine when compounds form. The ratio of the masses of t ...
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory Evidence for Atoms John Dalton studied the behavior of gases in air. Based on the way gases exert pressure, Dalton correctly concluded that a gas consists of individual particles. Dalton measured masses of elements that combine when compounds form. The ratio of the masses of t ...
4.3 Distinguishing Among Atoms
... How are the atoms of one element different from the atoms of another element? How are isotopes of the same element different? Atoms of different elements are different because they contain different numbers of protons. Isotopes of the same element are different because they have different numbers of ...
... How are the atoms of one element different from the atoms of another element? How are isotopes of the same element different? Atoms of different elements are different because they contain different numbers of protons. Isotopes of the same element are different because they have different numbers of ...
Scandium and Yttrium - Mercyhurst University
... As mentioned previously, the common oxidation state of Sc and Y is +3. Only scandium can form a lower oxidation state of +2, as MIScX3, but it is not very common.4 A coordination number of six for both Sc and Y is typical, but it can vary up to a value of nine.4 Scandium only has one known compound ...
... As mentioned previously, the common oxidation state of Sc and Y is +3. Only scandium can form a lower oxidation state of +2, as MIScX3, but it is not very common.4 A coordination number of six for both Sc and Y is typical, but it can vary up to a value of nine.4 Scandium only has one known compound ...
Introduction - Royal Society of Chemistry
... The sixth student worksheet is an information sheet, bringing the theory up-to-date. Following an introduction to the lesson, the class could be divided into groups of 4 or 5 students. Each group could work through one of the worksheets. To make the sheets more durable, they could be photocopied ont ...
... The sixth student worksheet is an information sheet, bringing the theory up-to-date. Following an introduction to the lesson, the class could be divided into groups of 4 or 5 students. Each group could work through one of the worksheets. To make the sheets more durable, they could be photocopied ont ...
Chpt1
... Matter can be classified into two broad groups: • Substances – this the type of matter that has definite composition and distinct properties. Substances can be either elements or compounds • Mixtures – a combination of two or more substances, where the substances retain their unique identities and c ...
... Matter can be classified into two broad groups: • Substances – this the type of matter that has definite composition and distinct properties. Substances can be either elements or compounds • Mixtures – a combination of two or more substances, where the substances retain their unique identities and c ...
Notebook LAyout for Atoms Unit- Page 46+
... Atomic _______ refers to the arrangement and number of smaller particles in an atom. ...
... Atomic _______ refers to the arrangement and number of smaller particles in an atom. ...
The atom: Introduction and models
... mass of a carbon atom is twelve times greater than the mass of a hydrogen atom. When we use atomic mass units instead of kilograms, it becomes easier to see this. Atomic mass units are therefore not giving us the actual mass of an atom, but rather its mass relative to the mass of one (carefully chos ...
... mass of a carbon atom is twelve times greater than the mass of a hydrogen atom. When we use atomic mass units instead of kilograms, it becomes easier to see this. Atomic mass units are therefore not giving us the actual mass of an atom, but rather its mass relative to the mass of one (carefully chos ...
atoms - WordPress.com
... All the positive charge, and almost all the mass is concentrated in a small area in the center. He called this a “nucleus” The nucleus is composed of protons and neutrons (they make the nucleus!) The electrons distributed around the nucleus, and occupy most of the volume His model was called ...
... All the positive charge, and almost all the mass is concentrated in a small area in the center. He called this a “nucleus” The nucleus is composed of protons and neutrons (they make the nucleus!) The electrons distributed around the nucleus, and occupy most of the volume His model was called ...
Types of Radiation - Kasson
... these differences in mass. • Calculations showed that such a particle should have a mass equal to that of a proton but no electrical charge. • The existence of this neutral particle, called a neutron, was confirmed in the early 1930s. ...
... these differences in mass. • Calculations showed that such a particle should have a mass equal to that of a proton but no electrical charge. • The existence of this neutral particle, called a neutron, was confirmed in the early 1930s. ...
Chapter 7 Periodic Properties of the Elements
... Development of Periodic Table • Elements in the ...
... Development of Periodic Table • Elements in the ...
File
... Elements are defined by the number of protons in an atom's nucleus. So, for example, an atom with 6 protons must be carbon and an atom with 92 protons must be uranium. If you change the protons, then you change the element. In addition to protons, the atoms of every element (except the simplest form ...
... Elements are defined by the number of protons in an atom's nucleus. So, for example, an atom with 6 protons must be carbon and an atom with 92 protons must be uranium. If you change the protons, then you change the element. In addition to protons, the atoms of every element (except the simplest form ...
The d- and f- Block Element Block Elements The d- and f
... Due to an increase in nuclear charge which accompanies the filling of the inner d orbitals, there is an increase in ionisation enthalpy along each series of the transition elements from left to right. However, many small variations occur. Table 8.2 gives the values for the first three ionisation ent ...
... Due to an increase in nuclear charge which accompanies the filling of the inner d orbitals, there is an increase in ionisation enthalpy along each series of the transition elements from left to right. However, many small variations occur. Table 8.2 gives the values for the first three ionisation ent ...
View PDF - CiteSeerX
... the structure of the periodic system. Explicit references to the periodic system were rare in the 1870s, even in the chemistry literature, and only by the late 1880s had Mendeleev’s system become widely accepted and incorporated into most textbooks (Brush, 1996). In 1892 Thomson pointed out, for the ...
... the structure of the periodic system. Explicit references to the periodic system were rare in the 1870s, even in the chemistry literature, and only by the late 1880s had Mendeleev’s system become widely accepted and incorporated into most textbooks (Brush, 1996). In 1892 Thomson pointed out, for the ...
Chemical element
A chemical element (or element) is a chemical substance consisting of atoms having the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei (i.e. the same atomic number, Z). There are 118 elements that have been identified, of which the first 94 occur naturally on Earth with the remaining 24 being synthetic elements. There are 80 elements that have at least one stable isotope and 38 that have exclusively radioactive isotopes, which decay over time into other elements. Iron is the most abundant element (by mass) making up the Earth, while oxygen is the most common element in the crust of the earth.Chemical elements constitute approximately 15% of the matter in the universe: the remainder is dark matter, the composition of it is unknown, but it is not composed of chemical elements.The two lightest elements, hydrogen and helium were mostly formed in the Big Bang and are the most common elements in the universe. The next three elements (lithium, beryllium and boron) were formed mostly by cosmic ray spallation, and are thus more rare than those that follow. Formation of elements with from six to twenty six protons occurred and continues to occur in main sequence stars via stellar nucleosynthesis. The high abundance of oxygen, silicon, and iron on Earth reflects their common production in such stars. Elements with greater than twenty six protons are formed by supernova nucleosynthesis in supernovae, which, when they explode, blast these elements far into space as planetary nebulae, where they may become incorporated into planets when they are formed.When different elements are chemically combined, with the atoms held together by chemical bonds, they form chemical compounds. Only a minority of elements are found uncombined as relatively pure minerals. Among the more common of such ""native elements"" are copper, silver, gold, carbon (as coal, graphite, or diamonds), and sulfur. All but a few of the most inert elements, such as noble gases and noble metals, are usually found on Earth in chemically combined form, as chemical compounds. While about 32 of the chemical elements occur on Earth in native uncombined forms, most of these occur as mixtures. For example, atmospheric air is primarily a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and argon, and native solid elements occur in alloys, such as that of iron and nickel.The history of the discovery and use of the elements began with primitive human societies that found native elements like carbon, sulfur, copper and gold. Later civilizations extracted elemental copper, tin, lead and iron from their ores by smelting, using charcoal. Alchemists and chemists subsequently identified many more, with almost all of the naturally-occurring elements becoming known by 1900. The properties of the chemical elements are summarized on the periodic table, which organizes the elements by increasing atomic number into rows (""periods"") in which the columns (""groups"") share recurring (""periodic"") physical and chemical properties. Save for unstable radioactive elements with short half-lives, all of the elements are available industrially, most of them in high degrees of purity.