Overview of our Solar System 1112 notes
... • At the center of our solar system • Contains 98.5% of all of the mass of the solar system • The first thing formed in our solar system • The largest and only star in our solar system • Provides almost all of the energy used in the solar system • Earth only gets 0.000000001% of the sun’s total ener ...
... • At the center of our solar system • Contains 98.5% of all of the mass of the solar system • The first thing formed in our solar system • The largest and only star in our solar system • Provides almost all of the energy used in the solar system • Earth only gets 0.000000001% of the sun’s total ener ...
EM_INDUCTION
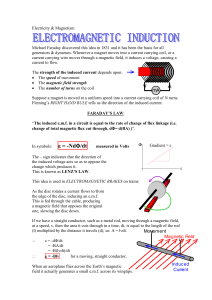
... The strength of the induced current depends upon: The speed of movement The magnetic field strength The number of turns on the coil Suppose a magnet is moved at a uniform speed into a current carrying coil of N turns. Fleming’s RIGHT HAND RULE tells us the direction of the induced current. FAR ...
... The strength of the induced current depends upon: The speed of movement The magnetic field strength The number of turns on the coil Suppose a magnet is moved at a uniform speed into a current carrying coil of N turns. Fleming’s RIGHT HAND RULE tells us the direction of the induced current. FAR ...
By Erik,Brianna,michael,wyatt
... is magnetism in credit cards, phones, and the earth. On Earth one needs a sensitive needle to find magnetic forces, and out in space they are usually a lot weaker. But beyond the dense atmosphere, such forces have a much bigger role, and a region exists around the Earth where they dominate the envir ...
... is magnetism in credit cards, phones, and the earth. On Earth one needs a sensitive needle to find magnetic forces, and out in space they are usually a lot weaker. But beyond the dense atmosphere, such forces have a much bigger role, and a region exists around the Earth where they dominate the envir ...
Astronomy Meteorology Review Sheet
... Higher altitude means air expands, cools, therefore condenses Unstable air rises Cirrus clouds are high and cold (icy), cumulus are puffy, stratus covers the whole sky, cumulonimbus is thunderstorm producer + hail (raindrop gets kicked up to top of cloud repeatedly and “grows” larger until it falls) ...
... Higher altitude means air expands, cools, therefore condenses Unstable air rises Cirrus clouds are high and cold (icy), cumulus are puffy, stratus covers the whole sky, cumulonimbus is thunderstorm producer + hail (raindrop gets kicked up to top of cloud repeatedly and “grows” larger until it falls) ...
Lecture Notes - NMSU Astronomy
... • Photosphere is dense enough to radiate light but not too dense so that photons can escape; thus it is where spectrum of star is emitted and where the absorption lines arise. • Chromosphere is active, hotter and lower density than photosphere is where emission occurs (hot, low density gas). This ...
... • Photosphere is dense enough to radiate light but not too dense so that photons can escape; thus it is where spectrum of star is emitted and where the absorption lines arise. • Chromosphere is active, hotter and lower density than photosphere is where emission occurs (hot, low density gas). This ...
D Careers for Physicists Dai Dee Pun
... world’s largest semiconductor equipment company, Applied Materials. She is now the Director of Quality and Reliability at Skyline Solar, a startup company in the Silicon Valley working on enabling affordable utility scale solar energy using concentrated photovoltaic technology. She will tell us abou ...
... world’s largest semiconductor equipment company, Applied Materials. She is now the Director of Quality and Reliability at Skyline Solar, a startup company in the Silicon Valley working on enabling affordable utility scale solar energy using concentrated photovoltaic technology. She will tell us abou ...
Structure of the Sun, our nearest star
... o Release the energy equivalent of ten million volcanic eruptions. o They can last just a few minutes or up to several hours. ...
... o Release the energy equivalent of ten million volcanic eruptions. o They can last just a few minutes or up to several hours. ...
Geomagnetic storm

A geomagnetic storm is a temporary disturbance of the Earth's magnetosphere caused by a solar wind shock wave and/or cloud of magnetic field that interacts with the Earth's magnetic field. The increase in the solar wind pressure initially compresses the magnetosphere. The solar wind's magnetic field interacts with the Earth’s magnetic field and transfers an increased energy into the magnetosphere. Both interactions cause an increase in plasma movement through the magnetosphere (driven by increased electric fields inside the magnetosphere) and an increase in electric current in the magnetosphere and ionosphere.During the main phase of a geomagnetic storm, electric current in the magnetosphere creates a magnetic force that pushes out the boundary between the magnetosphere and the solar wind. The disturbance in the interplanetary medium that drives the storm may be due to a solar coronal mass ejection (CME) or a high speed stream (co-rotating interaction region or CIR) of the solar wind originating from a region of weak magnetic field on the Sun’s surface. The frequency of geomagnetic storms increases and decreases with the sunspot cycle. CME driven storms are more common during the maximum of the solar cycle, while CIR driven storms are more common during the minimum of the solar cycle.Several space weather phenomena tend to be associated with or are caused by a geomagnetic storm. These include: solar energetic Particle (SEP) events, geomagnetically induced currents (GIC), ionospheric disturbances that cause radio and radar scintillation, disruption of navigation by magnetic compass and auroral displays at much lower latitudes than normal. In 1989, a geomagnetic storm energized ground induced currents that disrupted electric power distribution throughout most of the province of Quebec and caused aurorae as far south as Texas.