Now
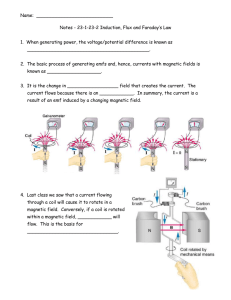
... magnetic field surrounding it. This is called the magnetosphere. • This magnetic field deflects some of the sun’s dangerous radiation. • For centuries, people have used Earth’s magnetism to navigate by the aid of a compass. • Many animals also have the Godgiven ability to use earth’s magnetic field ...
... magnetic field surrounding it. This is called the magnetosphere. • This magnetic field deflects some of the sun’s dangerous radiation. • For centuries, people have used Earth’s magnetism to navigate by the aid of a compass. • Many animals also have the Godgiven ability to use earth’s magnetic field ...
The Sun is our local star.
... The Sun is the only star in our solar system. Astronomers have been able to study the Sun in more detail than other stars because it is much closer to Earth. As a result, they have learned a great deal about its size and composition and the way it produces energy. The Sun is far larger than any of t ...
... The Sun is the only star in our solar system. Astronomers have been able to study the Sun in more detail than other stars because it is much closer to Earth. As a result, they have learned a great deal about its size and composition and the way it produces energy. The Sun is far larger than any of t ...
the solar system - Title: Brains at school
... • it is the coldest planet. • it is composed of hydrogen, helium and methane, which give an apparent blue color. • It has 13 satellites; Triton is the biggest. ...
... • it is the coldest planet. • it is composed of hydrogen, helium and methane, which give an apparent blue color. • It has 13 satellites; Triton is the biggest. ...
Record: 1 - GeorgiaStandards.Org
... Because the northern lights are associated with Arctic locations, people assume the lights can only appear when it is cold. Actually, the best displays often come in Spring and autumn, when Earth's magnetic field tends to connect more directly to the storm clouds coming from the sun. Even summer nig ...
... Because the northern lights are associated with Arctic locations, people assume the lights can only appear when it is cold. Actually, the best displays often come in Spring and autumn, when Earth's magnetic field tends to connect more directly to the storm clouds coming from the sun. Even summer nig ...
∫
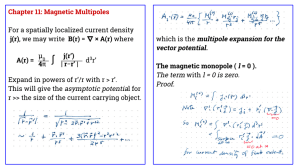
... Chapter 11: Magnetic Multipoles For a spatially localized current density j(r), we may write B(r) = ∇ × A(r) where A(r) = ...
... Chapter 11: Magnetic Multipoles For a spatially localized current density j(r), we may write B(r) = ∇ × A(r) where A(r) = ...
Stellar Evolution Stations
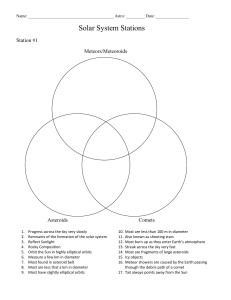
... Most are less than 100 m in diameter Also known as shooting stars Most burn up as they enter Earth’s atmosphere Streak across the sky very fast Most are fragments of large asteroids Icy objects Meteor showers are caused by the Earth passing through the debris path of a comet 17. Tail always points a ...
... Most are less than 100 m in diameter Also known as shooting stars Most burn up as they enter Earth’s atmosphere Streak across the sky very fast Most are fragments of large asteroids Icy objects Meteor showers are caused by the Earth passing through the debris path of a comet 17. Tail always points a ...
Explained in 60 Seconds: Why Visit a Comet?
... troves of dust and ice with the secrets of the early Solar System locked within. The Solar System was a chaotic place 4.6 billion years ago, but from tiny dust and ice particles to colliding boulders and swirling gas, the planets eventually took shape. Comets, the leftover detritus in this planetary ...
... troves of dust and ice with the secrets of the early Solar System locked within. The Solar System was a chaotic place 4.6 billion years ago, but from tiny dust and ice particles to colliding boulders and swirling gas, the planets eventually took shape. Comets, the leftover detritus in this planetary ...
The Sun: Our nearest star
... • There is one last solar phenomenon to talk about. • Hot charged particles (mostly p+ and e-) evaporate from the Sun and stream into the Solar System. • About 1 million tons/second stream away at 1 million mph. ...
... • There is one last solar phenomenon to talk about. • Hot charged particles (mostly p+ and e-) evaporate from the Sun and stream into the Solar System. • About 1 million tons/second stream away at 1 million mph. ...
Extract, Datei
... studied star. Due to the relatively short distance between the Earth and the Sun compared to the distance to other stars, we can reach high spatial resolution. The Swedish 1-m Solar Telescope (Scharmer et al. 2003) at the Roque de los Muchachos on the Canary island of la Palma offers today the best r ...
... studied star. Due to the relatively short distance between the Earth and the Sun compared to the distance to other stars, we can reach high spatial resolution. The Swedish 1-m Solar Telescope (Scharmer et al. 2003) at the Roque de los Muchachos on the Canary island of la Palma offers today the best r ...
The Sun`s Exterior
... Typical sunspots are about the size of Earth. They appear dark because they are cooler: 5000 K. ...
... Typical sunspots are about the size of Earth. They appear dark because they are cooler: 5000 K. ...
25.1
... b. Objects in the sky move around Earth. c. The sun is the center of the solar system. d. The planets revolve around the sun. 5. Name the center of the solar system in a heliocentric model. the sun ...
... b. Objects in the sky move around Earth. c. The sun is the center of the solar system. d. The planets revolve around the sun. 5. Name the center of the solar system in a heliocentric model. the sun ...
Solar System Unit Objectives
... List planets in order from the sun, rank their relative sizes, and approx. distances from the sun in rounded AUs From a scale model, give the planets distances and sizes in AUs and km From data giving planet sizes and distances from the sun construct a scale model of the solar system Identify unique ...
... List planets in order from the sun, rank their relative sizes, and approx. distances from the sun in rounded AUs From a scale model, give the planets distances and sizes in AUs and km From data giving planet sizes and distances from the sun construct a scale model of the solar system Identify unique ...
Geomagnetic storm

A geomagnetic storm is a temporary disturbance of the Earth's magnetosphere caused by a solar wind shock wave and/or cloud of magnetic field that interacts with the Earth's magnetic field. The increase in the solar wind pressure initially compresses the magnetosphere. The solar wind's magnetic field interacts with the Earth’s magnetic field and transfers an increased energy into the magnetosphere. Both interactions cause an increase in plasma movement through the magnetosphere (driven by increased electric fields inside the magnetosphere) and an increase in electric current in the magnetosphere and ionosphere.During the main phase of a geomagnetic storm, electric current in the magnetosphere creates a magnetic force that pushes out the boundary between the magnetosphere and the solar wind. The disturbance in the interplanetary medium that drives the storm may be due to a solar coronal mass ejection (CME) or a high speed stream (co-rotating interaction region or CIR) of the solar wind originating from a region of weak magnetic field on the Sun’s surface. The frequency of geomagnetic storms increases and decreases with the sunspot cycle. CME driven storms are more common during the maximum of the solar cycle, while CIR driven storms are more common during the minimum of the solar cycle.Several space weather phenomena tend to be associated with or are caused by a geomagnetic storm. These include: solar energetic Particle (SEP) events, geomagnetically induced currents (GIC), ionospheric disturbances that cause radio and radar scintillation, disruption of navigation by magnetic compass and auroral displays at much lower latitudes than normal. In 1989, a geomagnetic storm energized ground induced currents that disrupted electric power distribution throughout most of the province of Quebec and caused aurorae as far south as Texas.